CH 3 Notes
... B. Functional groups: clusters of atoms that influence the properties of the molecule 1. Alcohol: OH is attached to carbon and makes the molecule polar 2. Some alcohols are needed by organisms to carry out their life processes ...
... B. Functional groups: clusters of atoms that influence the properties of the molecule 1. Alcohol: OH is attached to carbon and makes the molecule polar 2. Some alcohols are needed by organisms to carry out their life processes ...
Connections of Carbohydrate, Protein, and Lipid
... muscle. The glycogen will be hydrolyzed into glucose monomers (G-1-P) if blood sugar levels drop. The presence of glycogen as a source of glucose allows ATP to be produced for a longer period of time during exercise. Glycogen is broken down into G-1-P and converted into G-6-P in both muscle and live ...
... muscle. The glycogen will be hydrolyzed into glucose monomers (G-1-P) if blood sugar levels drop. The presence of glycogen as a source of glucose allows ATP to be produced for a longer period of time during exercise. Glycogen is broken down into G-1-P and converted into G-6-P in both muscle and live ...
ch_12 - WordPress.com
... amination, in which it reacts with α-ketoglutaric acid to from glutamic acid (amino acid). Then by transfer of amino group form one amino acid (glutamic acid) to the keto group of a keto acid, other amino acids are produced and this process is called as transamination catalysed by an enzyme transa ...
... amination, in which it reacts with α-ketoglutaric acid to from glutamic acid (amino acid). Then by transfer of amino group form one amino acid (glutamic acid) to the keto group of a keto acid, other amino acids are produced and this process is called as transamination catalysed by an enzyme transa ...
C485 Exam I
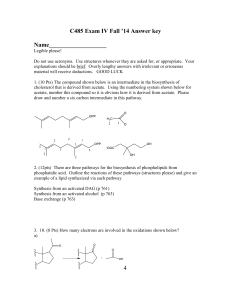
... 1. (10 Pts) The compound shown below is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of cholesterol that is derived from acetate. Using the numbering system shown below for acetate, number this compound so it is obvious how it is derived from acetate. Please draw and number a six carbon intermediate in this ...
... 1. (10 Pts) The compound shown below is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of cholesterol that is derived from acetate. Using the numbering system shown below for acetate, number this compound so it is obvious how it is derived from acetate. Please draw and number a six carbon intermediate in this ...
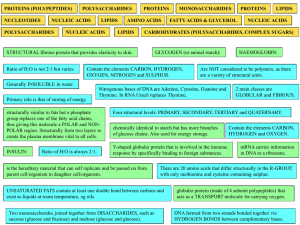
ANSWERS BIOCHEMISTRY CARBOHYDRATES
... *Alkali hydrolysis of triglycerides is known as saponification. *Sodium palmitate and glycerol are formed. When an oil or fat is exposed to moist air for a long time , it develops an unpleasant smell and sour taste. This phenomenon is called rancidity. Hydrolytic rancidity can be prevented by refrig ...
... *Alkali hydrolysis of triglycerides is known as saponification. *Sodium palmitate and glycerol are formed. When an oil or fat is exposed to moist air for a long time , it develops an unpleasant smell and sour taste. This phenomenon is called rancidity. Hydrolytic rancidity can be prevented by refrig ...
BIS103-002 (Spring 2008) - UC Davis Plant Sciences
... Proteins from animal sources contain a balanced set of essential amino acids. However, plant proteins are often deficient in certain essential amino acids, depending on the source of the plant diet (crop species; tissues, seeds or fruits consumed). d) The aromatic amino acids tryptophan and phenylal ...
... Proteins from animal sources contain a balanced set of essential amino acids. However, plant proteins are often deficient in certain essential amino acids, depending on the source of the plant diet (crop species; tissues, seeds or fruits consumed). d) The aromatic amino acids tryptophan and phenylal ...
Sticky end in protein synthesis - The School of Molecular and
... inset shows the aminoacylation of tRNA, in which an amino acid is paired with a tRNA by the enzyme aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS). It is a failure of quality control at this stage that Lee et al.2 show causes neurodegeneration in ‘sticky mice’. Once synthesized, a protein usually becomes functiona ...
... inset shows the aminoacylation of tRNA, in which an amino acid is paired with a tRNA by the enzyme aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS). It is a failure of quality control at this stage that Lee et al.2 show causes neurodegeneration in ‘sticky mice’. Once synthesized, a protein usually becomes functiona ...
Catalogue Number CTK-468 Introduction Insulin decreases blood
... It is recommended to reconstitute the lyophilized Insulin Porcine in sterile 18MΩ- ...
... It is recommended to reconstitute the lyophilized Insulin Porcine in sterile 18MΩ- ...
Steroidogenesis - Delta State University
... – Changes in the number of carbons – Location of double bond ...
... – Changes in the number of carbons – Location of double bond ...
Zoology – The Chemical Basis of Animal Life
... single functional protein 4. Enzymes – mostly large, complex proteins that function as biological catalysts under specific conditions. (A special type of RNA can also function as an enzyme.) a.Enzymes do the following: 1) Break bonds and allow new bonds to form, facilitating chemical reactions 2) Sp ...
... single functional protein 4. Enzymes – mostly large, complex proteins that function as biological catalysts under specific conditions. (A special type of RNA can also function as an enzyme.) a.Enzymes do the following: 1) Break bonds and allow new bonds to form, facilitating chemical reactions 2) Sp ...
