Functional groups - Montgomery County Schools
... plant cell walls d) Chitin- used by insects & crustaceans to ...
... plant cell walls d) Chitin- used by insects & crustaceans to ...
Chemistry of Life Chap 5
... slightly different glucose is a building material in cell walls. Cellulose is the most abundant organic molecule in biosphere. Lipids or Fats All lipids are Hydrophobic (hydro=water, phobic=repulsion). These are compounds of C,H and O. True fats are formed of a molecule of Glyecrol a 3C alcohol and ...
... slightly different glucose is a building material in cell walls. Cellulose is the most abundant organic molecule in biosphere. Lipids or Fats All lipids are Hydrophobic (hydro=water, phobic=repulsion). These are compounds of C,H and O. True fats are formed of a molecule of Glyecrol a 3C alcohol and ...
3.2 and 3.3
... • build larger molecules • carry substances into the cell • remove wastes from the cell • for mechanical work (like muscular activity). ...
... • build larger molecules • carry substances into the cell • remove wastes from the cell • for mechanical work (like muscular activity). ...
Chapter 2 ppt
... Water is taken away to build larger molecules-->condensation synthesis Water is added to break apart large molecules---> Hydrolysis. ...
... Water is taken away to build larger molecules-->condensation synthesis Water is added to break apart large molecules---> Hydrolysis. ...
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... There are 20 amino acids, 9 are essential = must eat them we cannot synthesize Polypeptides are many amino acids joined together ...
... There are 20 amino acids, 9 are essential = must eat them we cannot synthesize Polypeptides are many amino acids joined together ...
Beta Oxidation of Fatty Acids
... Repetition of the Beta Oxidation Cycle The shortened fatty acyl-CoA that was the ...
... Repetition of the Beta Oxidation Cycle The shortened fatty acyl-CoA that was the ...
2_3 Slides - Lipids _ Carbs
... • A positive correlation has been found between saturated fatty acid intake and rates of CHD in many studies. • Correlation ≠ causation. Another factor, e.g. dietary fiber could be responsible. • There are populations that do not fit the correlation such as the Masai of Kenya. They have a diet that ...
... • A positive correlation has been found between saturated fatty acid intake and rates of CHD in many studies. • Correlation ≠ causation. Another factor, e.g. dietary fiber could be responsible. • There are populations that do not fit the correlation such as the Masai of Kenya. They have a diet that ...
Macromolecule Notes
... of double bonds and presence of other elements 4. Forms ISOMERS (same chemical formula but different arrangements) EX C6H12O6 is same formula for Glucose, Fructose and Galactose ...
... of double bonds and presence of other elements 4. Forms ISOMERS (same chemical formula but different arrangements) EX C6H12O6 is same formula for Glucose, Fructose and Galactose ...
Biochem Study Guide for Test
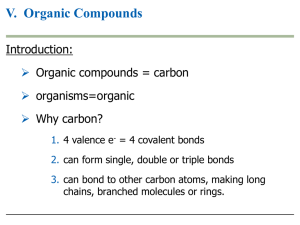
... 19. No other element can form the amount and variety of molecules that carbon can form. What characteristics does carbon have that explain this characteristic? ...
... 19. No other element can form the amount and variety of molecules that carbon can form. What characteristics does carbon have that explain this characteristic? ...
DISEASES OF LIPID METABOLISM
... are esterified with a fatty acid. Glycerophospholipids also contain a phosphate (ester) and frequently a nitrogen containing moeity (also esterified) on the third hydroxyl group of the glycerol. The most common glycerolipids are phosphatidyl choline, phosphatidyl serine, phosphatidyl ethanolamine an ...
... are esterified with a fatty acid. Glycerophospholipids also contain a phosphate (ester) and frequently a nitrogen containing moeity (also esterified) on the third hydroxyl group of the glycerol. The most common glycerolipids are phosphatidyl choline, phosphatidyl serine, phosphatidyl ethanolamine an ...
Chapter 1_summary notes
... Note: Lipids are not polymers as they are composed of distinct chemical groups of atoms. Monomers link together when the hydroxyl (-OH) group of one monomer reacts with the hydrogen of another monomer, forming a water molecule. This reaction is called condensation polymerisation. ...
