Slide 1
... 2. Carbon-based molecules have three general types of structures a. Straight chain b. Branched chain c. Ring ...
... 2. Carbon-based molecules have three general types of structures a. Straight chain b. Branched chain c. Ring ...
The Molecules of Life student
... • Complex carbs (like sugars) are found in most starches) are found in candy and sweet drinks, pasta, bread, potatoes, fruit, vegetables, and milk. legumes & corn. They take They are quickly digested longer to digest, and and give a short burst of provide energy longer. energy. ...
... • Complex carbs (like sugars) are found in most starches) are found in candy and sweet drinks, pasta, bread, potatoes, fruit, vegetables, and milk. legumes & corn. They take They are quickly digested longer to digest, and and give a short burst of provide energy longer. energy. ...
I-1 I. Introduction BIOCHEMISTRY = METABOLISM At first you may
... apparatus. The ATP is then utilized either to service the energetic and biosynthetic needs of the cell - or converted into storage forms such as phosphocreatine. The electron-transfer and ATP-synthesizing enzymes are integrated into the inner membrane of the mitochondrion, and they depend upon the i ...
... apparatus. The ATP is then utilized either to service the energetic and biosynthetic needs of the cell - or converted into storage forms such as phosphocreatine. The electron-transfer and ATP-synthesizing enzymes are integrated into the inner membrane of the mitochondrion, and they depend upon the i ...
Biology 231
... anabolic reactions (synthesis) – smaller reactants combine to form larger products; requires energy input catabolic reactions (decomposition) – larger reactants broken down into smaller products; releases energy Energy of Chemical Reactions activation energy – energy investment needed to start a rea ...
... anabolic reactions (synthesis) – smaller reactants combine to form larger products; requires energy input catabolic reactions (decomposition) – larger reactants broken down into smaller products; releases energy Energy of Chemical Reactions activation energy – energy investment needed to start a rea ...
Inorganic/Organic Chemistry
... Primary: The order in which the different amino acids are linked together in the polypeptide Secondary: the coiling of the polypeptide chain into an alpha helix, held by hydrogen bonds Tertiary : The bending and twisting of the helix in three dimensions, held in place by a combination of covalent, i ...
... Primary: The order in which the different amino acids are linked together in the polypeptide Secondary: the coiling of the polypeptide chain into an alpha helix, held by hydrogen bonds Tertiary : The bending and twisting of the helix in three dimensions, held in place by a combination of covalent, i ...
幻灯片 1
... Malonyl ACP is the main substrate for fatty acid biosynthesis. It is made in two steps, the first of which is the carboxylation of acetyl CoA in the cytosol to form malonyl CoA . The carboxylation reaction is catalyzed by the biotin- dependent enzyme acetyl-CoA carboxylase using a mechanism similar ...
... Malonyl ACP is the main substrate for fatty acid biosynthesis. It is made in two steps, the first of which is the carboxylation of acetyl CoA in the cytosol to form malonyl CoA . The carboxylation reaction is catalyzed by the biotin- dependent enzyme acetyl-CoA carboxylase using a mechanism similar ...
Lipids-I
... -It can be defined as nonpolar organic compound insoluble in polar solvent , but soluble in organic solvents such as benzene ,ether, chloroform and boiling alcohol. ...
... -It can be defined as nonpolar organic compound insoluble in polar solvent , but soluble in organic solvents such as benzene ,ether, chloroform and boiling alcohol. ...
R group
... In water glucose is constantly bending and forming itself into two different ring configurations millions of times a second. In both cases the oxygen at the end of the straight chain attaches itself to the carbon on opposite end. The hydrogen jumps off the oxygen and turns the double-bond oxygen (= ...
... In water glucose is constantly bending and forming itself into two different ring configurations millions of times a second. In both cases the oxygen at the end of the straight chain attaches itself to the carbon on opposite end. The hydrogen jumps off the oxygen and turns the double-bond oxygen (= ...
Organic Molecules
... organic. Oxygen and hydrogen are found in most organic molecules and nitrogen is also common. Hydrocarbons are organic molecules made only of carbon and hydrogen, such as ethane, or the tail portion of fatty acids. The C-C and C-H bonds in hydrocarbons are non-polar, meaning that electrons are distr ...
... organic. Oxygen and hydrogen are found in most organic molecules and nitrogen is also common. Hydrocarbons are organic molecules made only of carbon and hydrogen, such as ethane, or the tail portion of fatty acids. The C-C and C-H bonds in hydrocarbons are non-polar, meaning that electrons are distr ...
Chemical Organization of Life
... vary in number and locations of double bonds Saturated fatty acids Have maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible no double bonds Make up saturated fats Animal fats ...
... vary in number and locations of double bonds Saturated fatty acids Have maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible no double bonds Make up saturated fats Animal fats ...
Concentration of solutes and solvent in a solution
... o Definition--Reactants and products of each process for carbohydrates, lipids and proteins and nucleic acids. o Which one builds polymers from monomers and which one breaks down polymers into monomers o Which one has water as a reactant; which one has water as a product ...
