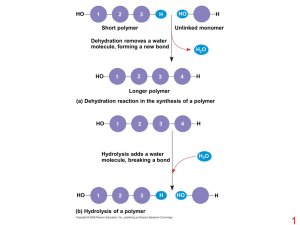
2.3 Carbon Compounds
... 1.Review- Name four groups of organic compounds found in living things Explain- Describe at least one function of each group of organic compounds Infer- Why are proteins considered polymers but lipids not ...
... 1.Review- Name four groups of organic compounds found in living things Explain- Describe at least one function of each group of organic compounds Infer- Why are proteins considered polymers but lipids not ...
2.3_Carbon_Compounds
... 1.Review- Name four groups of organic compounds found in living things Explain- Describe at least one function of each group of organic compounds Infer- Why are proteins considered polymers but lipids not ...
... 1.Review- Name four groups of organic compounds found in living things Explain- Describe at least one function of each group of organic compounds Infer- Why are proteins considered polymers but lipids not ...
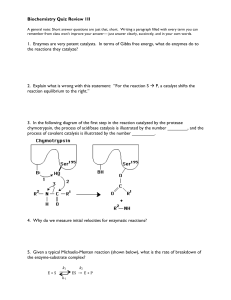
Biochemistry Quiz Review 1II 1. Enzymes are very potent catalysts
... cases of people having a genetic disease in which one of the enzymes of glycolysis is severely affected. Why do you suppose such mutations are seen so rarely? ...
... cases of people having a genetic disease in which one of the enzymes of glycolysis is severely affected. Why do you suppose such mutations are seen so rarely? ...
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein
... Next let’s look at the transfer RNA(tRNA) : It is a cloverleaf, double stranded is some places with three loops, the bottom loop has three bases called the anticodon. These three bases (the anticodon) is the mechanism for the correct tRNA to pair with the mRNA in the ribosome. At the top (3’ end) th ...
... Next let’s look at the transfer RNA(tRNA) : It is a cloverleaf, double stranded is some places with three loops, the bottom loop has three bases called the anticodon. These three bases (the anticodon) is the mechanism for the correct tRNA to pair with the mRNA in the ribosome. At the top (3’ end) th ...
Biology_Review-final
... http://www.cogs.susx.ac.uk/courses/gc/alcohol-dehydrogenase-protein.jpg ...
... http://www.cogs.susx.ac.uk/courses/gc/alcohol-dehydrogenase-protein.jpg ...
MedBiochem Exam For each of the following questions, choose the
... 21. The conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA is regulated by covalent modification. Which of the following causes an INCREASE in the level of phosphorylation of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC)? A. coenzyme A B. thiamine pyrophosphate C. NADH D. insulin E. lipoic acid 22. All of the followin ...
... 21. The conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA is regulated by covalent modification. Which of the following causes an INCREASE in the level of phosphorylation of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC)? A. coenzyme A B. thiamine pyrophosphate C. NADH D. insulin E. lipoic acid 22. All of the followin ...
A defined growth medium for Clostridium difficile
... tyrosine and valine - and four vitamins - biotin, pantothenate, pyridoxamine and riboflavin - were essential for growth of Clostriditlm perfringens BP6K. Fuchs & Bonde (1957) observed that 11 amino acids - arginine, aspartic acid, cysteine, glutamic acid, histidine, leucine, phenylalanine, threonine ...
... tyrosine and valine - and four vitamins - biotin, pantothenate, pyridoxamine and riboflavin - were essential for growth of Clostriditlm perfringens BP6K. Fuchs & Bonde (1957) observed that 11 amino acids - arginine, aspartic acid, cysteine, glutamic acid, histidine, leucine, phenylalanine, threonine ...
Carbohydrates are
... Steroids have the same four-ring structure as cholesterol, but each differs by the groups attached to these rings. ...
... Steroids have the same four-ring structure as cholesterol, but each differs by the groups attached to these rings. ...
gln.val.tyr.ala lys.arg.glu.trp met.his.leu.asp cys.pro.gly.asn F-A-D
... You have isolated an octapeptide with the amino acid composition (Lys2, Asp, Tyr, Phe, Gly, Ser, Ala) Reaction of the intact peptide with FDNB yields DNP-alanine. Cleavage with trypsin yields peptides with compositions (Lys, Ala, Ser) and (Gly, Phe, Lys) plus a dipeptide. Reaction with chymotrypsin ...
