Document
... Plants produce NADPH and ATP by photosynthesis in the chloroplast. However, most of the plants ATP needs are met by their mitochondria. Sugars are exported out of the chloroplasts into the mitochondria. During periods of light, photosynthetic cells convert some sugars made during photosynthesis int ...
... Plants produce NADPH and ATP by photosynthesis in the chloroplast. However, most of the plants ATP needs are met by their mitochondria. Sugars are exported out of the chloroplasts into the mitochondria. During periods of light, photosynthetic cells convert some sugars made during photosynthesis int ...
Biology Organic Molecules Notes
... 2.) Usually found in Long Chains called “fatty acids” 1.)Triglicerides: 3 fatty acids + alcohol glycerol Saturated: each carbon atom has 4 bonds Solid at room temp. (butter and animal fat) Unsaturated: double bonds formed between carbons Liquid at room temp. (vegetable oil) ...
... 2.) Usually found in Long Chains called “fatty acids” 1.)Triglicerides: 3 fatty acids + alcohol glycerol Saturated: each carbon atom has 4 bonds Solid at room temp. (butter and animal fat) Unsaturated: double bonds formed between carbons Liquid at room temp. (vegetable oil) ...
Note Pages for Monday 12/3 and Tuesday 12/4
... you must collect your energy in another way. All animals, all fungi, some protists, and some prokaryotes are ________________________, or “other makers,” which means they consume calories. We get your energy from _________. Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are reservoirs of energy. A series of chem ...
... you must collect your energy in another way. All animals, all fungi, some protists, and some prokaryotes are ________________________, or “other makers,” which means they consume calories. We get your energy from _________. Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are reservoirs of energy. A series of chem ...
lipid digestion - anslab.iastate.edu
... • Lipids leaving the rumen – 80-90% are free fatty acids bound to feed particles or microbes – 10% leaves as microbial phospholipids – If not protected, small quantities of undigested fats may pass – More fat leaves the rumen than enters ...
... • Lipids leaving the rumen – 80-90% are free fatty acids bound to feed particles or microbes – 10% leaves as microbial phospholipids – If not protected, small quantities of undigested fats may pass – More fat leaves the rumen than enters ...
Bio-Chemistry
... Carbon – is found in all living things. 4 electrons in its outer energy level ...
... Carbon – is found in all living things. 4 electrons in its outer energy level ...
Essential Question: What is biochemistry
... C, H, N, O, P, and S are the most important elements for organisms. Na, K, and Fe are also important. Atoms of elements are almost never found alone, thus they combine to form larger substances called molecules Exs. O2 , F2 or to form compounds Exs. H2O, C6H12O6 . The attraction that hold to atoms t ...
... C, H, N, O, P, and S are the most important elements for organisms. Na, K, and Fe are also important. Atoms of elements are almost never found alone, thus they combine to form larger substances called molecules Exs. O2 , F2 or to form compounds Exs. H2O, C6H12O6 . The attraction that hold to atoms t ...
Review Guide for Third Exam in Biochemistry 507 (1997)
... 1. Be able to define: homolytic and heterolytic reactions; Sn1 and Sn2 nucleophilic substitutions, carbocation and carbanion. 2. Thioesters: the basis of their high standard free energy of hydrolysis. Lecture 25: ATP and Phosphoryl Group Transfers 1. Structures of phosphate mono- and di-esters, phos ...
... 1. Be able to define: homolytic and heterolytic reactions; Sn1 and Sn2 nucleophilic substitutions, carbocation and carbanion. 2. Thioesters: the basis of their high standard free energy of hydrolysis. Lecture 25: ATP and Phosphoryl Group Transfers 1. Structures of phosphate mono- and di-esters, phos ...
Biomolecules
... • Glycogen is broken down into glucose when glucose levels decrease • Insulin stimulates the production of glycogen (without insulin, your blood sugar would increase) ...
... • Glycogen is broken down into glucose when glucose levels decrease • Insulin stimulates the production of glycogen (without insulin, your blood sugar would increase) ...
Repair/Recovery/Plasticity
... demonstrated safety and health benefits beyond the basic nutritional functions to supplement diet, presented in a non-food matrix or non-conventional food formats, in such a quantity that exceeds those that could be obtained from normal foods and with such frequency as required to ...
... demonstrated safety and health benefits beyond the basic nutritional functions to supplement diet, presented in a non-food matrix or non-conventional food formats, in such a quantity that exceeds those that could be obtained from normal foods and with such frequency as required to ...
EPA/DHA Vegetarian - Pure Encapsulations
... One study also suggests EPA may moderate protein kinase C, supporting arterial smooth muscle cells.* ...
... One study also suggests EPA may moderate protein kinase C, supporting arterial smooth muscle cells.* ...
Organic
... Sudan IV is not soluble in water; it is, however, soluble in lipids. Red Sudan IV is added to a solution along with ethanol to dissolve any possible lipids. If lipids are present the Sudan IV will stain them reddish-orange, giving a positive test, usu. Forming a layer on top. ...
... Sudan IV is not soluble in water; it is, however, soluble in lipids. Red Sudan IV is added to a solution along with ethanol to dissolve any possible lipids. If lipids are present the Sudan IV will stain them reddish-orange, giving a positive test, usu. Forming a layer on top. ...
25.4 ATP yield
... equivalent to the hydrolysis of 2AIP to 2ADP andzPi. Table 25.1 shows that for every molecule of palmitic acid completely oxidized to carbon dioxide and water, 129moleculesof AIP are formed. No wonderfats are an important source of energy for cellular work. Energy produciion is not the only useful f ...
