FST 123 - Enzymology Homework IS `13
... 3. The course website contains a link to a Kinemage file depicting the structures of four proteins. Download them, view them using Mage or King (http://kinemage.biochem.duke.edu/software/index.php), and classify them according to Chothia’s four categories. 4. A buffer was made by dissolving 18.92 g ...
... 3. The course website contains a link to a Kinemage file depicting the structures of four proteins. Download them, view them using Mage or King (http://kinemage.biochem.duke.edu/software/index.php), and classify them according to Chothia’s four categories. 4. A buffer was made by dissolving 18.92 g ...
Alpha 1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
... – Alpha 1 Antritrypsin secreted from the liver – The improperly folded protein cannot be secreted, and buildup causes liver damage. ...
... – Alpha 1 Antritrypsin secreted from the liver – The improperly folded protein cannot be secreted, and buildup causes liver damage. ...
9. AH Cell Enzymes - charlestonbiology
... Glucose and ATP act as negative modulators AMP (adenosine monophosphate) acts as a positive modulator This is useful, because AMP is a product of ATP breakdown and will be more plentiful when energy levels are low and more glucose is needed A further complication is that there is a hormonal control ...
... Glucose and ATP act as negative modulators AMP (adenosine monophosphate) acts as a positive modulator This is useful, because AMP is a product of ATP breakdown and will be more plentiful when energy levels are low and more glucose is needed A further complication is that there is a hormonal control ...
Document
... Asn is amidated version of Asp Gln is amidated version of Gln Asn and Gln are NOT charged, but are higly polar NH2 group on Gln in proteins can be site for carbohydrate addition (N-linked glycosylation) ...
... Asn is amidated version of Asp Gln is amidated version of Gln Asn and Gln are NOT charged, but are higly polar NH2 group on Gln in proteins can be site for carbohydrate addition (N-linked glycosylation) ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... (12) The energy required by the substrate to be converted to the transition state is known as ________. (13) Alkaptonuria is caused due to the lack of the enzyme _______. (14) The small subunit of anthranilate synthase catalyzes the conversion of ______ to ______. (15) Bio-bleaching of lignin contai ...
... (12) The energy required by the substrate to be converted to the transition state is known as ________. (13) Alkaptonuria is caused due to the lack of the enzyme _______. (14) The small subunit of anthranilate synthase catalyzes the conversion of ______ to ______. (15) Bio-bleaching of lignin contai ...
Document
... Lipids are a large and varied group of biological molecules. Lipids are made mostly from Carbon and Hydrogen atoms and are generally Not soluble in water . (Do not dissolve in water. The common categories of lipids are Fats Oils and Waxes. Lipids can be used to Store Energy. Some lipids are importan ...
... Lipids are a large and varied group of biological molecules. Lipids are made mostly from Carbon and Hydrogen atoms and are generally Not soluble in water . (Do not dissolve in water. The common categories of lipids are Fats Oils and Waxes. Lipids can be used to Store Energy. Some lipids are importan ...
Molecular Modelling of Copper(II) Complexes with Histidine
... Copper is an essential transition metal usually complexed in metalloproteins and low-molecular-weight complexes with peptides and amino acids in biological fluids. LHistidine was identified as the predominant amino acid bound to copper(II) in the bis(Lhistidinato)copper(II) complex (with imidazole n ...
... Copper is an essential transition metal usually complexed in metalloproteins and low-molecular-weight complexes with peptides and amino acids in biological fluids. LHistidine was identified as the predominant amino acid bound to copper(II) in the bis(Lhistidinato)copper(II) complex (with imidazole n ...
Fatty Acid Metabolism
... impairment of β-oxidation: 1. acquired and genetic deficiency of carnitine substance. 2.genetic deficiency of one or more of enzymes of pathway. ...
... impairment of β-oxidation: 1. acquired and genetic deficiency of carnitine substance. 2.genetic deficiency of one or more of enzymes of pathway. ...
Macromolecules
... • Macromolecules are formed by a process known as polymerization, in which large compounds are built by joining smaller ones together – like a puzzle. • The smaller units are called monomers. • The larger units they create are called polymers. ...
... • Macromolecules are formed by a process known as polymerization, in which large compounds are built by joining smaller ones together – like a puzzle. • The smaller units are called monomers. • The larger units they create are called polymers. ...
Unit 4 Test Review-Biomolecules Name Period ______ 1. Complete
... 19. Why do scientists use the “lock and key” model to explain how enzyme’s function? Because the shape of the substrate must match up with the active site of the enzyme 20. What type of macromolecule is an enzyme? What are the subunits “monomers” of an enzyme? Protein, Amino acid 21. Write the corre ...
... 19. Why do scientists use the “lock and key” model to explain how enzyme’s function? Because the shape of the substrate must match up with the active site of the enzyme 20. What type of macromolecule is an enzyme? What are the subunits “monomers” of an enzyme? Protein, Amino acid 21. Write the corre ...
Clicker game ?`s
... A cyclic phosphorylation B non cyclic phosphorylation C ATP synthase coupling D Calvin cycle E acetyl CoA formation 5 The P680 chlorophyll has its "holes" filled by electrons from A RuBP B Photosystem I C water D NADPH E NADH 6 Which steps in cellular respiration make the most ATP? A glycolysis B Kr ...
... A cyclic phosphorylation B non cyclic phosphorylation C ATP synthase coupling D Calvin cycle E acetyl CoA formation 5 The P680 chlorophyll has its "holes" filled by electrons from A RuBP B Photosystem I C water D NADPH E NADH 6 Which steps in cellular respiration make the most ATP? A glycolysis B Kr ...