... You have isolated an octapeptide with the amino acid composition (Lys2, Asp, Tyr, Phe, Gly, Ser, Ala) Reaction of the intact peptide with FDNB yields DNP-alanine. Cleavage with trypsin yields peptides with compositions (Lys, Ala, Ser) and (Gly, Phe, Lys) plus a dipeptide. Reaction with chymotrypsin ...
Organic Molecule Marshmallow Lab
... Gathered Information: Organic molecules all contain carbon. There are four different groups of organic molecules. Each group can be identified by the elements that comprise it and the functional groups that are present within it. The four groups of organic molecules are carbohydrates, lipids, protei ...
... Gathered Information: Organic molecules all contain carbon. There are four different groups of organic molecules. Each group can be identified by the elements that comprise it and the functional groups that are present within it. The four groups of organic molecules are carbohydrates, lipids, protei ...
Biochemistry PowerPoint
... up chemical reactions without being affected by the reactions themselves. Enzyme: a protein that increases the rate of reactions by lowering the activation energy. ...
... up chemical reactions without being affected by the reactions themselves. Enzyme: a protein that increases the rate of reactions by lowering the activation energy. ...
urea cycle
... Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Threonine Tryptophan Valine Arginine (not for adult) ...
... Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Threonine Tryptophan Valine Arginine (not for adult) ...
Vll. Nitrogen metabolism:
... Histidine Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Threonine Tryptophan Valine Arginine (not for adult) ...
... Histidine Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Threonine Tryptophan Valine Arginine (not for adult) ...
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
... (PFK-1) • PFK-1 catalyzes an early step in glycolysis • Phosphoenol pyruvate (PEP), an intermediate near the end of the pathway is an allosteric inhibitor of PFK-1 ...
... (PFK-1) • PFK-1 catalyzes an early step in glycolysis • Phosphoenol pyruvate (PEP), an intermediate near the end of the pathway is an allosteric inhibitor of PFK-1 ...
o"', ,jl w - 'J'
... Introduction to Metabolism - Overview of metabolic pathways (carbohydrates, amino acids, lipids, nucleic acids), key reactions of metabolic pathways, regulation of metabolic pathways, evolution of metabolic pathways-RNA world. ...
... Introduction to Metabolism - Overview of metabolic pathways (carbohydrates, amino acids, lipids, nucleic acids), key reactions of metabolic pathways, regulation of metabolic pathways, evolution of metabolic pathways-RNA world. ...
4. AMINO ACIDS
... therefore be supplied in a ready made form in the diet. • Non-essential amino acids • NEAA are those acids that can be synthesized in the body from a suitable carbon source, amino groups from other amino acids or simple compounds such as diammonium citrate, and consequently do not have to be supplie ...
... therefore be supplied in a ready made form in the diet. • Non-essential amino acids • NEAA are those acids that can be synthesized in the body from a suitable carbon source, amino groups from other amino acids or simple compounds such as diammonium citrate, and consequently do not have to be supplie ...
Exam I will be on lectures 1 to 6 (Introduction to )
... c. carbon atoms joined by single bonds. d. carbon atoms joined by double bonds. e. oxygen atoms joined by double bonds. ...
... c. carbon atoms joined by single bonds. d. carbon atoms joined by double bonds. e. oxygen atoms joined by double bonds. ...
ProBasics™
... Are There Any Potential Drug Interactions? At this time, there are no known adverse reactions when taken in conjunction with medications. (continued) ...
... Are There Any Potential Drug Interactions? At this time, there are no known adverse reactions when taken in conjunction with medications. (continued) ...
Immunosuppressive drugs: the first 50 years and a glance forward
... During the past 50 years, many immunosuppressive drugs have been described. Often their mechanisms of action were established long after their discovery. Eventually these mechanisms were found to fall into five groups: (i) regulators of gene expression; (ii) alkylating agents; (iii) inhibitors of de ...
... During the past 50 years, many immunosuppressive drugs have been described. Often their mechanisms of action were established long after their discovery. Eventually these mechanisms were found to fall into five groups: (i) regulators of gene expression; (ii) alkylating agents; (iii) inhibitors of de ...