... equivalent to the hydrolysis of 2AIP to 2ADP andzPi. Table 25.1 shows that for every molecule of palmitic acid completely oxidized to carbon dioxide and water, 129moleculesof AIP are formed. No wonderfats are an important source of energy for cellular work. Energy produciion is not the only useful f ...
Chapter 3: Section 3.2
... Carbohydrates saccharide=sugar • polysaccharide-many sugars (long chains) – Important source of nutrition & structure both for quick use and stored energy – examples: starch (plant storage), cellulose (plant structure=fiber), and glycogen (animal storage) ...
... Carbohydrates saccharide=sugar • polysaccharide-many sugars (long chains) – Important source of nutrition & structure both for quick use and stored energy – examples: starch (plant storage), cellulose (plant structure=fiber), and glycogen (animal storage) ...
Biochemistry notes
... 3. RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a single-stranded nucleic acid that translates the genetic code of DNA into the amino acid sequence of proteins. 4. DNA and RNA differ in the following ways: a. Nucleotides of DNA contain deoxyribose sugar; nucleotides of RNA contain ribose. ...
... 3. RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a single-stranded nucleic acid that translates the genetic code of DNA into the amino acid sequence of proteins. 4. DNA and RNA differ in the following ways: a. Nucleotides of DNA contain deoxyribose sugar; nucleotides of RNA contain ribose. ...
NUTRITIONAL INTEREST OF CHEESE FAT A lot of new datas
... Ø Short and middle chain SFA have a specific and « safe » metabolism, Ø Myristic acid and palmitic acid have not the same metabolic fate in the cell : Ø Myristic acid is rapidly b-oxidized, weakly secreted in the form of TGVLDL, but strongly elongated into palmitic acid. No accumulation ! Ø Palmitic ...
... Ø Short and middle chain SFA have a specific and « safe » metabolism, Ø Myristic acid and palmitic acid have not the same metabolic fate in the cell : Ø Myristic acid is rapidly b-oxidized, weakly secreted in the form of TGVLDL, but strongly elongated into palmitic acid. No accumulation ! Ø Palmitic ...
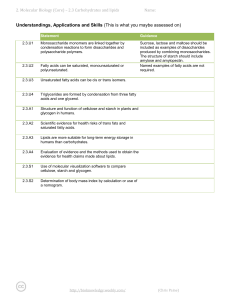
2.3 Building Carbohydrates and Lipids
... 2.3.U3 Unsaturated fatty acids can be cis or trans isomers. 6. Unsaturated fatty acids are described as being cis or trans isomers depending on the structure of the double bonds in the fatty acids. a. Complete the table to compare and contrast cis and trans isomers. ...
... 2.3.U3 Unsaturated fatty acids can be cis or trans isomers. 6. Unsaturated fatty acids are described as being cis or trans isomers depending on the structure of the double bonds in the fatty acids. a. Complete the table to compare and contrast cis and trans isomers. ...
Chapter 17 Fatty Acid Catabolism
... 19. Oxidation of fatty acids For each two-carbon increase in the length of a saturated fatty acid chain, how many additional moles of ATP can be formed upon complete oxidation of one mole of the fatty acid to CO2 and H2O? Ans: Each —CH2—CH2— unit yields 14 extra ATP molecules. The two oxidations of ...
... 19. Oxidation of fatty acids For each two-carbon increase in the length of a saturated fatty acid chain, how many additional moles of ATP can be formed upon complete oxidation of one mole of the fatty acid to CO2 and H2O? Ans: Each —CH2—CH2— unit yields 14 extra ATP molecules. The two oxidations of ...
Role of Liver In Triglyceride Homeostasis
... • De novo lipogenesis and the regulation of fatty acid synthesis • Sources of fatty acids for liver TG biosynthesis • Secretion of hepatic TG with VLDL and the fate of TG-rich particles • Insulin resistance and its impact on hepatic TG ...
... • De novo lipogenesis and the regulation of fatty acid synthesis • Sources of fatty acids for liver TG biosynthesis • Secretion of hepatic TG with VLDL and the fate of TG-rich particles • Insulin resistance and its impact on hepatic TG ...
1 of 3 Biochemistry Final exam Block 3, 2008 Name Answer all of
... (a) At rest, plenty of O2 is being delivered to the muscle, and pyruvate formed during glycolysis is oxidized to acetyl-CoA by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Acetyl groups then enter the citric acid cycle and are oxidized to CO2. (b) Under the conditions of all-out exertion, skeletal muscle can ...
... (a) At rest, plenty of O2 is being delivered to the muscle, and pyruvate formed during glycolysis is oxidized to acetyl-CoA by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Acetyl groups then enter the citric acid cycle and are oxidized to CO2. (b) Under the conditions of all-out exertion, skeletal muscle can ...
Notes Guide Part 2
... Protein- Amino acids join by _________________________________ rxn to form dipeptides and polypeptides. ...
... Protein- Amino acids join by _________________________________ rxn to form dipeptides and polypeptides. ...
Chapter 26
... • Amino acids & fatty acids stimulate release of CCK (appetite suppressant) from small intestine • Different neurotransmitters stimulate desire for different kinds of food -- carbohydrates, fats or protein ...
... • Amino acids & fatty acids stimulate release of CCK (appetite suppressant) from small intestine • Different neurotransmitters stimulate desire for different kinds of food -- carbohydrates, fats or protein ...