Unit 9 Test Review
... • Why are the messenger RNA molecules received by eukaryotic ribosomes shorter than the messenger RNA molecules formed by transcription of DNA? • A. Base deletion mutations make the mRNA shorter. • B. Start codons are not at the end of the mRNA molecule. • C. Introns are removed before the RNA is t ...
... • Why are the messenger RNA molecules received by eukaryotic ribosomes shorter than the messenger RNA molecules formed by transcription of DNA? • A. Base deletion mutations make the mRNA shorter. • B. Start codons are not at the end of the mRNA molecule. • C. Introns are removed before the RNA is t ...
Document
... • There is a single reading frame maintained throughout the process of translation • Each codon consists of three nucleotides • Code is nonoverlapping • Code is degenerate: each amino acid is specified by more than one codon ...
... • There is a single reading frame maintained throughout the process of translation • Each codon consists of three nucleotides • Code is nonoverlapping • Code is degenerate: each amino acid is specified by more than one codon ...
Macromolecules and Enzymes
... • The reaction occurs, and the products are released and the enzyme binds with another substrate ...
... • The reaction occurs, and the products are released and the enzyme binds with another substrate ...
g. ¶I - wwphs
... d.-Twists, bends, loops, and folds of a new polypeptide chain; hydrogen bonds between R groups make some stretches of amino acids coil, and other regions form sheets or ioops Comes in two slightly different forms, alpha and beta; two of each form make up one hemoglobin molecule in humans Airoteins t ...
... d.-Twists, bends, loops, and folds of a new polypeptide chain; hydrogen bonds between R groups make some stretches of amino acids coil, and other regions form sheets or ioops Comes in two slightly different forms, alpha and beta; two of each form make up one hemoglobin molecule in humans Airoteins t ...
Initiation
... 1. Initiation – attachment of mRNA to the ribosome (This was already covered in Step # 3) 2. Elongation – the addition of amino acids to the growing protein chain A Site P site ...
... 1. Initiation – attachment of mRNA to the ribosome (This was already covered in Step # 3) 2. Elongation – the addition of amino acids to the growing protein chain A Site P site ...
DNA Review Cards
... Explain why all mutations do not necessarily have a negative impact on the protein or on the organism as a whole. ...
... Explain why all mutations do not necessarily have a negative impact on the protein or on the organism as a whole. ...
PowerPoint - Center for Biological Sequence Analysis
... • A data-driven method to predict a feature, given a set of training data • In biology input features could be amino acid sequence or nucleotides • Secondary structure prediction • Signal peptide prediction • Surface accessibility • Propeptide prediction ...
... • A data-driven method to predict a feature, given a set of training data • In biology input features could be amino acid sequence or nucleotides • Secondary structure prediction • Signal peptide prediction • Surface accessibility • Propeptide prediction ...
4. Transcription in Detail
... The correct amino acids must be _________________to the polypeptide-building site. _______________________delivers the amino acids It is a small single-stranded nucleic acid whose structure resembles a _____________ At one _____ of tRNA a sequence of three bases (the ______________) recognizes the c ...
... The correct amino acids must be _________________to the polypeptide-building site. _______________________delivers the amino acids It is a small single-stranded nucleic acid whose structure resembles a _____________ At one _____ of tRNA a sequence of three bases (the ______________) recognizes the c ...
Dr. Ryals will give a seminar at IGBMC, focusing on global
... Dr. Ryals will give a seminar at IGBMC, focusing on global metabolism and the latest metabolom profiling technologies. Specifically, an overview of Metabolon’s global biochemical profiling technology platform will be presented with focus on the analytical approaches as well as applications to biolog ...
... Dr. Ryals will give a seminar at IGBMC, focusing on global metabolism and the latest metabolom profiling technologies. Specifically, an overview of Metabolon’s global biochemical profiling technology platform will be presented with focus on the analytical approaches as well as applications to biolog ...
11.2 Reading Guide - Lewis Center for Educational Research
... ____ When the ribosome reaches the stop codon ( UAA or UAG), it disconnectes from the mRNA strand and seeks another to read. ____ A peptide bond is made between adjacent amino acids. ____ A ribosome attaches on to a mRNA strand at the start codon (AUG). ____ Once the anticodon on the tRNA has been p ...
... ____ When the ribosome reaches the stop codon ( UAA or UAG), it disconnectes from the mRNA strand and seeks another to read. ____ A peptide bond is made between adjacent amino acids. ____ A ribosome attaches on to a mRNA strand at the start codon (AUG). ____ Once the anticodon on the tRNA has been p ...
Eukaryotic Gene Structure
... • There are 43, ( 64 codon ) total different triplets that can be created but only 20 different amino acids. • The DNA has a triplet code using only the 4 nucleotides, A,C,G and T. Only 3 nucleotides form a triplet which, when in a gene, codes for a part of a protein. • The code is degenerate i.e.th ...
... • There are 43, ( 64 codon ) total different triplets that can be created but only 20 different amino acids. • The DNA has a triplet code using only the 4 nucleotides, A,C,G and T. Only 3 nucleotides form a triplet which, when in a gene, codes for a part of a protein. • The code is degenerate i.e.th ...
