Chemistry of Life Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids ATP – The
... How does it work? DNA is made up of the four nucleotides adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T), which are arranged in a certain order along the strand. An example might be: ACGGTC. Each three-letter combination codes for a certain amino acid. In this case, ACG would code for one ...
... How does it work? DNA is made up of the four nucleotides adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T), which are arranged in a certain order along the strand. An example might be: ACGGTC. Each three-letter combination codes for a certain amino acid. In this case, ACG would code for one ...
Macromolecules Worksheet
... c. Polysaccharide - complex carbohydrate made up of chains of monosaccharides ex. Starch - food storage compound found in plants Cellulose - makes up the cell wall of plants Glycogen - a food storage compound in animals ...
... c. Polysaccharide - complex carbohydrate made up of chains of monosaccharides ex. Starch - food storage compound found in plants Cellulose - makes up the cell wall of plants Glycogen - a food storage compound in animals ...
Audesirk, Biology: Life on Earth 7e
... E) ATP 8) Which of the following can serve as both energy source and as structural support for cells? A) Proteins B) Carbohydrates C) Lipids D) Nucleic Acids 9) Which of the following is composed of monosaccharide monomer units? A) Proteins B) Carbohydrates C) Lipids D) Nucleic Acids 10) Starch is t ...
... E) ATP 8) Which of the following can serve as both energy source and as structural support for cells? A) Proteins B) Carbohydrates C) Lipids D) Nucleic Acids 9) Which of the following is composed of monosaccharide monomer units? A) Proteins B) Carbohydrates C) Lipids D) Nucleic Acids 10) Starch is t ...
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids Chapter 3 MACROMOLECULES
... • Structural proteins provide physical stability and movement. • Transport proteins carry substances within the organism (e.g., hemoglobin ) • Genetic regulatory proteins regulate when, how, and to what extent a gene is expressed. AMINO ACIDS Amino acids have carboxyl and amino groups—so they functi ...
... • Structural proteins provide physical stability and movement. • Transport proteins carry substances within the organism (e.g., hemoglobin ) • Genetic regulatory proteins regulate when, how, and to what extent a gene is expressed. AMINO ACIDS Amino acids have carboxyl and amino groups—so they functi ...
NORMAL NUTRITION NURP 102 ANDERSON
... Sterols: portion of other 5% of lipids found in the body Forms are cholesterol, Vitamin D, and sex hormones Cholesterol is found in cells and used in metabolism—rec. level is below 200 mg/dl in the blood ...
... Sterols: portion of other 5% of lipids found in the body Forms are cholesterol, Vitamin D, and sex hormones Cholesterol is found in cells and used in metabolism—rec. level is below 200 mg/dl in the blood ...
Enzymes - WordPress.com
... 16. Which of the following is the main reason that humans need to include carbohydrates in their diet? A. Carbohydrates are broken down in cells for energy. B. Carbohydrates combine to form many different proteins. C. Carbohydrates act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions. D. Carbohydrates ar ...
... 16. Which of the following is the main reason that humans need to include carbohydrates in their diet? A. Carbohydrates are broken down in cells for energy. B. Carbohydrates combine to form many different proteins. C. Carbohydrates act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions. D. Carbohydrates ar ...
Macromolecules Worksheet - High School Science Help
... ____________________ 2. What kind of solution contains more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions? ____________________ 3. This is the name for a compound with many sugar subunits linked together. ____________________ 4. What are the positively charged particles of a nucleus called? ____________________ ...
... ____________________ 2. What kind of solution contains more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions? ____________________ 3. This is the name for a compound with many sugar subunits linked together. ____________________ 4. What are the positively charged particles of a nucleus called? ____________________ ...
MCB Lecture 7 – Peroxisomes
... The Peroxisome can be biosynthetic. What is one of the important molecules it synthesizes? o It undergoes Plasmalogen synthesis, which is used in Myelin Sheaths of Axons The Peroxisome is also degradative. What is one of the important molecules it breaks down? o VLCFA (Very Long Chain Fatty Acids) W ...
... The Peroxisome can be biosynthetic. What is one of the important molecules it synthesizes? o It undergoes Plasmalogen synthesis, which is used in Myelin Sheaths of Axons The Peroxisome is also degradative. What is one of the important molecules it breaks down? o VLCFA (Very Long Chain Fatty Acids) W ...
Nutrition - GEOCITIES.ws
... Nutrients: Substances necessary for body function. Absorbed nutrients carried to LIVER. The LIVER regulates energy through its control of glucose metabolism. Glucose: The primary fuel for the body. The LIVER and muscles store glucose in the form of glycogen. Lipogenesis: The storing of excess glucos ...
... Nutrients: Substances necessary for body function. Absorbed nutrients carried to LIVER. The LIVER regulates energy through its control of glucose metabolism. Glucose: The primary fuel for the body. The LIVER and muscles store glucose in the form of glycogen. Lipogenesis: The storing of excess glucos ...
