Slide 1
... – Ketoacidosis: results if oxaloacetate in short supply; acetyl-CoA converted into ketones, which are weak acids; can occur due to starvation, low-carbohydrate diet, or by uncontrolled diabetes ...
... – Ketoacidosis: results if oxaloacetate in short supply; acetyl-CoA converted into ketones, which are weak acids; can occur due to starvation, low-carbohydrate diet, or by uncontrolled diabetes ...
Unit 2 Test Retake Review Sheet – Cell Biology Answer questions
... data” graph and discuss what happened when a base or acid was added. Which two elements must be found in organic molecules? All enzymes are catalysts but not all catalysts are _________________. Explain the lock and key model and relate it to enzymes and substrates. Explain why specific enzymes only ...
... data” graph and discuss what happened when a base or acid was added. Which two elements must be found in organic molecules? All enzymes are catalysts but not all catalysts are _________________. Explain the lock and key model and relate it to enzymes and substrates. Explain why specific enzymes only ...
Macromolecules Vocabulary and Concepts
... Glycerol + 3 fatty acids Ester Linkage joins fatty acids to the glycerol molecule ? What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats? o Phospholipid Glycerol, 2 fatty acids, 1 phosphate Amphipathic Cell membranes ? How does the degree of saturation of fatty acids in a cell mem ...
... Glycerol + 3 fatty acids Ester Linkage joins fatty acids to the glycerol molecule ? What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats? o Phospholipid Glycerol, 2 fatty acids, 1 phosphate Amphipathic Cell membranes ? How does the degree of saturation of fatty acids in a cell mem ...
A2 Module 2814: Chains, Rings and Spectroscopy
... small molecule, such as H2O or HCl is lost), and if several amino acids are joined to form a polypeptide, this is an example of condensation polymerisation. If more than about forty amino acid units are involved, the polymer is classed as a protein. Natural peptides and proteins can use any of the t ...
... small molecule, such as H2O or HCl is lost), and if several amino acids are joined to form a polypeptide, this is an example of condensation polymerisation. If more than about forty amino acid units are involved, the polymer is classed as a protein. Natural peptides and proteins can use any of the t ...
PPT 4
... H –C–C–H + Cl2 H–C–C–Cl + HCl H H H H If more chlorine is provided, the reaction will produce... H H H H H –C–C–Cl + Cl2 Cl–C–C–Cl + HCl H H H H AND SO ON. ...
... H –C–C–H + Cl2 H–C–C–Cl + HCl H H H H If more chlorine is provided, the reaction will produce... H H H H H –C–C–Cl + Cl2 Cl–C–C–Cl + HCl H H H H AND SO ON. ...
Week 2 Handout with No answers
... Water’s _____ and _______ allow it to form __________ bonds which are central to the behavior of macromolecules dissolved in it. When lipids are placed in a water solvent the corresponding effect is that water forms a hydration shell around the lipid. This highly ordered water shell results in decre ...
... Water’s _____ and _______ allow it to form __________ bonds which are central to the behavior of macromolecules dissolved in it. When lipids are placed in a water solvent the corresponding effect is that water forms a hydration shell around the lipid. This highly ordered water shell results in decre ...
Chapter 9. Cellular Respiration Other Metabolites
... balance the supply of raw materials with the products produced these molecules become feedback regulators they control enzymes at strategic points in ...
... balance the supply of raw materials with the products produced these molecules become feedback regulators they control enzymes at strategic points in ...
chapter 24
... If the amino acid skeleton has 3 carbons, it can be converted to pyruvate. If they have 4 or 5 carbons, they can be converted to another intermediate in the citric acid cycle (oxaloacetate, or a-ketoglutarate). ...
... If the amino acid skeleton has 3 carbons, it can be converted to pyruvate. If they have 4 or 5 carbons, they can be converted to another intermediate in the citric acid cycle (oxaloacetate, or a-ketoglutarate). ...
Exam II answer key
... e) can phosphorylate themselves on their own cytoplasmic domains when activated f) that have been actiated by hormone binding are recognized by target poroteins hainvg SH2 (src protein homology region 2) sequences g) are so named because they contain extraordinarily high amounts of tyrosine. Ch 14 q ...
... e) can phosphorylate themselves on their own cytoplasmic domains when activated f) that have been actiated by hormone binding are recognized by target poroteins hainvg SH2 (src protein homology region 2) sequences g) are so named because they contain extraordinarily high amounts of tyrosine. Ch 14 q ...
Exam II
... e) can phosphorylate themselves on their own cytoplasmic domains when activated f) that have been actiated by hormone binding are recognized by target poroteins hainvg SH2 (src protein homology region 2) sequences g) are so named because they contain extraordinarily high amounts of tyrosine. Ch 14 q ...
... e) can phosphorylate themselves on their own cytoplasmic domains when activated f) that have been actiated by hormone binding are recognized by target poroteins hainvg SH2 (src protein homology region 2) sequences g) are so named because they contain extraordinarily high amounts of tyrosine. Ch 14 q ...
Fab Four – The Muscle-Building Supplements
... Dr. Robert G. Silverman graduated Magna cum Laude from the University of Bridgeport, College of Chiropractic. He is a Certified Nutrition Specialist, Certified Clinical Nutritionist, has a Masters of Science in Human Nutrition, is a Certified Strength and Conditioning Specialist, and is a Diplomat w ...
... Dr. Robert G. Silverman graduated Magna cum Laude from the University of Bridgeport, College of Chiropractic. He is a Certified Nutrition Specialist, Certified Clinical Nutritionist, has a Masters of Science in Human Nutrition, is a Certified Strength and Conditioning Specialist, and is a Diplomat w ...