... o Definition--Reactants and products of each process for carbohydrates, lipids and proteins and nucleic acids. o Which one builds polymers from monomers and which one breaks down polymers into monomers o Which one has water as a reactant; which one has water as a product ...
METABOLIC COMPARTMENTATION
... • The complete oxidation of glucose to carbon dioxide directly yields 2 ATP, 2 GTP, 10 NADH and 2 FADH. Depending on the assumptions used with respect to electron shuttle and ATP yield this could be the equivalent of 30 to 38 ATP molecules per molecule of glucose oxidized to carbon dioxide. Whatever ...
... • The complete oxidation of glucose to carbon dioxide directly yields 2 ATP, 2 GTP, 10 NADH and 2 FADH. Depending on the assumptions used with respect to electron shuttle and ATP yield this could be the equivalent of 30 to 38 ATP molecules per molecule of glucose oxidized to carbon dioxide. Whatever ...
Document
... Bile emulsifies fats so that lipase can break fats down. Small intestine- has glands which also secretes digestive enzymes. 1. Dipeptidases- dipeptides-> single amino acids 2. Carboxyl peptidase removes the end amino acid off of protein chain at the carboxyl end. ...
... Bile emulsifies fats so that lipase can break fats down. Small intestine- has glands which also secretes digestive enzymes. 1. Dipeptidases- dipeptides-> single amino acids 2. Carboxyl peptidase removes the end amino acid off of protein chain at the carboxyl end. ...
Ch 26 Notes
... Liver. First lipids are split into glycerol & fatty acids by lipases. Then, by beta oxidation, cleaves the A's into 2C fragments and attaches them to CoA to form Acetyl CoA for Kreb’s cycle, or converts 2Acetyl CoA’s to acetoacetic acid & then to beta-hydroxybutyric acid and acetone [all 3 are calle ...
... Liver. First lipids are split into glycerol & fatty acids by lipases. Then, by beta oxidation, cleaves the A's into 2C fragments and attaches them to CoA to form Acetyl CoA for Kreb’s cycle, or converts 2Acetyl CoA’s to acetoacetic acid & then to beta-hydroxybutyric acid and acetone [all 3 are calle ...
Amino acids - Zanichelli online
... Cellulose: very stable, good for structural components. Starch: storage of glucose in plants. Glycogen: storage of glucose in animals. ...
... Cellulose: very stable, good for structural components. Starch: storage of glucose in plants. Glycogen: storage of glucose in animals. ...
2007
... CH2OPO3H218. [2] Gluconeogenesis shares some, but not all, enzymes with the glycolytic pathway. It would appear to be more efficient if both pathways used all of the same enzymes since the pathways are essentially the reverse of each other. Why don’t both pathways use all of the same enzymes? A) The ...
... CH2OPO3H218. [2] Gluconeogenesis shares some, but not all, enzymes with the glycolytic pathway. It would appear to be more efficient if both pathways used all of the same enzymes since the pathways are essentially the reverse of each other. Why don’t both pathways use all of the same enzymes? A) The ...
C h e m g u i d e ... CARBOXYLIC ACIDS: REDUCTION
... 1. Carboxylic acids can be reduced using lithium tetrahydridoaluminate, LiAlH4, which contains the [AlH4]- ion. a) Carboxylic acids are reduced to alcohols in this way. What kind of alcohols? b) Describe the bonding between the aluminium and the four hydrogens in the [AlH4]- ion. c) Writing the redu ...
... 1. Carboxylic acids can be reduced using lithium tetrahydridoaluminate, LiAlH4, which contains the [AlH4]- ion. a) Carboxylic acids are reduced to alcohols in this way. What kind of alcohols? b) Describe the bonding between the aluminium and the four hydrogens in the [AlH4]- ion. c) Writing the redu ...
PTHR18866 CARBOXYLASE:PYRUVATE/ACETYL
... PTHR18866 – annotations • After pruning, the alignment is good • “Biotin carboxylase activity” can be propagated to all • Could also propagate “biotin binding” and “ATP binding” ...
... PTHR18866 – annotations • After pruning, the alignment is good • “Biotin carboxylase activity” can be propagated to all • Could also propagate “biotin binding” and “ATP binding” ...
Chapter 3 - Haiku Learning
... molecules that store genetic information in the cell 1. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid): contains all the information for almost all cell activities 2. RNA (ribonucleic acid): stores and transfers information needed for making proteins 3. Nucleotides- linked monomers made up of three ...
... molecules that store genetic information in the cell 1. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid): contains all the information for almost all cell activities 2. RNA (ribonucleic acid): stores and transfers information needed for making proteins 3. Nucleotides- linked monomers made up of three ...
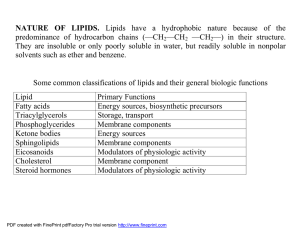
NATURE OF LIPIDS. Lipids have a hydrophobic nature because of
... PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.fineprint.com ...
... PDF created with FinePrint pdfFactory Pro trial version http://www.fineprint.com ...