Lesson on Proteins
... A bonus question that perhaps requires a bit more thought can be asked for the “R” group marker. A research extension from this can be made be providing unique “R” groups that represent each of the 20 different acids. Questions: 100 points Which of these is ONLY found in proteins and not in carbohyd ...
... A bonus question that perhaps requires a bit more thought can be asked for the “R” group marker. A research extension from this can be made be providing unique “R” groups that represent each of the 20 different acids. Questions: 100 points Which of these is ONLY found in proteins and not in carbohyd ...
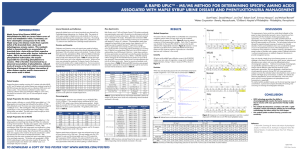
a rapid uplc™ - ms/ms method for determining specific
... Phenylketonuria (PKU) are severe inborn errors of amino acid metabolism which, if untreated, can have catastrophic consequences for the child. Maple syrup urine disease results from a genetic defect of the branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase enzyme system. This metabolic defect is characterized ...
... Phenylketonuria (PKU) are severe inborn errors of amino acid metabolism which, if untreated, can have catastrophic consequences for the child. Maple syrup urine disease results from a genetic defect of the branched-chain α-keto acid dehydrogenase enzyme system. This metabolic defect is characterized ...
Protein - Peoria Public Schools
... fatty acid end and a “polar” phosphate end. This is how cell membranes regulate what enters and leaves the cell. Cholesterol is the final fat we will talk about. You hear a lot of bad things about cholesterol, but your body needs it to function ...
... fatty acid end and a “polar” phosphate end. This is how cell membranes regulate what enters and leaves the cell. Cholesterol is the final fat we will talk about. You hear a lot of bad things about cholesterol, but your body needs it to function ...
Study guide for Midterm 3.
... c. DNP is a hydrophobic acid molecule. Explain its effect. 2. The acetyl group of acetyl-CoA, produced by the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate in the mitochondrion, is transferred to the cytosol by the acetyl group shuttle outlined in Figure 21-10. a. Write the overall equation for the transfer ...
... c. DNP is a hydrophobic acid molecule. Explain its effect. 2. The acetyl group of acetyl-CoA, produced by the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate in the mitochondrion, is transferred to the cytosol by the acetyl group shuttle outlined in Figure 21-10. a. Write the overall equation for the transfer ...
Translation Tjian lec 26
... Amino Acid activation. The two-step process in which an amino acid (with its side chain denoted by R) is activated for protein synthesis by an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase enzyme is shown. As indicated, the energy of ATP hydrolysis is used to attach each amino acid to its tRNA molecule in a high-energ ...
... Amino Acid activation. The two-step process in which an amino acid (with its side chain denoted by R) is activated for protein synthesis by an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase enzyme is shown. As indicated, the energy of ATP hydrolysis is used to attach each amino acid to its tRNA molecule in a high-energ ...
ХРОМАТОГРАММЫ
... We were the first to demonstrate that endogenous levels of free amino acids’ of men’s fluids and tissues are the most important integral indicators and regulators of metabolism. This enables to prove the use of individual amino acids or their combinations for guided correction of metabolism with sp ...
... We were the first to demonstrate that endogenous levels of free amino acids’ of men’s fluids and tissues are the most important integral indicators and regulators of metabolism. This enables to prove the use of individual amino acids or their combinations for guided correction of metabolism with sp ...
Protein Synthesis
... • eukaroytic mRNAs must go through further processing – posttranscriptional modification and processing: • At the 5’ end of the pre-mRNA molecule, a modified form of guanine is added, the 5’ cap. – This helps protect mRNA from hydrolytic enzymes. – It also functions as an “attach here” signal for r ...
... • eukaroytic mRNAs must go through further processing – posttranscriptional modification and processing: • At the 5’ end of the pre-mRNA molecule, a modified form of guanine is added, the 5’ cap. – This helps protect mRNA from hydrolytic enzymes. – It also functions as an “attach here” signal for r ...
Platelet-derived Growth Factor BB (human)
... The ED50, calculated by the dose-dependant proliferation of murine BALB/c 3T3 indicator cells (measured by 3H-thymidine uptake) is < 1 ng/ml, corresponding to a Specific Activity of 1 MIU/mg. ...
... The ED50, calculated by the dose-dependant proliferation of murine BALB/c 3T3 indicator cells (measured by 3H-thymidine uptake) is < 1 ng/ml, corresponding to a Specific Activity of 1 MIU/mg. ...
Biochemistry of Amino acid
... The equilibrium reactions, as written, demonstrate that amino acids contain at least two weakly acidic groups. However, the carboxyl group is a far stronger acid than the amino group. At physiological pH (around 7.4) the carboxyl group will be unprotonated and the amino group will be protonated. An ...
... The equilibrium reactions, as written, demonstrate that amino acids contain at least two weakly acidic groups. However, the carboxyl group is a far stronger acid than the amino group. At physiological pH (around 7.4) the carboxyl group will be unprotonated and the amino group will be protonated. An ...
Table S1.
... In conjunction with Cry genes forms negative components of the circadian clock. Nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group D, NR1D1 is regulated in a circadian manner by BMAL member 1 and via E-box elements regulates a number of clock controlled genes. Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein Indirectly i ...