Unit 1 – Introduction to Biology STUDY GUIDE
... our cells? Which of these contains the greatest amount of energy? Explain how you know this. Carbohydrates and Lipids are the most important macromolecules for energy in our cells. Lipids contain more energy, because they released more energy when we burned them in lab. 13. How many amino acid monom ...
... our cells? Which of these contains the greatest amount of energy? Explain how you know this. Carbohydrates and Lipids are the most important macromolecules for energy in our cells. Lipids contain more energy, because they released more energy when we burned them in lab. 13. How many amino acid monom ...
Document
... IV. (4 pts) Complete the analogy by filling in the blank with the appropriate response: 1. Pyruvate is to Alanine as -Ketoglutarate is to __Glutamate__ 2. Phosphofructokinase-1 is to Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphatase as Hexokinase is to Glucose-6phosphatase_ 3. Marasmus is to inadequate protein and energ ...
... IV. (4 pts) Complete the analogy by filling in the blank with the appropriate response: 1. Pyruvate is to Alanine as -Ketoglutarate is to __Glutamate__ 2. Phosphofructokinase-1 is to Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphatase as Hexokinase is to Glucose-6phosphatase_ 3. Marasmus is to inadequate protein and energ ...
A look at macromolecules (Text pages 38
... • Quaternary: more than one polypeptide chain Structure determined by order of amino acids • Degree of hydrogen bonding • Structure can be ‘denatured’ • Gentle vs. harsh ...
... • Quaternary: more than one polypeptide chain Structure determined by order of amino acids • Degree of hydrogen bonding • Structure can be ‘denatured’ • Gentle vs. harsh ...
Notes Chemical Basis for Life BIO.A.2
... occur at normal temperatures • Without enzymes, too much energy would be needed to start all of the thousands of reactions your body performs all of the time! ...
... occur at normal temperatures • Without enzymes, too much energy would be needed to start all of the thousands of reactions your body performs all of the time! ...
Amino Acid Catabolism 2
... Often the first step of amino acid degradation Transfer of amino group from many amino acids to limited number of keto acid acceptors ...
... Often the first step of amino acid degradation Transfer of amino group from many amino acids to limited number of keto acid acceptors ...
Classifying Organic Molecules Lab
... 14. If n=6, how many carbon atoms are there? How many hydrogen atoms are there? How many oxygen atoms are there? 15. Take your non-nitrogen pile and sort out those cards that have OH attached to most carbons. Be aware that organic chemists use many shortcuts in drawing complex molecules. They often ...
... 14. If n=6, how many carbon atoms are there? How many hydrogen atoms are there? How many oxygen atoms are there? 15. Take your non-nitrogen pile and sort out those cards that have OH attached to most carbons. Be aware that organic chemists use many shortcuts in drawing complex molecules. They often ...
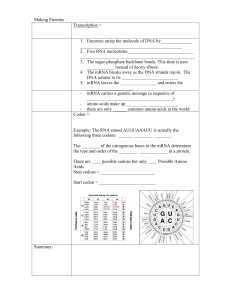
Modeling Protein synthesis lab
... In a process called transcripaon which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNlt's nucleotide sequences in the form of a complementary RNA molecule. Then the mRNA carries this information in the form of a code to the ribosomes, where protein synthesis tak ...
... In a process called transcripaon which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNlt's nucleotide sequences in the form of a complementary RNA molecule. Then the mRNA carries this information in the form of a code to the ribosomes, where protein synthesis tak ...
ETC Details
... • How cells take molecules from food and turn them into molecules for growth and repair • Aka Metabolic Pool • Intermediaries of all cycles can be removed and used to build molecules! • Ex. pyruvate glucose • Acetyl CoA fatty acids ...
... • How cells take molecules from food and turn them into molecules for growth and repair • Aka Metabolic Pool • Intermediaries of all cycles can be removed and used to build molecules! • Ex. pyruvate glucose • Acetyl CoA fatty acids ...
File
... Helps to produce enzymes needed to bond amino acids together during protein synthesis ...
... Helps to produce enzymes needed to bond amino acids together during protein synthesis ...
Review on Biochemistry: Protein Chemistry
... -carboxyglutamate: found in prothrombin and certain Ca2+-binding protein. Desmosine (a derivative of four Lys residues): found in the fibrous protein elastin. Selenocysteine: Selenium replaces sulfur in cysteine during amino acid synthesis (derived from serine). Amino acids not as constitue ...
... -carboxyglutamate: found in prothrombin and certain Ca2+-binding protein. Desmosine (a derivative of four Lys residues): found in the fibrous protein elastin. Selenocysteine: Selenium replaces sulfur in cysteine during amino acid synthesis (derived from serine). Amino acids not as constitue ...
ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
... Oncogenes – turned on to make cells divide too quickly Tumor Suppressor genes – turned off to make cells divide too ...
... Oncogenes – turned on to make cells divide too quickly Tumor Suppressor genes – turned off to make cells divide too ...
Chapter 4: Amino Acids General Features of Amino Acids
... Peptide bond formation is a condensation reaction leading to the polymerization of amino acids into peptides and proteins. (Peptide: hormones, neurotransmitters, several antibiotics and antitumor agents) The presence of the carbonyl group in a peptide bond allows electron resonance stabilization to ...
... Peptide bond formation is a condensation reaction leading to the polymerization of amino acids into peptides and proteins. (Peptide: hormones, neurotransmitters, several antibiotics and antitumor agents) The presence of the carbonyl group in a peptide bond allows electron resonance stabilization to ...