Reading Quiz 4 (with answers)
... (e) a ‘spore’ that seeds life. (p. 199). Protocells are suggested tiny enclosures that allow molecular processes to proceed relatively unmolested by the environment. Question 6: The Miller-Urey experiment showed (a) compounds essential to life can form in the presence of Hydrogen. (b) compounds esse ...
... (e) a ‘spore’ that seeds life. (p. 199). Protocells are suggested tiny enclosures that allow molecular processes to proceed relatively unmolested by the environment. Question 6: The Miller-Urey experiment showed (a) compounds essential to life can form in the presence of Hydrogen. (b) compounds esse ...
What meaning(s) do these two photos represent? (Hint* dna,rna
... which can make several forms of a protein. Takes a lot of energy to make initial large molecule. Rule for gene expression, use to state until the 1990s: 1 gene = 1 protein Not true any more 1 gene = can make many proteins ...
... which can make several forms of a protein. Takes a lot of energy to make initial large molecule. Rule for gene expression, use to state until the 1990s: 1 gene = 1 protein Not true any more 1 gene = can make many proteins ...
How do digestive enzymes work
... The shape of an enzyme is very important because it has a direct effect on how it catalyzes a reaction. Why do enzymes have different shapes? An enzyme’s shape is determined by the sequence of amino acids in its structure, and the bonds which form between the atoms of those molecules. ...
... The shape of an enzyme is very important because it has a direct effect on how it catalyzes a reaction. Why do enzymes have different shapes? An enzyme’s shape is determined by the sequence of amino acids in its structure, and the bonds which form between the atoms of those molecules. ...
Characterization of AtAAP1 function in amino acid uptake by the root
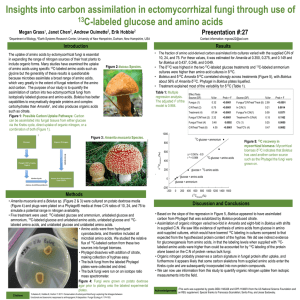
... expected from the hypothesized protein content of the hyphae. We did see indirect evidence for gluconeogenesis from amino acids, in that the labeling levels when supplied with 13Clabeled amino acids were higher than could be accounted for by 13C labeling of the protein alone based on the C:N of prot ...
... expected from the hypothesized protein content of the hyphae. We did see indirect evidence for gluconeogenesis from amino acids, in that the labeling levels when supplied with 13Clabeled amino acids were higher than could be accounted for by 13C labeling of the protein alone based on the C:N of prot ...
26.5 Cotobolism of smino ocids
... higher nutritional value than vegetable proteins becausethey have more essentialamino acids. ...
... higher nutritional value than vegetable proteins becausethey have more essentialamino acids. ...
Extension worksheet – Option C - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... the active site to change so that the substrate cannot bind to it. Such inhibitors, if they bind reversibly, can act in end-product inhibition of metabolic reactions. End-product inhibition is an example of negative feedback. a ...
... the active site to change so that the substrate cannot bind to it. Such inhibitors, if they bind reversibly, can act in end-product inhibition of metabolic reactions. End-product inhibition is an example of negative feedback. a ...
Document
... 4. The amino group for most other amino acids comes from glutamate through transamination (amino transfer). ...
... 4. The amino group for most other amino acids comes from glutamate through transamination (amino transfer). ...
Chemistry & Biochemistry
... Fats – Solid at room temperature Oil – Liquid at room temperature Waxes Steroids Cholesterol is an example Doesn’t contain fatty acids ...
... Fats – Solid at room temperature Oil – Liquid at room temperature Waxes Steroids Cholesterol is an example Doesn’t contain fatty acids ...
Biochemistry
... water lost The bond holding the sugars together is a glycosidic bond Isomers—same chemical formula with different structures ...
... water lost The bond holding the sugars together is a glycosidic bond Isomers—same chemical formula with different structures ...
Molecules of Life Worksheet
... 5. Name the 3 MOST common monosaccharides. How do they compare? Write the chemical formula for all three. 6. Because all 3 simple sugars have the same chemical formula, but different structural formulas, they are called _______________. 7. What are double sugars called? Name & describe the process t ...
... 5. Name the 3 MOST common monosaccharides. How do they compare? Write the chemical formula for all three. 6. Because all 3 simple sugars have the same chemical formula, but different structural formulas, they are called _______________. 7. What are double sugars called? Name & describe the process t ...
Text S1.
... organization of bacterial orthologs encoded by the cysDNC operon [19]. The role of the Cterminal pyrophosphatase domain of heterokont and CCMP1779 putative PAPS synthetase remains uninvestigated, although it appears to be an essential component similar to GTPase (cysN) which drives the energetically ...
