PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... 5. Each codon on mRNA is read and a tRNA with the matching anti-codon carries the correct amino acid to the ribosome 6. There, the tRNA binds to the ribosome and the amino acid is linked to the previous one by a peptide bond 7. Process continues, amino acids are linked, and the polypeptide chain gro ...
... 5. Each codon on mRNA is read and a tRNA with the matching anti-codon carries the correct amino acid to the ribosome 6. There, the tRNA binds to the ribosome and the amino acid is linked to the previous one by a peptide bond 7. Process continues, amino acids are linked, and the polypeptide chain gro ...
What happens to proteins
... Each cell contains DNA for making every protein in the body, but each cell does not make them all. ...
... Each cell contains DNA for making every protein in the body, but each cell does not make them all. ...
Style D 36 by 54 - Bourns College of Engineering
... Genetic incorporation of unnatural amino acids site-specifically into proteins provides a way to manipulate the structures of proteins, monitor protein function and create proteins with novel properties. In previous studies, by creating orthogonal tRNA- synthetase pairs with specificity to unnatural ...
... Genetic incorporation of unnatural amino acids site-specifically into proteins provides a way to manipulate the structures of proteins, monitor protein function and create proteins with novel properties. In previous studies, by creating orthogonal tRNA- synthetase pairs with specificity to unnatural ...
Biochem Option (D)
... Explain the double helical structure of DNA • Secondary structure • Why do Adenine and Thymine only pair with each other (and Cytosine and Guanine)? ...
... Explain the double helical structure of DNA • Secondary structure • Why do Adenine and Thymine only pair with each other (and Cytosine and Guanine)? ...
Protein Synthesis - Manhasset Public Schools
... 3) mRNA strand leaves the DNA strand when a “stop codon” is reached 3) the mRNA strand carries the code for the production of one polypeptide (protein) to the ribosome ...
... 3) mRNA strand leaves the DNA strand when a “stop codon” is reached 3) the mRNA strand carries the code for the production of one polypeptide (protein) to the ribosome ...
Nonsense-suppressing mutation causes addition of amino acid at
... Three nucleotides complementary to an mRNA codon Primary – nucleotide sequence Secondary – short complementary sequences pair and make clover leaf shape Tertiary – folding into three dimensional space shape like an L ...
... Three nucleotides complementary to an mRNA codon Primary – nucleotide sequence Secondary – short complementary sequences pair and make clover leaf shape Tertiary – folding into three dimensional space shape like an L ...
71071_Protein_synthesis
... • DNA is a large and bulky molecules, it does not travel well, so when it wants to make a protein it makes and mRNA copy of the instructions ...
... • DNA is a large and bulky molecules, it does not travel well, so when it wants to make a protein it makes and mRNA copy of the instructions ...
Topic 3 The Chemistry of Life - wfs
... 6. It is at the ribosomes where the process of translation occurs. Translation is the process that leads to the formation of polypeptides, proteins. 7. In the cytoplasm tRNA molecules contain anticodons. The tRNA anticodons pair with the mRNA codons through base pairing. Because each tRNA with a par ...
... 6. It is at the ribosomes where the process of translation occurs. Translation is the process that leads to the formation of polypeptides, proteins. 7. In the cytoplasm tRNA molecules contain anticodons. The tRNA anticodons pair with the mRNA codons through base pairing. Because each tRNA with a par ...
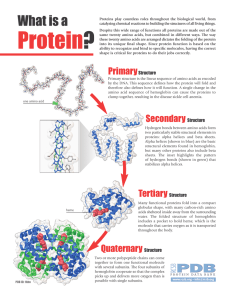
Protein?
... catalyzing chemical reactions to building the structures of all living things. Despite this wide range of functions all proteins are made out of the same twenty amino acids, but combined in different ways. The way these twenty amino acids are arranged dictates the folding of the protein into its uni ...
... catalyzing chemical reactions to building the structures of all living things. Despite this wide range of functions all proteins are made out of the same twenty amino acids, but combined in different ways. The way these twenty amino acids are arranged dictates the folding of the protein into its uni ...
DNA functions worksheet
... A. it stays in the nucleus and is copied by DNA B. it carries amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain C. it makes up the ribosomes and provides the site for protein synthesis D. it is transcribed from the DNA and carries the information to the ribosome 6. Read the following DNA sequence left to ...
... A. it stays in the nucleus and is copied by DNA B. it carries amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain C. it makes up the ribosomes and provides the site for protein synthesis D. it is transcribed from the DNA and carries the information to the ribosome 6. Read the following DNA sequence left to ...
Biology EOC One Page Quick Review Prokaryote – a unicellular
... Carbon cycle – a cycle that shows how carbon moves through the biosphere – includes food chains, photosynthesis, fossil fuels, etc. Nitrogen cycle – a cycle that shows how nitrogen moves through the biosphere – includes nitrogen fixation and various reactions in the soil Mitochondria – organelle fou ...
... Carbon cycle – a cycle that shows how carbon moves through the biosphere – includes food chains, photosynthesis, fossil fuels, etc. Nitrogen cycle – a cycle that shows how nitrogen moves through the biosphere – includes nitrogen fixation and various reactions in the soil Mitochondria – organelle fou ...