PP - Chemistry Courses: About
... • Looks allosteric, but this is monomeric enzyme • May be due to conformational change upon product release— stays in active state at high concentration of glucose ...
... • Looks allosteric, but this is monomeric enzyme • May be due to conformational change upon product release— stays in active state at high concentration of glucose ...
Macromolecules Notes
... ____________________ 2. What kind of solution contains more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions? ____________________ 3. This is the name for a compound with many sugar subunits linked together. ____________________ 4. What are the positively charged particles of a nucleus called? ____________________ ...
... ____________________ 2. What kind of solution contains more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions? ____________________ 3. This is the name for a compound with many sugar subunits linked together. ____________________ 4. What are the positively charged particles of a nucleus called? ____________________ ...
Meat and Bean Chili
... Bring to a boil; then reduce heat and simmer for 60 minutes. Step 4 Sprinkle grated cheddar cheese on each bowl. Serve with hot cornbread and cold milk. ...
... Bring to a boil; then reduce heat and simmer for 60 minutes. Step 4 Sprinkle grated cheddar cheese on each bowl. Serve with hot cornbread and cold milk. ...
LIPIDS CHEMISTRY
... In the blood (the total cholesterol amounts about 200 mg/dl of which 2/3 is esterified, chiefly to unsaturated fatty acids while the remainder occurs as the free cholesterol. ...
... In the blood (the total cholesterol amounts about 200 mg/dl of which 2/3 is esterified, chiefly to unsaturated fatty acids while the remainder occurs as the free cholesterol. ...
Glycolysis
... Energy for the body • Trapped in chemical bonds of fats, proteins, and carbs (potential) • liberate energy – break bonds – release energy, CO2 and H20 – Energy is transferred to ATP for use in the body ...
... Energy for the body • Trapped in chemical bonds of fats, proteins, and carbs (potential) • liberate energy – break bonds – release energy, CO2 and H20 – Energy is transferred to ATP for use in the body ...
The mechanism of monosaccharide absorption by intestinal
... Absorption of lipid 1- the product of lipid digestion are solubilized in the intestinal lumen in mixed micelles except glycerol, which is water soluble. The outer layer of micelle which is cylindrical shape is composed of bile acids. 2- The micelles diffuse to apical membrane of the intestinal epit ...
... Absorption of lipid 1- the product of lipid digestion are solubilized in the intestinal lumen in mixed micelles except glycerol, which is water soluble. The outer layer of micelle which is cylindrical shape is composed of bile acids. 2- The micelles diffuse to apical membrane of the intestinal epit ...
Metabolism and Energetics
... Fatty acids are long chains of carbon atoms (often 20 or more C’s) with many hydrogen atoms attached. Fatty acids are highly reduced (energy rich) molecules. Beta oxidation is a repeating 4 step process in which sequential 2-C groups (“acetyl groups”) are cut from the long chain; they are attached t ...
... Fatty acids are long chains of carbon atoms (often 20 or more C’s) with many hydrogen atoms attached. Fatty acids are highly reduced (energy rich) molecules. Beta oxidation is a repeating 4 step process in which sequential 2-C groups (“acetyl groups”) are cut from the long chain; they are attached t ...
Chapter 2 Notes: The Chemistry of Life
... The 2 in front of 2HCl, means that there is 2 of the _______________ molecule, so 2 atoms of H and 2 atoms of Cl. ...
... The 2 in front of 2HCl, means that there is 2 of the _______________ molecule, so 2 atoms of H and 2 atoms of Cl. ...
UNIT 2 BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY ORGANIC MOLECULES
... -The Carboxyl end of a fatty acid is polar and therefore Hydrophilic. -The hydrocarbon chain end however is hydrophobic because it is non-polar. These characteristics make fatty acids an integral part of cell membranes. ...
... -The Carboxyl end of a fatty acid is polar and therefore Hydrophilic. -The hydrocarbon chain end however is hydrophobic because it is non-polar. These characteristics make fatty acids an integral part of cell membranes. ...
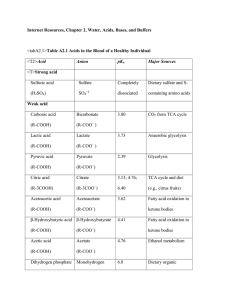
Acid - Perkins Science
... 2)Enantiomers (optical isomers) that are mirror images of each other. They are like left- and right-handed gloves: if the palms are facing the same direction, they cannot be superimposed on each other. See D- and L-glyceraldehyde ...
... 2)Enantiomers (optical isomers) that are mirror images of each other. They are like left- and right-handed gloves: if the palms are facing the same direction, they cannot be superimposed on each other. See D- and L-glyceraldehyde ...
Functional groups - Montgomery County Schools
... plant cell walls d) Chitin- used by insects & crustaceans to ...
... plant cell walls d) Chitin- used by insects & crustaceans to ...