AP Biology 042 – Biological Molecules Video
... monomers together in a certain sequence/order they have a. The process of “putting monomers together” is called b. What is lost during the process of #11? c. What kind of bond is formed generally? Specifically between amino acids of a protein? d. What must be added to break the bonds? e. What is the ...
... monomers together in a certain sequence/order they have a. The process of “putting monomers together” is called b. What is lost during the process of #11? c. What kind of bond is formed generally? Specifically between amino acids of a protein? d. What must be added to break the bonds? e. What is the ...
From DNA to Proteins
... The genetic code matches each codon to its amino acid or function. –three stop codons –one start codon, codes for methionine ...
... The genetic code matches each codon to its amino acid or function. –three stop codons –one start codon, codes for methionine ...
04-05 Biochem review sheet answers ws
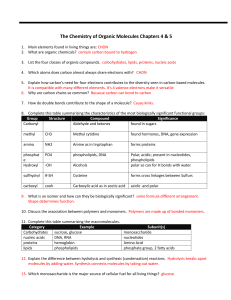
... 4. Which atoms does carbon almost always share electrons with? CHON 5. Explain how carbon’s need for four electrons contributes to the diversity seen in carbon-based molecules. It is compatible with many different elements. It’s 4 valence electrons make it versatile 6. Why are carbon chains so commo ...
... 4. Which atoms does carbon almost always share electrons with? CHON 5. Explain how carbon’s need for four electrons contributes to the diversity seen in carbon-based molecules. It is compatible with many different elements. It’s 4 valence electrons make it versatile 6. Why are carbon chains so commo ...
Elements Made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and
... regulating other proteins carrying out chemical reactions (enzymes) ...
... regulating other proteins carrying out chemical reactions (enzymes) ...
File
... • The mRNA carries genetic information from DNA in the nucleus through pores in the nuclear membrane (in eukaryotic cells) to the cytoplasm which is the site of protein synthesis. ...
... • The mRNA carries genetic information from DNA in the nucleus through pores in the nuclear membrane (in eukaryotic cells) to the cytoplasm which is the site of protein synthesis. ...
Animation Script for Translation
... 1. In translation, the cell uses an mRNA strand as a template to assemble proteins. The cell has just transcribed this mRNA strand from its DNA, and it now translates the mRNA’s nucleotide sequence into a chain of amino acids. This chain, called a polypeptide, forms the basic structure of a protein. ...
... 1. In translation, the cell uses an mRNA strand as a template to assemble proteins. The cell has just transcribed this mRNA strand from its DNA, and it now translates the mRNA’s nucleotide sequence into a chain of amino acids. This chain, called a polypeptide, forms the basic structure of a protein. ...
Powerpoint
... PROTEINS IN THE HUMAN BODY Made of 21 different amino acids Our cells can only make some of them We need to eat the rest ...
... PROTEINS IN THE HUMAN BODY Made of 21 different amino acids Our cells can only make some of them We need to eat the rest ...
Macromolecules Notes File
... twisting of the secondary structure. Stabilized by hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonds, ionic interactions and disulfide bonds. ...
... twisting of the secondary structure. Stabilized by hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonds, ionic interactions and disulfide bonds. ...
A look at macromolecules (Text pages 38
... • Tertiary: continued folding post secondary structure • Quaternary: more than one polypeptide chain Structure determined by order of amino acids • Degree of hydrogen bonding • Structure can be ‘denatured’ • Gentle vs. harsh ...
... • Tertiary: continued folding post secondary structure • Quaternary: more than one polypeptide chain Structure determined by order of amino acids • Degree of hydrogen bonding • Structure can be ‘denatured’ • Gentle vs. harsh ...
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY.rtf
... tRNA has the anticodon; read from 3’ to 5’ and is complementary and antiparallel to the codon of mRNA) and brings the correct amino acid to the correct codon. For each amino acid, there is a codon (3 letter base code of mRNA) Ribosome—catalyzes the translation of RNA into protein by linking the amin ...
... tRNA has the anticodon; read from 3’ to 5’ and is complementary and antiparallel to the codon of mRNA) and brings the correct amino acid to the correct codon. For each amino acid, there is a codon (3 letter base code of mRNA) Ribosome—catalyzes the translation of RNA into protein by linking the amin ...
Complementary base pairing Hydrogen bonding between purines
... environmental mutagen Environmental influences causing mutations in humans genetic disorder An illness caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome eg.sicsickle eg. Sickle cell anemia is caused by a point mutation initiation First step of protein synthesis, in which all the translation co ...
... environmental mutagen Environmental influences causing mutations in humans genetic disorder An illness caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome eg.sicsickle eg. Sickle cell anemia is caused by a point mutation initiation First step of protein synthesis, in which all the translation co ...
File
... How many amino acids exist in nature (count the number in the chart above)? How then are there thousands of proteins? 20 (THE ORDER AND NUMBER OF THESE AMINO ACIDS RESULT IN ALL OF THESE DIFFERENT ...
... How many amino acids exist in nature (count the number in the chart above)? How then are there thousands of proteins? 20 (THE ORDER AND NUMBER OF THESE AMINO ACIDS RESULT IN ALL OF THESE DIFFERENT ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.