Organic Molecule Worksheet
... 12. What are the subunits called that make up carbohydrates? 13. What is the ratio of C, H, and O in monosaccharides? 14. Name 3 monosaccharides. 15. Monosaccharides are ___ sugars. 16. What are disaccharides & give an example? 17. Long chains of sugars are ___. Name three. Part 3 Questions: Color ...
... 12. What are the subunits called that make up carbohydrates? 13. What is the ratio of C, H, and O in monosaccharides? 14. Name 3 monosaccharides. 15. Monosaccharides are ___ sugars. 16. What are disaccharides & give an example? 17. Long chains of sugars are ___. Name three. Part 3 Questions: Color ...
Unit 4: Genetics Name: Date: Aim #23 Translation: How does DNA
... nucleus, allowing the mRNA strand to leave the nucleus with the genetic message and head for the ribosome to make proteins through another process called translation. What is Translation? Where does translation occur? What are the steps of translation? ...
... nucleus, allowing the mRNA strand to leave the nucleus with the genetic message and head for the ribosome to make proteins through another process called translation. What is Translation? Where does translation occur? What are the steps of translation? ...
File
... Biochemistry is the branch of science that explores the ____________processes within and related to ________organisms. It is a laboratory based science that brings together biology and chemistry. By using chemical knowledge and techniques, biochemists can understand and solve ______________ ...
... Biochemistry is the branch of science that explores the ____________processes within and related to ________organisms. It is a laboratory based science that brings together biology and chemistry. By using chemical knowledge and techniques, biochemists can understand and solve ______________ ...
CHE 4310 Fall 2011
... 12. In a plot of 1/V versus 1/S, what will the presence of a competitive inhibitor alter on the graph? ...
... 12. In a plot of 1/V versus 1/S, what will the presence of a competitive inhibitor alter on the graph? ...
07_Metabolism of aminoacids
... •Humans can make only 11 of the 20 amino acids (“nonessential” amino acids) •Nonessential amino acids for mammals are usually derived from intermediates of glycolysis or the citric acid cycle •The others are classed as "essential" amino acids and must be obtained in the diet ...
... •Humans can make only 11 of the 20 amino acids (“nonessential” amino acids) •Nonessential amino acids for mammals are usually derived from intermediates of glycolysis or the citric acid cycle •The others are classed as "essential" amino acids and must be obtained in the diet ...
Metabolism
... A substance is oxidized when it loses one or more electrons A substance is reduced when it gains one or more electrons Oxidation-reduction reactions are controlled by enzymes Antioxidants – compounds that donate electrons to oxidized compounds, putting them into a more reduced (stable) state ...
... A substance is oxidized when it loses one or more electrons A substance is reduced when it gains one or more electrons Oxidation-reduction reactions are controlled by enzymes Antioxidants – compounds that donate electrons to oxidized compounds, putting them into a more reduced (stable) state ...
chemistryandmacromolecules3
... • formed by interactions of lipid monomers, such as fatty acids and glycerol backbones. • Contain hydrocarbons (composed of C and H atoms); they are insoluble in water because of many nonpolar covalent bonds. • When close together, weak but additive van der Waals interactions hold them together. Sto ...
... • formed by interactions of lipid monomers, such as fatty acids and glycerol backbones. • Contain hydrocarbons (composed of C and H atoms); they are insoluble in water because of many nonpolar covalent bonds. • When close together, weak but additive van der Waals interactions hold them together. Sto ...
C h e m g u id e –... AMINO ACIDS: ACID-BASE BEHAVIOUR
... electrophoresis. Describe how you would carry out simple electrophoresis on a solution containing one of these ions. e) The final result of the electrophoresis you have described will probably be a spot on a piece of paper. How does this spot give you information about the charge on the ion? Illustr ...
... electrophoresis. Describe how you would carry out simple electrophoresis on a solution containing one of these ions. e) The final result of the electrophoresis you have described will probably be a spot on a piece of paper. How does this spot give you information about the charge on the ion? Illustr ...
Macromolecules 1
... fatty acids joined to one glycerol through dehydration synthesis (condensation) a. Fatty acids composed of a long hydrocarbon skeleton that are ...
... fatty acids joined to one glycerol through dehydration synthesis (condensation) a. Fatty acids composed of a long hydrocarbon skeleton that are ...
슬라이드 1 - Tistory
... Figure 1.10: Inborn errors of metabolism in the breakdown of phenylalanine and tyrosine ...
... Figure 1.10: Inborn errors of metabolism in the breakdown of phenylalanine and tyrosine ...
Free Form Amino Caps
... blood-brain barrier. As a result, alterations in the plasma amino acid profile can lead to changes in the aminoacid dependent synthesis of neurotransmitters and other nitrogenous compounds in the brain. Free Form Amino Acid Caps was formulated to provide optimal amounts of those dietary amino acids ...
... blood-brain barrier. As a result, alterations in the plasma amino acid profile can lead to changes in the aminoacid dependent synthesis of neurotransmitters and other nitrogenous compounds in the brain. Free Form Amino Acid Caps was formulated to provide optimal amounts of those dietary amino acids ...
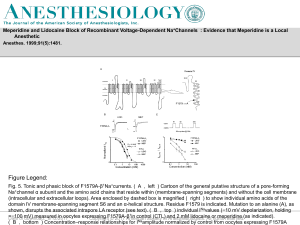
Slide () - Anesthesiology - American Society of Anesthesiologists
... Na+channel α subunit and the amino acid chains that reside within (membrane-spanning segments) and without the cell membrane (intracellular and extracellular loops). Area enclosed by dashed box is magnified ( right ) to show individual amino acids of the domain IV membrane-spanning segment S6 and an ...
