9/5/08 Transcript I
... Methylene oxidation state exists as a bridge-head between the 5 & 10. This is produced when we metabolize serine to glycine or when we cleave glycine to CO2 + ammonia. It wil also be used to convert deoxyUMP (dUMP; deoxyuridinemonophosphate) to deoxyTMP (deoxythymadinemonophosphate) ...
... Methylene oxidation state exists as a bridge-head between the 5 & 10. This is produced when we metabolize serine to glycine or when we cleave glycine to CO2 + ammonia. It wil also be used to convert deoxyUMP (dUMP; deoxyuridinemonophosphate) to deoxyTMP (deoxythymadinemonophosphate) ...
Immunosuppressive drugs: the first 50 years and a glance forward
... During the past 50 years, many immunosuppressive drugs have been described. Often their mechanisms of action were established long after their discovery. Eventually these mechanisms were found to fall into five groups: (i) regulators of gene expression; (ii) alkylating agents; (iii) inhibitors of de ...
... During the past 50 years, many immunosuppressive drugs have been described. Often their mechanisms of action were established long after their discovery. Eventually these mechanisms were found to fall into five groups: (i) regulators of gene expression; (ii) alkylating agents; (iii) inhibitors of de ...
Asian Odyssey
... Having never been to Asia like Chris Shugart or some of my other friends, the trip was more like traveling to another planet or immersing myself in an adventure film than other scientific trips I’ve taken. The cultures were so different and extremely foreign to me, yet simultaneously parts of the tr ...
... Having never been to Asia like Chris Shugart or some of my other friends, the trip was more like traveling to another planet or immersing myself in an adventure film than other scientific trips I’ve taken. The cultures were so different and extremely foreign to me, yet simultaneously parts of the tr ...
Enzymes are proteins which control biochemical reactions in cells
... o Chemical permanently binds to the enzyme or massively denatures the enzyme o Nerve gas permanently blocks pathways involved in nerve message transmission, resulting in death o Penicillin, the first of "wonder drug" antibiotics, permanently blocks pathways certain bacteria use to assemble their cel ...
... o Chemical permanently binds to the enzyme or massively denatures the enzyme o Nerve gas permanently blocks pathways involved in nerve message transmission, resulting in death o Penicillin, the first of "wonder drug" antibiotics, permanently blocks pathways certain bacteria use to assemble their cel ...
Recombinant Human Epiregulin (rh EREG)
... Physical Appearance: Sterile filtered white lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder. Formulation: lyophilized from 0.5mg/ml solution containing 20mM PBS pH-7.4 + 130mM NaCl. The samples of 1µg contain Trehalose 5% (w/vol) for better recovery Solubility: It is recommended to reconstitute the lyophilized rh ...
... Physical Appearance: Sterile filtered white lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder. Formulation: lyophilized from 0.5mg/ml solution containing 20mM PBS pH-7.4 + 130mM NaCl. The samples of 1µg contain Trehalose 5% (w/vol) for better recovery Solubility: It is recommended to reconstitute the lyophilized rh ...
The Biology of
... hydrogen bonding: alpha helix and beta sheets • (A) is example of an alpha helix. The hydrogen bonds (dotted lines) are between oxygen atoms (red) and hydrogen atoms (white) (shown in this case as occurring every fourth pair of amino acids along the protein). • (B) shows examples of beta-sheets held ...
... hydrogen bonding: alpha helix and beta sheets • (A) is example of an alpha helix. The hydrogen bonds (dotted lines) are between oxygen atoms (red) and hydrogen atoms (white) (shown in this case as occurring every fourth pair of amino acids along the protein). • (B) shows examples of beta-sheets held ...
Camp 1
... • The biosynthesis of other di-, oligo-, and polysaccharides also uses this common activation step to form an appropriate UDP derivative. ...
... • The biosynthesis of other di-, oligo-, and polysaccharides also uses this common activation step to form an appropriate UDP derivative. ...
FREE Sample Here
... thereby, introducing a number of double bonds between the carbon atoms. 2. The double bonds would physically put a kink in the long chain of carbons. This kink would not allow the molecules to associate in a manner necessary to produce a solid. In essence, the molecules would not pack together as ni ...
... thereby, introducing a number of double bonds between the carbon atoms. 2. The double bonds would physically put a kink in the long chain of carbons. This kink would not allow the molecules to associate in a manner necessary to produce a solid. In essence, the molecules would not pack together as ni ...
3.PROTEIN SYNTHESIS overview
... The same genetic code is used for translation in every organism from bacteria to mammals It’s universality is powerful evidence that evolution of the code happened ________________________________________________ _______ amino acids found in proteins are coded for by _____ different bases of RNA 3 n ...
... The same genetic code is used for translation in every organism from bacteria to mammals It’s universality is powerful evidence that evolution of the code happened ________________________________________________ _______ amino acids found in proteins are coded for by _____ different bases of RNA 3 n ...
Chapter 5: What are the major types of organic molecules?
... 2. Carbohydrates: what are they, and what are they used for? What terms are associated with them (including the monomers and the polymer bond name)? Give some examples of molecules in this group. 3. Lipids: what are they, and what are they used for? What terms are associated with them (including maj ...
... 2. Carbohydrates: what are they, and what are they used for? What terms are associated with them (including the monomers and the polymer bond name)? Give some examples of molecules in this group. 3. Lipids: what are they, and what are they used for? What terms are associated with them (including maj ...
Latent fingermark detection using amino acid sensitive reagents
... • Conditions of development have a large impact on contrast and luminescence of fingermark produced • Ninhydrin better than both DFO and 1,2indanedione for colour contrast • DFO and 1,2-indanedione create more sensitive luminescence than ninhydrin ...