Information Sheet - HJ Baker & Bro., Inc.
... Numerous alternate proteins have been used to reduce or replace fishmeal, but each varies in nutrient composition and digestibility. A combination of feed ingredients is often a better match for the nutrient requirements of the target species. For example, proteins are comprised of 20 amino acids of ...
... Numerous alternate proteins have been used to reduce or replace fishmeal, but each varies in nutrient composition and digestibility. A combination of feed ingredients is often a better match for the nutrient requirements of the target species. For example, proteins are comprised of 20 amino acids of ...
Summary for Chapter 7 – Metabolism: Transformations
... The fatty acids of a triglyceride, on the other hand, cannot make glucose, but they can provide abundant acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA may then enter the TCA cycle to release energy or combine with other molecules of acetyl CoA to make body fat. The body can use some amino acids to produce glucose, whereas ...
... The fatty acids of a triglyceride, on the other hand, cannot make glucose, but they can provide abundant acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA may then enter the TCA cycle to release energy or combine with other molecules of acetyl CoA to make body fat. The body can use some amino acids to produce glucose, whereas ...
Macromolecules
... Denaturing of Proteins: Proteins have a specific structure, which is important for their function. If the structure is distorted or destroyed by heat / ionic concentration / pH change, then the protein is said to be ‘denatured’. Denatured proteins cannot function any more. Enzymes speed up the rates ...
... Denaturing of Proteins: Proteins have a specific structure, which is important for their function. If the structure is distorted or destroyed by heat / ionic concentration / pH change, then the protein is said to be ‘denatured’. Denatured proteins cannot function any more. Enzymes speed up the rates ...
1) From
... Reference only, Glutamate metabolism, 4 possible synthetic pathways 1) From -ketoglutarate (2-oxoglutarate) and ammonia via glutamate dehydrogenase. This pathway is of fundamental importance in the synthesis of all amino acids, since it is the key mechanism for the formation of -amino groups dir ...
... Reference only, Glutamate metabolism, 4 possible synthetic pathways 1) From -ketoglutarate (2-oxoglutarate) and ammonia via glutamate dehydrogenase. This pathway is of fundamental importance in the synthesis of all amino acids, since it is the key mechanism for the formation of -amino groups dir ...
- Applied Science University
... After studying this course the student should be able to: Successful completion of this course should lead to the following learning outcomes : 1- Students should be able to follow the saftey procedures and lab instruction. 2- Student should be able to identify and effeciently use the glasswares and ...
... After studying this course the student should be able to: Successful completion of this course should lead to the following learning outcomes : 1- Students should be able to follow the saftey procedures and lab instruction. 2- Student should be able to identify and effeciently use the glasswares and ...
Other Pathways of Carbohydrate Metabolism Gluconeogenesis
... With fasting, 12 hour supply of glucose from glycogen stores Gluconeogenesis provides new glucose from noncarbohydrate precursors (lactate, pyruvate, glycerol, citric acid cycle intermediates, carbon skeletons of amino acids except leucine and lysine) All must be converted to oxaloacetate Note: No p ...
... With fasting, 12 hour supply of glucose from glycogen stores Gluconeogenesis provides new glucose from noncarbohydrate precursors (lactate, pyruvate, glycerol, citric acid cycle intermediates, carbon skeletons of amino acids except leucine and lysine) All must be converted to oxaloacetate Note: No p ...
Chapter 3 Topic: Biomolecules Main concepts: •In chemistry, the
... when the helix or pleated sheet folds back on itself to form twisted or knot-like structures. This is caused by hydrogen bonding, and special bonds called disulfide bridges that form between amino acids. Quaternary structure is where multiple proteins are linked together into one large structure. He ...
... when the helix or pleated sheet folds back on itself to form twisted or knot-like structures. This is caused by hydrogen bonding, and special bonds called disulfide bridges that form between amino acids. Quaternary structure is where multiple proteins are linked together into one large structure. He ...
Oxidative Phosphorylation
... is the sum of all chemical changes occurring in a cell , tissue or the body It is composed of pathways Pathway is a multistep sequence of reactions in which the product of one reaction serves as the substrate of the subsequent reaction Each reaction is catalyzed by a specific enzyme (may be with hel ...
... is the sum of all chemical changes occurring in a cell , tissue or the body It is composed of pathways Pathway is a multistep sequence of reactions in which the product of one reaction serves as the substrate of the subsequent reaction Each reaction is catalyzed by a specific enzyme (may be with hel ...
Proteins synthesisand expression
... • Storage proteins: e.g. aleurone in seeds helps germination, and casein in milk helps supply valuable protein to babies. • Buffer proteins: e.g. blood proteins, due to their high charge, help maintain the pH of plasma. ...
... • Storage proteins: e.g. aleurone in seeds helps germination, and casein in milk helps supply valuable protein to babies. • Buffer proteins: e.g. blood proteins, due to their high charge, help maintain the pH of plasma. ...
Biochemistry with Elements of Chemistry - Collegium Medicum
... 2. The retake of a failed test has to be in the same form as the original test. The first retake must take place before the next test. The second retake, called additional test, takes place right before the admission to the exam. If a student fails more than one test as a first retake, they need to ...
... 2. The retake of a failed test has to be in the same form as the original test. The first retake must take place before the next test. The second retake, called additional test, takes place right before the admission to the exam. If a student fails more than one test as a first retake, they need to ...