* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Do patients with advanced cancer have any potential for protein
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
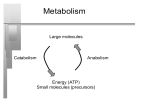
Câncer avançado e aminoácidos Do patients with advanced cancer have any potential for protein anabolism in response toamino acid therapy? Chevalier S1, Winter A. Author information Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2014 May;17(3):213-8. Abstract PURPOSE OF REVIEW: There is evidence that protein anabolism is achievable before cancer evolves into refractory cachexia with attenuation of muscle loss and even muscle gain. This review summarizes recent observations on the role of total and specific amino acids in promoting protein anabolism in human cancer and revisits prior studies in this context. RECENT FINDINGS: Analysis of muscle changes in advanced cancer patients indicated opportunities for inducing anabolism. Maintenance and gain in muscle was reported in a majority of patients, from initiation of oncologic treatment and before the final refractory stage. In addition to being substrates, some amino acids, for example leucine, act as intracellular signals to promote protein synthesis. Recent acute studies demonstrated that provision of amino acids, sufficient to considerably elevate circulating leucine concentrations concurrent with other amino acid and nutrient availability, resulted in significant protein anabolism in cancer patients. This occurred even during weight loss and inflammation. SUMMARY: Patients with cancer have an anabolic potential to be exploited early on in cachexia development. High-leucine and protein supplements are worth testing as part of a multimodal anabolic approach in long-term trials to confirm their efficacy to sustain anabolism, and attenuate or even reverse muscle wasting. PMID: 24572834