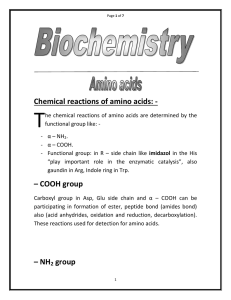
Chemical reactions of amino acids:
... peptide bond, the COOH group must be first activated. Chemically this done by conversion to an acid chloride. Biologically done by condensation with ATP forming an amino acyladenlate. There are different reactions for detections amino acids in general like ninhydrin test or fluorescamine, or for ...
... peptide bond, the COOH group must be first activated. Chemically this done by conversion to an acid chloride. Biologically done by condensation with ATP forming an amino acyladenlate. There are different reactions for detections amino acids in general like ninhydrin test or fluorescamine, or for ...
The Molecular Connection: DNA Evidence for Evolution
... Background: Cytochrome C is a protein that is part of the electron transport chain of cellular respiration. Since almost all organisms on earth have cytochrome C, it is useful to compare the amino acid sequence of this protein from different organisms as a measure for their similarity as a whole. On ...
... Background: Cytochrome C is a protein that is part of the electron transport chain of cellular respiration. Since almost all organisms on earth have cytochrome C, it is useful to compare the amino acid sequence of this protein from different organisms as a measure for their similarity as a whole. On ...
Molecular Evolution - Integrative Biology
... because of the finite size of populations and consequent chance events, alleles always eventually become lost from a population, so there is eventual replacement of allelic types by another. (This will be covered later in section on genetic drift.) The more distantly related two species are the more ...
... because of the finite size of populations and consequent chance events, alleles always eventually become lost from a population, so there is eventual replacement of allelic types by another. (This will be covered later in section on genetic drift.) The more distantly related two species are the more ...
3.1 Teacher Notes
... g. How does mRNA code for proteins? i. mRNA leaves the nucleus ii. goes to the ribosome in cytoplasm iii. proteins are built from instructions on the mRNA iv. mRNA codes for amino acids in triplets! 1. A codon is a block of 3 mRNA bases v. This means that there are four different letters for each ba ...
... g. How does mRNA code for proteins? i. mRNA leaves the nucleus ii. goes to the ribosome in cytoplasm iii. proteins are built from instructions on the mRNA iv. mRNA codes for amino acids in triplets! 1. A codon is a block of 3 mRNA bases v. This means that there are four different letters for each ba ...
Chapter 10.1
... Each has an Anticodon: a three nucleotide sequence on a tRNA that is complementary to an mRNA codon ...
... Each has an Anticodon: a three nucleotide sequence on a tRNA that is complementary to an mRNA codon ...
Learning Targets
... transcription during protein synthesis. Explain the steps of translation in protein synthesis. Transcribe DNA to mRNA and translate mRNA to tRNA to amino acids to make proteins utilizing the mRNA codon chart to figure out the proper amino acids. Identify the similarities and differences between DNA ...
... transcription during protein synthesis. Explain the steps of translation in protein synthesis. Transcribe DNA to mRNA and translate mRNA to tRNA to amino acids to make proteins utilizing the mRNA codon chart to figure out the proper amino acids. Identify the similarities and differences between DNA ...
[edit]More recent updates
... synthetases. Each type of tRNA molecule can be attached to only one type of amino acid, but, because the genetic code contains multiple codons that specify the same amino acid, tRNA molecules bearing different anticodons may also carry the same amino acid. During protein synthesis, tRNAs are deliver ...
... synthetases. Each type of tRNA molecule can be attached to only one type of amino acid, but, because the genetic code contains multiple codons that specify the same amino acid, tRNA molecules bearing different anticodons may also carry the same amino acid. During protein synthesis, tRNAs are deliver ...
Nucleic Acid Notes
... can’t be synthesized by humans; must come from diet especially Lysine and tryptophan (in low amounts in most plant proteins) Strict vegetarians need to make sure that their diet contains sufficient amounts of these ...
... can’t be synthesized by humans; must come from diet especially Lysine and tryptophan (in low amounts in most plant proteins) Strict vegetarians need to make sure that their diet contains sufficient amounts of these ...
12.3 Transcription and Translation PPT
... The genetic code is written in a language that only has four letters: A,U,G &C! These letters (nucleotides) combine in different ways to form the code for twenty different amino acids. The genetic code is read three letters (nucleotides) at a time in groups called codons. ...
... The genetic code is written in a language that only has four letters: A,U,G &C! These letters (nucleotides) combine in different ways to form the code for twenty different amino acids. The genetic code is read three letters (nucleotides) at a time in groups called codons. ...
2.24 MB - KFUPM Resources v3
... chains of nucleotides twisted together into a double helix with links of hydrogen bonds Contains all inherited information necessary to build/maintain an organism, coded in the order of the nucleotide bases, with each three base “letters” forming a genetic code “word” All living organisms have D ...
... chains of nucleotides twisted together into a double helix with links of hydrogen bonds Contains all inherited information necessary to build/maintain an organism, coded in the order of the nucleotide bases, with each three base “letters” forming a genetic code “word” All living organisms have D ...
NOTES: 13.1-13.2 - Protein Synthesis (powerpoint)
... nucleotides in DNA contain INFORMATION! • This information is put to work through the production of PROTEINS. ...
... nucleotides in DNA contain INFORMATION! • This information is put to work through the production of PROTEINS. ...
DNA - Laboratory of Theory of Biopolymers
... A. Kolinski, J. Skolnick and R. Yaris, "Monte Carlo Studies on the Long Time Dynamic Properties of Dense Cubic Lattice Multichain Systems. I. The Homopolymeric Melt", J. Chem. Phys. 86:71647174 (1987). A. Kolinski, J. Skolnick and R. Yaris, "Monte Carlo Studies on the Long Time Dynamic Properties of ...