... organization of bacterial orthologs encoded by the cysDNC operon [19]. The role of the Cterminal pyrophosphatase domain of heterokont and CCMP1779 putative PAPS synthetase remains uninvestigated, although it appears to be an essential component similar to GTPase (cysN) which drives the energetically ...
Genetic Information DNA - Barnegat Township School District
... RNA – another type of nucleic acid Very similar to DNA, but not exactly the same Only one chain of nucleotides – one strand Made of nucleotides that have A, C, G and U as nitrogenous bases • U replaces T • C pairs with G, A with U • Carries the coded message of DNA from the nucleus to the ribosomes ...
... RNA – another type of nucleic acid Very similar to DNA, but not exactly the same Only one chain of nucleotides – one strand Made of nucleotides that have A, C, G and U as nitrogenous bases • U replaces T • C pairs with G, A with U • Carries the coded message of DNA from the nucleus to the ribosomes ...
Slide 1
... (UACUACUA → UAC UAC UAC, or ACU ACU ACU, or CUA CUA CUA) produced three different strings of amino acids ...
... (UACUACUA → UAC UAC UAC, or ACU ACU ACU, or CUA CUA CUA) produced three different strings of amino acids ...
Constructing a Model of Protein Synthesis
... determines the sequence of amino acids in proteins. In a process called transcription, which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA’s nucleotide sequence into the form of a complementary RNA molecule. Then the mRNA carries this code out to the ribosomes ...
... determines the sequence of amino acids in proteins. In a process called transcription, which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA’s nucleotide sequence into the form of a complementary RNA molecule. Then the mRNA carries this code out to the ribosomes ...
Amino Acids
... charged/uncharged forms. • The ratio is determined by pH at site of absorption, and by strength of the weak acid or base which is represented by pKa of the ionizable group • The eq. is useful in determining how much drug found on either side of a membrane separating two compartments that differ in p ...
... charged/uncharged forms. • The ratio is determined by pH at site of absorption, and by strength of the weak acid or base which is represented by pKa of the ionizable group • The eq. is useful in determining how much drug found on either side of a membrane separating two compartments that differ in p ...
Protein Structure Predictions 1
... Consider a 100 residue protein. If each residue can take only 3 positions, there are ? 3100 = 5 1047 possible conformations. If it takes 10-13s to convert from 1 structure to another, exhaustive search would take ? 1.6 1027 years! ...
... Consider a 100 residue protein. If each residue can take only 3 positions, there are ? 3100 = 5 1047 possible conformations. If it takes 10-13s to convert from 1 structure to another, exhaustive search would take ? 1.6 1027 years! ...
Chapter 1
... • Lysine – Ketogenic - catabolism yields acetyl CoA – Disorders of lysine metabolism ...
... • Lysine – Ketogenic - catabolism yields acetyl CoA – Disorders of lysine metabolism ...
No Slide Title - Docenti.unina
... Subset of helix-lovers. If we forget alanine (I don’t understand that things affair with the helix at all), they share the presence of a (hydrophobic) C-b, C-g and C-d (S-d in Met). These hydrophobic atoms pack on top of each other in the helix. That creates a ...
... Subset of helix-lovers. If we forget alanine (I don’t understand that things affair with the helix at all), they share the presence of a (hydrophobic) C-b, C-g and C-d (S-d in Met). These hydrophobic atoms pack on top of each other in the helix. That creates a ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 11. __________is an inborn error of amino acid metabolism. 12. _________ is the pH at which the analyte is neither negative nor positively charged. 13. Transporter of free fatty acids is the serum ___________. 14. _________________interactions are also referred as Salt linkages or ionic bonds. 15. E ...
... 11. __________is an inborn error of amino acid metabolism. 12. _________ is the pH at which the analyte is neither negative nor positively charged. 13. Transporter of free fatty acids is the serum ___________. 14. _________________interactions are also referred as Salt linkages or ionic bonds. 15. E ...
HW #2
... amino acid, and (2) in addition to the amino acids, there are special Stop codons which terminate the string of amino acids that forms a protein. Next implement the CODON CODE (Codon Code) module which takes in a trio of base pairs as twelve bits of input (F irstA ,F irstC , F irstG ,F irstU ,Second ...
... amino acid, and (2) in addition to the amino acids, there are special Stop codons which terminate the string of amino acids that forms a protein. Next implement the CODON CODE (Codon Code) module which takes in a trio of base pairs as twelve bits of input (F irstA ,F irstC , F irstG ,F irstU ,Second ...