Study Guide Nucleotide metabolism 2015
... 1. In the synthesis of IMP, why is the second reaction the first committed step? What other pathways utilize PRPP? 2. What is the rate-limiting step of purine synthesis? 3. How is the purine synthetic pathway controlled? 4. What are the amino acid sources for the NH2 come from to form AMP & GMP from ...
... 1. In the synthesis of IMP, why is the second reaction the first committed step? What other pathways utilize PRPP? 2. What is the rate-limiting step of purine synthesis? 3. How is the purine synthetic pathway controlled? 4. What are the amino acid sources for the NH2 come from to form AMP & GMP from ...
Unit 1: Biology Review
... a hydrophobic (nonpolar, water fearing) tail/s. Proteins serve a variety of functions in your body including structure and reaction catalysis. Proteins are composed of uniquely sequenced amino acids. Depending on the sequence of the amino acids, each protein has an extremely unique and complex struc ...
... a hydrophobic (nonpolar, water fearing) tail/s. Proteins serve a variety of functions in your body including structure and reaction catalysis. Proteins are composed of uniquely sequenced amino acids. Depending on the sequence of the amino acids, each protein has an extremely unique and complex struc ...
3. Organic Compounds
... 3 phosphate groups attached to it in a chain. The energy is stored because the phosphates each have a negative charge. These charges repel each other, but they are forced to stay together by the covalent ...
... 3 phosphate groups attached to it in a chain. The energy is stored because the phosphates each have a negative charge. These charges repel each other, but they are forced to stay together by the covalent ...
Biochemistry Notes 2012
... • Matter- anything that has mass and takes up space. • Atoms - basic building blocks of all matter. • Elements – pure substances that can’t be broken down into other substances. (atoms) • Molecules – two or more atoms joined together by chemical bonds. (smallest combination that can’t be divided wit ...
... • Matter- anything that has mass and takes up space. • Atoms - basic building blocks of all matter. • Elements – pure substances that can’t be broken down into other substances. (atoms) • Molecules – two or more atoms joined together by chemical bonds. (smallest combination that can’t be divided wit ...
Handbook of Protein Sequences: A Compilation of Amino Acid
... The transparent sheet provided for the location of residues (which are in lines of 17 units) is not without its drawbacks: for instance, aspartate aminotransferase (p. 26) has 412 and bovine glutamate dehydrogenase(p. 4) has 500 residues whereas the acetate sheet stops short at 340. If the Handbook ...
... The transparent sheet provided for the location of residues (which are in lines of 17 units) is not without its drawbacks: for instance, aspartate aminotransferase (p. 26) has 412 and bovine glutamate dehydrogenase(p. 4) has 500 residues whereas the acetate sheet stops short at 340. If the Handbook ...
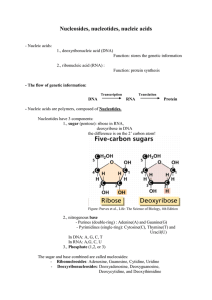
Nucleosides, nucleotides, nucleic acids
... The nucleotide sequence (=base sequence) carries the genetic information, this information will be translated into amino-acid sequence during protein synthesis. - Types and structure of RNA: - messenger RNA = mRNA: carries the information from the DNA to the site of protein synthesis. Single strande ...
... The nucleotide sequence (=base sequence) carries the genetic information, this information will be translated into amino-acid sequence during protein synthesis. - Types and structure of RNA: - messenger RNA = mRNA: carries the information from the DNA to the site of protein synthesis. Single strande ...
File
... • Waxes: A wax is made of one long fatty acid chain joined to one long alcohol. Protect animal ears and plant leaves. • Steroids: A steroid is a lipid composed of four fused carbon rings that help regulate body functions-testerone and estrogen Cholesterol is a steroid found in cell membranes that co ...
... • Waxes: A wax is made of one long fatty acid chain joined to one long alcohol. Protect animal ears and plant leaves. • Steroids: A steroid is a lipid composed of four fused carbon rings that help regulate body functions-testerone and estrogen Cholesterol is a steroid found in cell membranes that co ...
Fats and Proteins
... smaller molecules. The smaller molecules in fats are called glycerol and fatty acid. There are many different fatty acids but they are all similar in several ways. As with all molecules, a molecular formula can be written for a fatty acid by counting the numbers of different atoms and inserting thos ...
... smaller molecules. The smaller molecules in fats are called glycerol and fatty acid. There are many different fatty acids but they are all similar in several ways. As with all molecules, a molecular formula can be written for a fatty acid by counting the numbers of different atoms and inserting thos ...
Chapter Three: The Chemistry of Organic Molecules
... Lipids: Phospholipids • Phospholipids- similar to fats except one fatty acid is replaced by a phosphate group or a group with both phosphate and nitrogen. • Phosphate group= polar head. • Hydrocarbon chains = nonpolar tails. • Phospholipids can arrange themselves in a double layer, the phospholipid ...
... Lipids: Phospholipids • Phospholipids- similar to fats except one fatty acid is replaced by a phosphate group or a group with both phosphate and nitrogen. • Phosphate group= polar head. • Hydrocarbon chains = nonpolar tails. • Phospholipids can arrange themselves in a double layer, the phospholipid ...
PPT
... Both plants and animals contain proteins. Vegetarians, who do not eat meat, can obtain sufficient protein using only plant material for food. A source of protein is meat. ...
... Both plants and animals contain proteins. Vegetarians, who do not eat meat, can obtain sufficient protein using only plant material for food. A source of protein is meat. ...