Chapter 3 Lecture
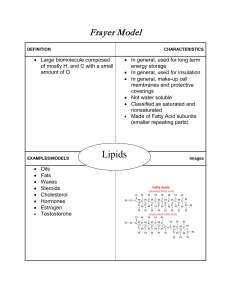
... Classes of Lipids triglyceride- composed of three molecules of fatty acid joined to one molecule of alcohol glycerol phospholipids- have two fatty acids joind by a molecule of glycerol wax- long fatty-acid chain joind to a long alcohol change ...
... Classes of Lipids triglyceride- composed of three molecules of fatty acid joined to one molecule of alcohol glycerol phospholipids- have two fatty acids joind by a molecule of glycerol wax- long fatty-acid chain joind to a long alcohol change ...
42P PROCEEDINGS OF THE BIOCHEMICAL SOCIETY
... by plant chloroplasts but into protochlorophyll via protoporphyrin IX in plant proplastids (Granick, 1961). Thusthechloroplastinitsimmatureproplastid form seems competent to synthesize both haem and chlorophylls from ALA. It was now decided to test whether the plant proplastids also possess the abil ...
... by plant chloroplasts but into protochlorophyll via protoporphyrin IX in plant proplastids (Granick, 1961). Thusthechloroplastinitsimmatureproplastid form seems competent to synthesize both haem and chlorophylls from ALA. It was now decided to test whether the plant proplastids also possess the abil ...
Structure of Macromolecules Dr. Nakhshab
... structure sufficient to cause loss of function is called denaturation. Proteins are denatured by heat, alterations in pH, or certain chemicals lose their tertiary and secondary structure as well as their biological function. Renaturation is not often possible. ...
... structure sufficient to cause loss of function is called denaturation. Proteins are denatured by heat, alterations in pH, or certain chemicals lose their tertiary and secondary structure as well as their biological function. Renaturation is not often possible. ...
BHS 150.1 – Biochemistry II Date: 2/8/2013, 2sndhalf Notetaker: Kim
... 12. Ascorbate in the aqueous is needed by the cornea for which two of the following functions: antioxidant properties collagen synthesis 13. A missense mutation occurs when the: amino acid sequence changes 14. During fasting, what are some possible sources of carbons for gluconeogenesis: amino acids ...
... 12. Ascorbate in the aqueous is needed by the cornea for which two of the following functions: antioxidant properties collagen synthesis 13. A missense mutation occurs when the: amino acid sequence changes 14. During fasting, what are some possible sources of carbons for gluconeogenesis: amino acids ...
IV. Microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA)
... The EPS may remain associated with the cell as a capsule or slime or simply dissolved in the medium, depending on the chemical structure and how vigorously the culture is agitated. On solid media, large slimy colonies may be produced. ...
... The EPS may remain associated with the cell as a capsule or slime or simply dissolved in the medium, depending on the chemical structure and how vigorously the culture is agitated. On solid media, large slimy colonies may be produced. ...
structure of organic molecules
... “groups.” Reexamine the glycine and alanine molecules shown below. a. An amino group (NH2) is found in every amino acid. Put a square around the amino group (NH2) in glycine and alanine. b. A carboxylic acid group (COOH) is found in every amino acid. Put a circle around the carboxylic acid group (CO ...
... “groups.” Reexamine the glycine and alanine molecules shown below. a. An amino group (NH2) is found in every amino acid. Put a square around the amino group (NH2) in glycine and alanine. b. A carboxylic acid group (COOH) is found in every amino acid. Put a circle around the carboxylic acid group (CO ...
Ch 2 - Biochemistry
... Fats are nonpolar; they do not dissolve in water and tend to form “globules” (oil and vinegar dressing) Emulsifier breaks down the globules of fat into smaller droplets Emulsifiers have a nonpolar end which attaches to the fat, and a polar end which interacts with water molecules so that the droplet ...
... Fats are nonpolar; they do not dissolve in water and tend to form “globules” (oil and vinegar dressing) Emulsifier breaks down the globules of fat into smaller droplets Emulsifiers have a nonpolar end which attaches to the fat, and a polar end which interacts with water molecules so that the droplet ...
Digestion processes
... are recombined to form triglycerides and then combined with other lipids and Small proteins within the cells to make intestine chylomicrons, which are extruded by exocytosis. • The chylomicrons enter the lacteals of the villi and are transported to the systemic circulation via the lymph in the thora ...
... are recombined to form triglycerides and then combined with other lipids and Small proteins within the cells to make intestine chylomicrons, which are extruded by exocytosis. • The chylomicrons enter the lacteals of the villi and are transported to the systemic circulation via the lymph in the thora ...