... • Conditions of development have a large impact on contrast and luminescence of fingermark produced • Ninhydrin better than both DFO and 1,2indanedione for colour contrast • DFO and 1,2-indanedione create more sensitive luminescence than ninhydrin ...
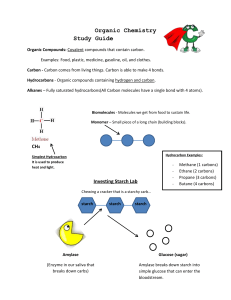
Organic Chemistry Study Guide Organic Compounds: Covalent
... Examples: Food, plastic, medicine, gasoline, oil, and clothes. Carbon - Carbon comes from living things. Carbon is able to make 4 bonds. Hydrocarbons - Organic compounds containing hydrogen and carbon. Alkanes – Fully saturated hydrocarbons(All Carbon molecules have a single bond with 4 atoms). ...
... Examples: Food, plastic, medicine, gasoline, oil, and clothes. Carbon - Carbon comes from living things. Carbon is able to make 4 bonds. Hydrocarbons - Organic compounds containing hydrogen and carbon. Alkanes – Fully saturated hydrocarbons(All Carbon molecules have a single bond with 4 atoms). ...
The Chemistry of Life
... 4. Proteins and Nucleic Acids a. Proteins 1) Make a person unique 2) Needed for every function 3) C, H, O, N, plus others ...
... 4. Proteins and Nucleic Acids a. Proteins 1) Make a person unique 2) Needed for every function 3) C, H, O, N, plus others ...
WATER SOLUBLE VITA
... -pyruvate dehydrogenase and alphaketoglutarate complexes -succinate dehydrogenase (Krebs cycle) -fatty acids oxidation (acyl CoA dehydrogenase) -uric acid formation (xanthine oxidase) -electron transport in respiration chain ...
... -pyruvate dehydrogenase and alphaketoglutarate complexes -succinate dehydrogenase (Krebs cycle) -fatty acids oxidation (acyl CoA dehydrogenase) -uric acid formation (xanthine oxidase) -electron transport in respiration chain ...
All rights reserved. AP Biology Interaction among Living Systems
... 11. Scientists classify amino acids into groups based on their chemical properties. When the amino acid is joined into a protein, its properties determine its effect on the structure and function of the protein. The diagram shows the structure of two amino acids: alanine and phenylalanine. Both are ...
... 11. Scientists classify amino acids into groups based on their chemical properties. When the amino acid is joined into a protein, its properties determine its effect on the structure and function of the protein. The diagram shows the structure of two amino acids: alanine and phenylalanine. Both are ...
Amino acid - Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
... group, which is referred to as the side-chain, varies in different amino acids. It may simply be a hydrogen atom, as in glycine, or it may be a more complex radical containing, for example, a phenyl group [8] There are nine essential (indispensable) amino acids, which cannot be synthesised in the bo ...
... group, which is referred to as the side-chain, varies in different amino acids. It may simply be a hydrogen atom, as in glycine, or it may be a more complex radical containing, for example, a phenyl group [8] There are nine essential (indispensable) amino acids, which cannot be synthesised in the bo ...
Introductory Chemistry: Concepts & Connections 4th Edition
... intermolecular forces. Chapter 20 ...
... intermolecular forces. Chapter 20 ...
VILLIN MODEL CONSTRUCTION
... The model is intended to show how the tertiary structure of villin is critical to its function. Other than making the villin model, two hinges will replace the peptide bond between amino acids. One hinge will occur between amino acids two and three, while the other will occur between amino acids sev ...
... The model is intended to show how the tertiary structure of villin is critical to its function. Other than making the villin model, two hinges will replace the peptide bond between amino acids. One hinge will occur between amino acids two and three, while the other will occur between amino acids sev ...
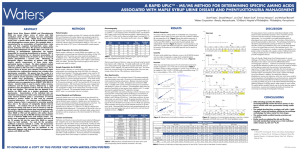
A Rapid UPLC™ MS/MS Method for Determining Specific
... metabolism which, if left untreated, can have catastrophic consequences for the child. Maple Syrup Urine Disease results from a genetic defect of the branched-chain a-keto acid dehydrogenase enzyme system. This metabolic defect is characterized by an accumulation of branched-chain α-keto acids and t ...
... metabolism which, if left untreated, can have catastrophic consequences for the child. Maple Syrup Urine Disease results from a genetic defect of the branched-chain a-keto acid dehydrogenase enzyme system. This metabolic defect is characterized by an accumulation of branched-chain α-keto acids and t ...
Hormones of the Gut
... bladder to contract--cholecystokinin. 2. 1940s: Extract of duodenal mucosa stimulates pancreas to secrete enzymes--pancreozymin. 3. 1964-8: Purification of a single substance that stimulated both contraction of the gall bladder and pancreatic enzyme secretion--settled on one name: cholecystokinin (C ...
... bladder to contract--cholecystokinin. 2. 1940s: Extract of duodenal mucosa stimulates pancreas to secrete enzymes--pancreozymin. 3. 1964-8: Purification of a single substance that stimulated both contraction of the gall bladder and pancreatic enzyme secretion--settled on one name: cholecystokinin (C ...
MACROMOLECULE WEBQUEST Name: Site 1 The Lipids Site
... Site Location:http://www.quia.com/cb/86263.html Test your knowledge of the macromolecules -- compete against yourself in Biochemistry Jeopardy! Do you need more practice? Try it again. How did you do? Things to Know for Monday’s Test: ( use google if you need to) What is a protease? ...
... Site Location:http://www.quia.com/cb/86263.html Test your knowledge of the macromolecules -- compete against yourself in Biochemistry Jeopardy! Do you need more practice? Try it again. How did you do? Things to Know for Monday’s Test: ( use google if you need to) What is a protease? ...