... In conjunction with Cry genes forms negative components of the circadian clock. Nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group D, NR1D1 is regulated in a circadian manner by BMAL member 1 and via E-box elements regulates a number of clock controlled genes. Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein Indirectly i ...
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids Chapter 3 MACROMOLECULES
... • Structural proteins provide physical stability and movement. • Transport proteins carry substances within the organism (e.g., hemoglobin ) • Genetic regulatory proteins regulate when, how, and to what extent a gene is expressed. AMINO ACIDS Amino acids have carboxyl and amino groups—so they functi ...
... • Structural proteins provide physical stability and movement. • Transport proteins carry substances within the organism (e.g., hemoglobin ) • Genetic regulatory proteins regulate when, how, and to what extent a gene is expressed. AMINO ACIDS Amino acids have carboxyl and amino groups—so they functi ...
Name: :______ Genetic Mutations—Online Model Go to: http
... 1. For translation to begin, tRNA (4) binds to a start codon and signals the ribosome to assemble. 2. A complementary tRNA molecule binds to the exposed codon, bringing its amino acid close to the first amino acid. 3. The ribosome helps form a polypeptide bond between the amino acids and breaks the ...
... 1. For translation to begin, tRNA (4) binds to a start codon and signals the ribosome to assemble. 2. A complementary tRNA molecule binds to the exposed codon, bringing its amino acid close to the first amino acid. 3. The ribosome helps form a polypeptide bond between the amino acids and breaks the ...
Primary structure: the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
... and developed to make the separated amino acids visible ...
... and developed to make the separated amino acids visible ...
SPECIFIKÁCIÓS TÁBLÁZAT Vegyszer neve Specifikáció Kiszerelés
... Isolation of RNA from 1 kit/50 prep. small sample quantities. rDNase included for oncolumn DNA removal. (For RT-PCR) It must contain Enzyme Mix, Reaction Mix, Loading Mix. The Enzyme Mix must contain: Reverse Transcriptase, RNase Inhibitor and DNA Polymerase. The Reaction Mix contains 1 kit/ 30 prep ...
... Isolation of RNA from 1 kit/50 prep. small sample quantities. rDNase included for oncolumn DNA removal. (For RT-PCR) It must contain Enzyme Mix, Reaction Mix, Loading Mix. The Enzyme Mix must contain: Reverse Transcriptase, RNase Inhibitor and DNA Polymerase. The Reaction Mix contains 1 kit/ 30 prep ...
Anatomy & Physiology
... the blood (hemoglobin) and across cell membranes Catalysts (Enzymes)-act as biological catalysts, to regulate and accelerate the rate of biochemical reactions without being used up in the process. ...
... the blood (hemoglobin) and across cell membranes Catalysts (Enzymes)-act as biological catalysts, to regulate and accelerate the rate of biochemical reactions without being used up in the process. ...
200 µmol /L is far too low a concentration of ammonium to affect
... ketoglutarate, which is a key intermediate in the citric acid cycle. As a result, the rate of citric acid cycle activity falls, so reducing very considerably the rate of formation of ATP. It is this lack of ATP that affects ion transport across nerve cell membranes, so resulting in disturbance, then ...
... ketoglutarate, which is a key intermediate in the citric acid cycle. As a result, the rate of citric acid cycle activity falls, so reducing very considerably the rate of formation of ATP. It is this lack of ATP that affects ion transport across nerve cell membranes, so resulting in disturbance, then ...
3. What are macromolecules? LARGE ORGANIC
... 18. Proteins also act as ENZYMES in cells to control reactions. 19. Name the 2 functional groups in amino acids. carboxyl group (-COOH) and the amino group (-NH2). 20. Cells have THOUSANDS of enzymes to act as biological CATALYST 21. Enzymes have an attachment site called the ACTIVE site for the SUB ...
... 18. Proteins also act as ENZYMES in cells to control reactions. 19. Name the 2 functional groups in amino acids. carboxyl group (-COOH) and the amino group (-NH2). 20. Cells have THOUSANDS of enzymes to act as biological CATALYST 21. Enzymes have an attachment site called the ACTIVE site for the SUB ...
Lecture 7-enzymes 3
... Oxygenases Oxygenases catalyze substrate oxidation by molecular O2 The reduced product of the reaction in this case is water and not hydrogen peroxide There are two types of oxygenases: Monooxygenases; transfer one oxygen atom to the substrate, and reduce the other oxygen atom to water Di ...
... Oxygenases Oxygenases catalyze substrate oxidation by molecular O2 The reduced product of the reaction in this case is water and not hydrogen peroxide There are two types of oxygenases: Monooxygenases; transfer one oxygen atom to the substrate, and reduce the other oxygen atom to water Di ...
Extra Credit to replace the Survival of the Fittest Lab
... 23. Amino acids are linked together to make proteins by removing a molecule of ________ in a process called ____________. 24. Chains of amino acids make _______________ which can join together to make a __________. 25. __________ bonds form when water is removed to hold _________ acids together. Lip ...
... 23. Amino acids are linked together to make proteins by removing a molecule of ________ in a process called ____________. 24. Chains of amino acids make _______________ which can join together to make a __________. 25. __________ bonds form when water is removed to hold _________ acids together. Lip ...