... A. Kolinski, J. Skolnick and R. Yaris, "Monte Carlo Studies on the Long Time Dynamic Properties of Dense Cubic Lattice Multichain Systems. I. The Homopolymeric Melt", J. Chem. Phys. 86:71647174 (1987). A. Kolinski, J. Skolnick and R. Yaris, "Monte Carlo Studies on the Long Time Dynamic Properties of ...
RNA and Translation notes
... *Promoter: Binding site for RNA polymerase *Shine-Dalgarno site: Binding site for the 30S ribosomal subunit Open reading frame: Nucleic acid that does, or might encode a protein. It begins with a start codon (ATG, TTG, GTG) and ends with a stop codon (TAA, TAG and TGA) and is long enough to encode a ...
... *Promoter: Binding site for RNA polymerase *Shine-Dalgarno site: Binding site for the 30S ribosomal subunit Open reading frame: Nucleic acid that does, or might encode a protein. It begins with a start codon (ATG, TTG, GTG) and ends with a stop codon (TAA, TAG and TGA) and is long enough to encode a ...
P{11/27/11 PPPP RNA and Protein Synthesis Notes Review DNA 1
... Cool facts about mRNA 45. mRNA has a __________on one end and a ______________ on the other end. 46. There are parts that are not used caused _____________that are edited out before the mRNA gets to the ribosomes. 47.The _______________are the parts that are not edited out and thus used to make the ...
... Cool facts about mRNA 45. mRNA has a __________on one end and a ______________ on the other end. 46. There are parts that are not used caused _____________that are edited out before the mRNA gets to the ribosomes. 47.The _______________are the parts that are not edited out and thus used to make the ...
Chapter 13: Carbohydrates
... The specific sequence of amino acids in a protein is called the primary structure. Our DNA codes for only a limited number of specific sequences for making proteins. Approximately 100,000 different proteins found in humans. ...
... The specific sequence of amino acids in a protein is called the primary structure. Our DNA codes for only a limited number of specific sequences for making proteins. Approximately 100,000 different proteins found in humans. ...
Transcription and Translation
... polypeptide how many amino acids in length? 22…you all are Math whizzes • A protein 300 amino acid units in length was synthesized from an mRNA strand how many nucleotides in length? ...
... polypeptide how many amino acids in length? 22…you all are Math whizzes • A protein 300 amino acid units in length was synthesized from an mRNA strand how many nucleotides in length? ...
the efficient expression of a eukaryotic gene in a prokaryotic cell free
... t s 236, which contains a mutation i n t h e gene coding f o r t h e P3 p o l y p e p t i d e , was i n v e s t i g a t e d . Synthesis o f t h e HA polypeptide could n o t be detected i n chick embryo f i b r o b l a s t s i n f e c t e d a t the r e s t r i c t i v e temperature. The HA could be d ...
... t s 236, which contains a mutation i n t h e gene coding f o r t h e P3 p o l y p e p t i d e , was i n v e s t i g a t e d . Synthesis o f t h e HA polypeptide could n o t be detected i n chick embryo f i b r o b l a s t s i n f e c t e d a t the r e s t r i c t i v e temperature. The HA could be d ...
A Physiological Approach to DNA Music
... equivalent (Mole) of the substance. There are 6.02 X 1023 molecules in every Mole (Avogadro's number). Any algorithm whose purpose is to convey information in a meaningful way regarding structure and function of proteins must take into account both the primary (amino acid sequence) and secondary (ch ...
... equivalent (Mole) of the substance. There are 6.02 X 1023 molecules in every Mole (Avogadro's number). Any algorithm whose purpose is to convey information in a meaningful way regarding structure and function of proteins must take into account both the primary (amino acid sequence) and secondary (ch ...
0c5168dab2ecd61778b5bb175973dab5 UNPDF
... 10. The significance of “directionality” of the monomers in a polymer is that when you put the monomers together in a certain sequence/order they have ______________________ a. The process of “putting monomers together” is called b. What is lost during the process ? c. What kind of bond is formed ge ...
... 10. The significance of “directionality” of the monomers in a polymer is that when you put the monomers together in a certain sequence/order they have ______________________ a. The process of “putting monomers together” is called b. What is lost during the process ? c. What kind of bond is formed ge ...
Chapter 3: The Chemistry of Life: Organic Compounds
... and a unique R group 2. There are 20 commonly occurring amino acids 3. Essential amino acids are those that must be ingested in the diet of an animal B. Peptide bonds join amino acids 1. 2 amino acids form a dipeptide 2. Polypeptides are formed from more than 2 amino acids C. Proteins have 4 levels ...
... and a unique R group 2. There are 20 commonly occurring amino acids 3. Essential amino acids are those that must be ingested in the diet of an animal B. Peptide bonds join amino acids 1. 2 amino acids form a dipeptide 2. Polypeptides are formed from more than 2 amino acids C. Proteins have 4 levels ...
Fall 2005 Due: 9/9 GENETICS Homework 1 1. (1 point) The
... An anticodon on a tRNA has the sequence ...
... An anticodon on a tRNA has the sequence ...
The Mechanism of Translation II
... This project is funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community Based Job Training Grant as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration (CB-15-162-06-60). NCC is an equal opportunity employer and does not discriminate on the following basis: against ...
... This project is funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community Based Job Training Grant as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration (CB-15-162-06-60). NCC is an equal opportunity employer and does not discriminate on the following basis: against ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.






![[edit]More recent updates](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022145907_1-8f0620400434ad236b249c9cd08f1aa3-300x300.png)
