Slide 1
... codons. Release factors are used in the process. • It leads to hydrolysis of the terminal peptidyl-tRNA bond. • Free polypeptide and the last tRNA is released. • Dissociation of 70S ribosome into 50S & 30S subunits. Termination codons do not have corresponding tRNA or amino acid. There are 3 RF’s us ...
... codons. Release factors are used in the process. • It leads to hydrolysis of the terminal peptidyl-tRNA bond. • Free polypeptide and the last tRNA is released. • Dissociation of 70S ribosome into 50S & 30S subunits. Termination codons do not have corresponding tRNA or amino acid. There are 3 RF’s us ...
Protein - Canon-MacFCS
... Protein Basics The building blocks of protein are called amino acids. They are referred to as “nitrogen containing” because they contain nitrogen (CHO and fats do not). Protein foods are made of several molecular chains of amino acids. Each type of protein food has a different combination of am ...
... Protein Basics The building blocks of protein are called amino acids. They are referred to as “nitrogen containing” because they contain nitrogen (CHO and fats do not). Protein foods are made of several molecular chains of amino acids. Each type of protein food has a different combination of am ...
DNA Synthesis (Replication)
... rRNA (Ribosomal RNA) – in nucleolus gives rise to ribosomal precursors; makes Ribosome, and is the central component of the Ribosome’s protein-manufacturing machinery. ...
... rRNA (Ribosomal RNA) – in nucleolus gives rise to ribosomal precursors; makes Ribosome, and is the central component of the Ribosome’s protein-manufacturing machinery. ...
Chapter 14
... not yet ready for use • mRNA transcripts are modified before leaving the nucleus – The 5’ end is capped with a special nucleotide that may serve as a “start” signal for translation – Noncoding portions (introns) are snipped out, and actual coding regions (exons) are spliced together to produce the m ...
... not yet ready for use • mRNA transcripts are modified before leaving the nucleus – The 5’ end is capped with a special nucleotide that may serve as a “start” signal for translation – Noncoding portions (introns) are snipped out, and actual coding regions (exons) are spliced together to produce the m ...
Protein Translation
... Commaless: there is no punctuation within a mRNA sequence. Nonoverlapping: any one ribonucleotide is part of only one codon (some exceptions exist). Universal: the same code is used by viruses, bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. ...
... Commaless: there is no punctuation within a mRNA sequence. Nonoverlapping: any one ribonucleotide is part of only one codon (some exceptions exist). Universal: the same code is used by viruses, bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes. ...
Molecular genetics and molecular evolution
... eventually become lost from a population, so there is eventual replacement of allelic types by another. (This will be covered later in section on genetic drift.) The more distantly related two species are the more genetic differences (amino acid changes or nucleotide changes) that will have accumula ...
... eventually become lost from a population, so there is eventual replacement of allelic types by another. (This will be covered later in section on genetic drift.) The more distantly related two species are the more genetic differences (amino acid changes or nucleotide changes) that will have accumula ...
Can Darwinism Explain New Life Forms?
... number of possible amino acid combination sequences for a modest-length protein of 150 sites (amino acid residues) is 20 to the 150th power which is 1 in 10 to 195th power. Then it was asked, what is the ratio of functional sequences to all possible sequences? This would establish the probability of ...
... number of possible amino acid combination sequences for a modest-length protein of 150 sites (amino acid residues) is 20 to the 150th power which is 1 in 10 to 195th power. Then it was asked, what is the ratio of functional sequences to all possible sequences? This would establish the probability of ...
From Gene to Protein
... Example: In hemoglobin, each polypeptide chain is specified by a separate gene Other genes code for RNA that is not translated to polypeptides; some genes are ...
... Example: In hemoglobin, each polypeptide chain is specified by a separate gene Other genes code for RNA that is not translated to polypeptides; some genes are ...
In experiments with a 3 base codon system it was shown that the
... were similar lead to the proposal by Crick of the ‘wobble’ hypothesis. In this hypothesis the specificity of the code is more in the first two bases allowing for variation in pairing at the third base without changing the amino acid . ...
... were similar lead to the proposal by Crick of the ‘wobble’ hypothesis. In this hypothesis the specificity of the code is more in the first two bases allowing for variation in pairing at the third base without changing the amino acid . ...
Protein Synthesis
... Thymine (T), and Cytosine (C) which always bonds with Guanine (G). Each stand of DNA is complementary to the other. ...
... Thymine (T), and Cytosine (C) which always bonds with Guanine (G). Each stand of DNA is complementary to the other. ...
17-Gene to Protein
... • Introns: noncoding sequences that are removed • Exons: coding sequences that are spliced together • Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs): identify and help bring about the splicing process • Spliceosome: catalyzes splicing reactions ...
... • Introns: noncoding sequences that are removed • Exons: coding sequences that are spliced together • Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs): identify and help bring about the splicing process • Spliceosome: catalyzes splicing reactions ...
Mutations - Hicksville Public Schools
... the nucleus 3. Translation: tRNA reads mRNA codons (3 bases) and brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome 4. Sugar: DNA= deoxribose, RNA= ribose Bases: DNA has T and RNA has U DNA: double stranded, RNA: single stranded 5. UGG CAG UGC Try Glu Cys ...
... the nucleus 3. Translation: tRNA reads mRNA codons (3 bases) and brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome 4. Sugar: DNA= deoxribose, RNA= ribose Bases: DNA has T and RNA has U DNA: double stranded, RNA: single stranded 5. UGG CAG UGC Try Glu Cys ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.