Test # 1
... The body has a large capacity for storage of triglycerides. Triglycerides, as compared to glycogen, are more highly reduced and thus provide more calories per gram when oxidized. They have lower density than does water and are stored largely in anhydrous form. Triglycerides can supply energy under b ...
... The body has a large capacity for storage of triglycerides. Triglycerides, as compared to glycogen, are more highly reduced and thus provide more calories per gram when oxidized. They have lower density than does water and are stored largely in anhydrous form. Triglycerides can supply energy under b ...
SHOW Biochemistry- atoms, acids,macro
... HYDROLYSIS REACTION • Larger molecules broken down into smaller molecules by the addition of water • Draw ...
... HYDROLYSIS REACTION • Larger molecules broken down into smaller molecules by the addition of water • Draw ...
Plant Defense - Unit3and4Biology
... in areas that are dry or in other ways “stressful”? Other roles - competition, camouflage? ...
... in areas that are dry or in other ways “stressful”? Other roles - competition, camouflage? ...
The Digestive Process
... • HCl in gastric juice causes the low pH of the stomach • required for the conversion of pepsinogen into pepsin What other functions does the acidity of the stomach have? ...
... • HCl in gastric juice causes the low pH of the stomach • required for the conversion of pepsinogen into pepsin What other functions does the acidity of the stomach have? ...
Nutrients
... larger ones; reactions are endergonic (requires energy) and consume more energy than they produce Chemical reactions of living systems depend on efficiently transforming energy from one molecule to another. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) accomplishes this task. ATP à ADP + P + ENERGY ...
... larger ones; reactions are endergonic (requires energy) and consume more energy than they produce Chemical reactions of living systems depend on efficiently transforming energy from one molecule to another. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) accomplishes this task. ATP à ADP + P + ENERGY ...
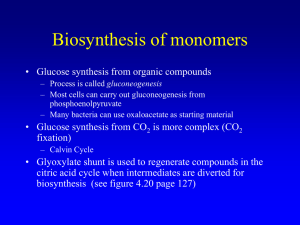
Biosynthesis of monomers
... Biosynthesis of monomers • Glucose synthesis from organic compounds – Process is called gluconeogenesis – Most cells can carry out gluconeogenesis from phosphoenolpyruvate – Many bacteria can use oxaloacetate as starting material ...
... Biosynthesis of monomers • Glucose synthesis from organic compounds – Process is called gluconeogenesis – Most cells can carry out gluconeogenesis from phosphoenolpyruvate – Many bacteria can use oxaloacetate as starting material ...
Organic Chemistry IB
... State one function of glucose, lactose and glycogen in animals, and of fructose, sucrose and cellulose in plants. ...
... State one function of glucose, lactose and glycogen in animals, and of fructose, sucrose and cellulose in plants. ...
Carbon compounds - Sonoma Valley High School
... polymer of amino acids. • 20 different types of amino acids are found in nature. • Proteins are for structure, hormones, and enzymes. • Composed of elements N,O,C,H. ...
... polymer of amino acids. • 20 different types of amino acids are found in nature. • Proteins are for structure, hormones, and enzymes. • Composed of elements N,O,C,H. ...
1 - Medical Mastermind Community
... within the mitochondrial matrix. Three carbon units are added as malonyl-CoA in fatty acid synthesis, while two carbon units are liberated as acetyl-CoA in fatty acid degradation. NADPH is the electron donor in fatty acid synthesis, while FAD and NAD+ are electron acceptors in fatty acid degradation ...
... within the mitochondrial matrix. Three carbon units are added as malonyl-CoA in fatty acid synthesis, while two carbon units are liberated as acetyl-CoA in fatty acid degradation. NADPH is the electron donor in fatty acid synthesis, while FAD and NAD+ are electron acceptors in fatty acid degradation ...
Lipids and Proteins
... amount of HDL and make your arteries rigid, causing them to clog more easily. ...
... amount of HDL and make your arteries rigid, causing them to clog more easily. ...
Quizon ch5-6-7-8new.doc
... 2. Proteins which act as catalysts of chemical reactions [in cells] are called: a. enzymes. b. coenzymes. c. reaction cofactors. d. substrates. e. reactants 3. A final product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an early enzyme in the pathway. This is likely to be an example of: a. competitive inhibitio ...
... 2. Proteins which act as catalysts of chemical reactions [in cells] are called: a. enzymes. b. coenzymes. c. reaction cofactors. d. substrates. e. reactants 3. A final product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an early enzyme in the pathway. This is likely to be an example of: a. competitive inhibitio ...