DNA functions worksheet
... a) Does it represent transcription or translation? b) What is molecule X and where was it produced? c) ...
... a) Does it represent transcription or translation? b) What is molecule X and where was it produced? c) ...
Practice Questions for Exam IV
... Using the answer code below, indicate which chemoreceptors are being described. A = peripheral chemoreceptors, B = central chemoreceptors, C = both chemoreceptors, D = neither 2. ____ stimulated by an arterial PO2 of 80 mm Hg. 3. ____ strongly stimulated by an elevated [H+] in CSF. 4. ____ stimulate ...
... Using the answer code below, indicate which chemoreceptors are being described. A = peripheral chemoreceptors, B = central chemoreceptors, C = both chemoreceptors, D = neither 2. ____ stimulated by an arterial PO2 of 80 mm Hg. 3. ____ strongly stimulated by an elevated [H+] in CSF. 4. ____ stimulate ...
www.d3technologies.co.uk
... understand how the elemental blocks are assembled in living organisms and how they modify under certain conditions such as diseases or new drugs. Proteins, which carry out the body's life functions, are composed of amino acid molecules, which are strung together in long chains. These chains loop abo ...
... understand how the elemental blocks are assembled in living organisms and how they modify under certain conditions such as diseases or new drugs. Proteins, which carry out the body's life functions, are composed of amino acid molecules, which are strung together in long chains. These chains loop abo ...
Sept10
... mRNA, rRNA, tRNA and protein synthesis In translation, the language of nucleic acids is translated into a new language, that of proteins mRNA provides the code, in linear digital form, for making a protein tRNA provides an adaptor that links the code in a polynucleotide chain to amino acids that ma ...
... mRNA, rRNA, tRNA and protein synthesis In translation, the language of nucleic acids is translated into a new language, that of proteins mRNA provides the code, in linear digital form, for making a protein tRNA provides an adaptor that links the code in a polynucleotide chain to amino acids that ma ...
Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein
... codons is specified by the sequence of nucleotides on DNA, which is transcribed into the codons found on mRNA and translated into their corresponding amino acids. There are 64 possible mRNA codons created from the our nucleotides used in the triplet code (43) Redundancy of the code refers to the fac ...
... codons is specified by the sequence of nucleotides on DNA, which is transcribed into the codons found on mRNA and translated into their corresponding amino acids. There are 64 possible mRNA codons created from the our nucleotides used in the triplet code (43) Redundancy of the code refers to the fac ...
3.1 Review PBS
... What is a mutation? How does a change in the DNA code affect the shape of a protein? • A mutation is change in one base (point mutation) or bases (frameshift mutation due to addition or deletion of base) of DNA. • This can change the codon, which then can change the amino acid(s). • If an amino aci ...
... What is a mutation? How does a change in the DNA code affect the shape of a protein? • A mutation is change in one base (point mutation) or bases (frameshift mutation due to addition or deletion of base) of DNA. • This can change the codon, which then can change the amino acid(s). • If an amino aci ...
Chapter 17 - HCC Learning Web
... C) shape of the A and P sites of ribosomes. D) bonding of the anticodon to the codon. E) bonding of the anticodon to the codon and the attachment of amino acids to tRNAs. 10) What is the effect of a nonsense mutation in a gene? 10) ______ A) It alters the reading frame of the mRNA. B) It has no effe ...
... C) shape of the A and P sites of ribosomes. D) bonding of the anticodon to the codon. E) bonding of the anticodon to the codon and the attachment of amino acids to tRNAs. 10) What is the effect of a nonsense mutation in a gene? 10) ______ A) It alters the reading frame of the mRNA. B) It has no effe ...
Nucleic Acids (DNA and RNA) are not boring long polymers
... nucleic acids, DNA and RNAs. They are particularly abundant in noncoding RNAs, such as transfer RNAs and ribosomal RNAs of metazoan. By increasing the structural diversity of nucleic acids, naturally occurring modified nucleosides play important roles in gene ex ...
... nucleic acids, DNA and RNAs. They are particularly abundant in noncoding RNAs, such as transfer RNAs and ribosomal RNAs of metazoan. By increasing the structural diversity of nucleic acids, naturally occurring modified nucleosides play important roles in gene ex ...
From Gene to Protein—Transcription and Translation
... Complete the following sentence to describe how differences in a gene can result in normal hemoglobin vs. sickle cell. Differences in the sequence of _____________________ in the gene result in differences in the sequence of ______________________ in mRNA which result in differences in the sequence ...
... Complete the following sentence to describe how differences in a gene can result in normal hemoglobin vs. sickle cell. Differences in the sequence of _____________________ in the gene result in differences in the sequence of ______________________ in mRNA which result in differences in the sequence ...
Replication, Transcription, Translation
... 4. Be able to name each of the 3 types of RNA and be able to explain what each does. 5. Know the types of RNA involved in protein synthesis. 6. Know how to use the genetic code to identify amino acids. 7. Why is it possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than 1 kind of codon? 8. Genes con ...
... 4. Be able to name each of the 3 types of RNA and be able to explain what each does. 5. Know the types of RNA involved in protein synthesis. 6. Know how to use the genetic code to identify amino acids. 7. Why is it possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than 1 kind of codon? 8. Genes con ...
Information Flow 2
... carrying amino acids enter at this site during protein synthesis P site - Peptidyl site - tRNAs that hold the growing polypeptide chain reside at this site. E site - Exit site - tRNAs stripped of their amino acids reside here and then leave the ribosome. ...