... Na+channel α subunit and the amino acid chains that reside within (membrane-spanning segments) and without the cell membrane (intracellular and extracellular loops). Area enclosed by dashed box is magnified ( right ) to show individual amino acids of the domain IV membrane-spanning segment S6 and an ...
BIOCHEMISTRY (CHEM 360)
... Many cancer cells grow anaerobically, and PDH is not active in these cells. Speculate the effect of DCA on cancer cells. Outline your train of thought. Inhibiting PDH-phosphorylase kinase would activate PDH, which allow the citric acid cycle to function at its full rate, thus maintain aerobic condit ...
... Many cancer cells grow anaerobically, and PDH is not active in these cells. Speculate the effect of DCA on cancer cells. Outline your train of thought. Inhibiting PDH-phosphorylase kinase would activate PDH, which allow the citric acid cycle to function at its full rate, thus maintain aerobic condit ...
Final Review
... 8. Which statement concerning coenzymes and redox reactions is incorrect? Explain. A. Oxidation can be considered as loss of hydrogen or gain of oxygen. B. Reduction can be considered as gain of hydrogen or loss of oxygen. C. NADè is the oxidized form of NADH. D. An oxidation reaction cannot occur u ...
... 8. Which statement concerning coenzymes and redox reactions is incorrect? Explain. A. Oxidation can be considered as loss of hydrogen or gain of oxygen. B. Reduction can be considered as gain of hydrogen or loss of oxygen. C. NADè is the oxidized form of NADH. D. An oxidation reaction cannot occur u ...
Chem 2B
... 8. Which statement concerning coenzymes and redox reactions is incorrect? Explain. A. Oxidation can be considered as loss of hydrogen or gain of oxygen. B. Reduction can be considered as gain of hydrogen or loss of oxygen. C. NADè is the oxidized form of NADH. D. An oxidation reaction cannot occur u ...
... 8. Which statement concerning coenzymes and redox reactions is incorrect? Explain. A. Oxidation can be considered as loss of hydrogen or gain of oxygen. B. Reduction can be considered as gain of hydrogen or loss of oxygen. C. NADè is the oxidized form of NADH. D. An oxidation reaction cannot occur u ...
Lecture 6
... f. DNA replication traps random error in time, for natural selection to work on Origin of LCA a. Problem of improbability before DNA, random mutation traps history b. Two models, not mutually exclusive i. RNA world can from 3-D structures and be catalysts, replicate and carry information ii. Probl ...
... f. DNA replication traps random error in time, for natural selection to work on Origin of LCA a. Problem of improbability before DNA, random mutation traps history b. Two models, not mutually exclusive i. RNA world can from 3-D structures and be catalysts, replicate and carry information ii. Probl ...
What you need to Know for Chapter 1 Quiz
... o Compare fats to oils (saturated versus unsaturated – how do they differ? Review Protein note: o Key definitions: amino acids, essential amino acid, peptide bond o What are the functions of polypeptides? o Describe the general structure of amino acids – what is the R group? o Describe the 4 levels ...
... o Compare fats to oils (saturated versus unsaturated – how do they differ? Review Protein note: o Key definitions: amino acids, essential amino acid, peptide bond o What are the functions of polypeptides? o Describe the general structure of amino acids – what is the R group? o Describe the 4 levels ...
Unit 1 – Biochemisty
... I can describe and identify (visually) the structure of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. ...
... I can describe and identify (visually) the structure of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. ...
Transcription and Translation
... Describe the genetic code (3.5.3) • A set of rules by which information encoded in a gene is converted into a polypeptide sequence • Codon: A triplet of bases which code for amino acids • The order of the codons determines the amino acid sequence of the protein (1° structure) • The genetic code has ...
... Describe the genetic code (3.5.3) • A set of rules by which information encoded in a gene is converted into a polypeptide sequence • Codon: A triplet of bases which code for amino acids • The order of the codons determines the amino acid sequence of the protein (1° structure) • The genetic code has ...
2. Where does translation take place
... 5. What is the role of ribosomes in protein production? 6. Below you’ll be given an mRNA codon. Write down the tRNA anticodon and the corresponding amino acid that the codon codes for. You will need the handout Genetic Code. mRNA codon tRNA anticodon Amino acid (AA) UAC CGU AUG UUC AAA AUU AAC CCA ...
... 5. What is the role of ribosomes in protein production? 6. Below you’ll be given an mRNA codon. Write down the tRNA anticodon and the corresponding amino acid that the codon codes for. You will need the handout Genetic Code. mRNA codon tRNA anticodon Amino acid (AA) UAC CGU AUG UUC AAA AUU AAC CCA ...
Macromolecules Notes Macromolecules Notes
... Proteins are also called Polypeptides The monomer is called an amino acid •20 different kinds of amino acids 5 functions of proteins: • Transport (e.g., hemoglobin) • Provides immunity (e.g., immune system) • Regulate the body (e.g., hormones, enzymes, metabolism) • Muscle tissue (e.g., movement) • ...
... Proteins are also called Polypeptides The monomer is called an amino acid •20 different kinds of amino acids 5 functions of proteins: • Transport (e.g., hemoglobin) • Provides immunity (e.g., immune system) • Regulate the body (e.g., hormones, enzymes, metabolism) • Muscle tissue (e.g., movement) • ...
View Ch. 3 PowerPoint here.
... protein with 2 or more polypeptide chains A protein must be in its quaternary structure to be functional!!!! ...
... protein with 2 or more polypeptide chains A protein must be in its quaternary structure to be functional!!!! ...