... carrying amino acids enter at this site during protein synthesis P site - Peptidyl site - tRNAs that hold the growing polypeptide chain reside at this site. E site - Exit site - tRNAs stripped of their amino acids reside here and then leave the ribosome. ...
Translation PPT
... Steps to Protein Synthesis and the Genetic Code 1. Obtain a DNA Template (a strand of DNA bases) 2. Transcribe DNA into mRNA (occurs in nucleus) 3. Translate mRNA into tRNA (occurs at ribosome) 4. Use the codons on mRNA to translate into amino acids using Genetic Code Chart ...
... Steps to Protein Synthesis and the Genetic Code 1. Obtain a DNA Template (a strand of DNA bases) 2. Transcribe DNA into mRNA (occurs in nucleus) 3. Translate mRNA into tRNA (occurs at ribosome) 4. Use the codons on mRNA to translate into amino acids using Genetic Code Chart ...
Name:
... Transcription directions: Transcribe the following DNA sequence into messenger RNA (mRNA.) It’s easiest to break the DNA sequence into triplets, and then find the mRNA codons from that point: i.e. AGA TTC CCC DNA triplets transcription UCU AAG GGG ...
... Transcription directions: Transcribe the following DNA sequence into messenger RNA (mRNA.) It’s easiest to break the DNA sequence into triplets, and then find the mRNA codons from that point: i.e. AGA TTC CCC DNA triplets transcription UCU AAG GGG ...
The Path From Genes to Proteins
... Ribosomal RNA catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between the amino acids ...
... Ribosomal RNA catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between the amino acids ...
From DNA to Protein
... group. The worksheet may need to be modified depending on the grade level and background knowledge of the students. ...
... group. The worksheet may need to be modified depending on the grade level and background knowledge of the students. ...
Chlorella CGF
... spherical or elliptical, containing a single elongated chloroplast that fills most cell. Fine powder, hygroscopic dark green color, characteristic flavor and odor. ...
... spherical or elliptical, containing a single elongated chloroplast that fills most cell. Fine powder, hygroscopic dark green color, characteristic flavor and odor. ...
Alien Protein Synthesis
... amino acid. Amino acids combine to form proteins. In a process known as transcription (takes place in the nucleus) messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA. mRNA then takes the message out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm and finally to the ribosome (rRNA), the site of protein synthesis in a p ...
... amino acid. Amino acids combine to form proteins. In a process known as transcription (takes place in the nucleus) messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA. mRNA then takes the message out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm and finally to the ribosome (rRNA), the site of protein synthesis in a p ...
Protein Synthesis Simulation
... by the sequence of the nucleotides in the DNA of an organism. In the first step of protein synthesis, the nucleotide sequence of the DNA is transcribed(the process is transcription) into a long single-stranded molecule of mRNA (messenger). The mRNA moves through pores in the nuclear membrane to the ...
... by the sequence of the nucleotides in the DNA of an organism. In the first step of protein synthesis, the nucleotide sequence of the DNA is transcribed(the process is transcription) into a long single-stranded molecule of mRNA (messenger). The mRNA moves through pores in the nuclear membrane to the ...
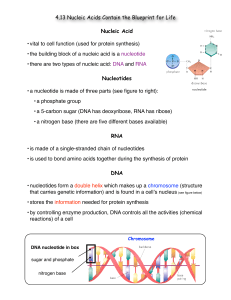
4.13 notes
... • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded cha ...
... • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded cha ...
Chemistry Review
... acids) which gives them a specific function. If the interactions between the side chains of the amino acids are disrupted, the protein will unfold and lose its specific shape and, therefore, its function. If you heat up a protein to a certain point or put it in a solution with a low pH (acidic), the ...
... acids) which gives them a specific function. If the interactions between the side chains of the amino acids are disrupted, the protein will unfold and lose its specific shape and, therefore, its function. If you heat up a protein to a certain point or put it in a solution with a low pH (acidic), the ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
... Chain of aa called polypeptide Peptide bonds hold aa together 1 or more polypeptide chains can link and fold together to form a 3-dimensional protein • Proteins differ in number and sequence of aa • Protein structure determines their function ...
... Chain of aa called polypeptide Peptide bonds hold aa together 1 or more polypeptide chains can link and fold together to form a 3-dimensional protein • Proteins differ in number and sequence of aa • Protein structure determines their function ...
RNA & Protein Synthesis
... 1) Title (reflects main concept of poem) 2 ) Minimum 2 stanzas 4 lines each (grouping of lines, set off by a space, that usually has a set pattern of meter and rhyme) ...
... 1) Title (reflects main concept of poem) 2 ) Minimum 2 stanzas 4 lines each (grouping of lines, set off by a space, that usually has a set pattern of meter and rhyme) ...
Replication, Transcription, and Translation
... Elongation of the chain continues until a stop codon is encountered. At that point the peptide chain is released from the tRNA. A single mRNA can be read repeatedly to make many copies of a polypeptide. Once a tRNA gives up its amino acid it can return to the cytoplasm and attach to another of its s ...
... Elongation of the chain continues until a stop codon is encountered. At that point the peptide chain is released from the tRNA. A single mRNA can be read repeatedly to make many copies of a polypeptide. Once a tRNA gives up its amino acid it can return to the cytoplasm and attach to another of its s ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.