... Note: Lipids are not polymers as they are composed of distinct chemical groups of atoms. Monomers link together when the hydroxyl (-OH) group of one monomer reacts with the hydrogen of another monomer, forming a water molecule. This reaction is called condensation polymerisation. ...
Accessory Organs and Enzymes
... (HCO3-) ions. Bicarbonate ions are basic or alkaline and neutralize the acidic stomach fluids. ...
... (HCO3-) ions. Bicarbonate ions are basic or alkaline and neutralize the acidic stomach fluids. ...
Cellular Biology I
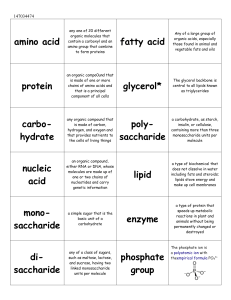
... Macromolecules associated with living organisms Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids 1. Carbohydrates – have C, H, O Two linked together form a disaccharide Polysaccharides are long chains consisting of 8 or more monomers – usually glucose A. starch – energy storage in plants B. glycogen ...
... Macromolecules associated with living organisms Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids 1. Carbohydrates – have C, H, O Two linked together form a disaccharide Polysaccharides are long chains consisting of 8 or more monomers – usually glucose A. starch – energy storage in plants B. glycogen ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 11. Transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another is referred to as ….. 12. A carbon is said to be asymmetric when it is attached to …. different atoms or groups. 13. The R group in Glycine is ….. 14. ………. fatty acids do not contain double bond. 15. ……….. catalyzes bond formation betwee ...
... 11. Transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to another is referred to as ….. 12. A carbon is said to be asymmetric when it is attached to …. different atoms or groups. 13. The R group in Glycine is ….. 14. ………. fatty acids do not contain double bond. 15. ……….. catalyzes bond formation betwee ...
video slide
... • Chitin, another structural polysaccharide, is found in the exoskeleton of insects and the cell walls of fungi. • Chitin can be used as surgical thread because it is gradually reabsorbed by the body. • Chitin is not very digestible; only species that eat mainly insects can break it down easily. ...
... • Chitin, another structural polysaccharide, is found in the exoskeleton of insects and the cell walls of fungi. • Chitin can be used as surgical thread because it is gradually reabsorbed by the body. • Chitin is not very digestible; only species that eat mainly insects can break it down easily. ...
Document
... Pathway of conversion of (A) galactose to glucose in the liver and (B) glucose to lactose in the lactating mammary gland. ...
... Pathway of conversion of (A) galactose to glucose in the liver and (B) glucose to lactose in the lactating mammary gland. ...
BB350 Lecture 36 Highlights
... as a donor of methyl groups. After SAM donates its methyl group, it forms S-Adenylhomocysteine (SAH) that can be readily broken down to homocysteine. Elevated levels of homocysteine in the blood are associated with atherosclerosis. Reduction of homocysteine in the blood is accomplished with suppleme ...
... as a donor of methyl groups. After SAM donates its methyl group, it forms S-Adenylhomocysteine (SAH) that can be readily broken down to homocysteine. Elevated levels of homocysteine in the blood are associated with atherosclerosis. Reduction of homocysteine in the blood is accomplished with suppleme ...
Organic Molecules
... • Simple hydrocarbons not common in living organisms • They form the building blocks of more complex organic molecules that make up living organisms ...
... • Simple hydrocarbons not common in living organisms • They form the building blocks of more complex organic molecules that make up living organisms ...
Honors Biology Chapter 3 Study Guide
... 4. Why is HFCS used in so many foods? What is it made of? What complaints have been blamed on HFCS? Are they justified? ...
... 4. Why is HFCS used in so many foods? What is it made of? What complaints have been blamed on HFCS? Are they justified? ...
GUTS Lecture Syllabus for Lipid Structure and Nomenclature
... other hydrophilic groups may be added, the core structure of each lipid consists of long hydrocarbon chains or rings that are hydrophobic in character. This property affects all of the functions of ...
... other hydrophilic groups may be added, the core structure of each lipid consists of long hydrocarbon chains or rings that are hydrophobic in character. This property affects all of the functions of ...
Biomacromolecules ppt
... Carbohydrates The function of carbohydrate is to store short(glucose) and long term(starch) energy supply; structural function of cellulose. ...
... Carbohydrates The function of carbohydrate is to store short(glucose) and long term(starch) energy supply; structural function of cellulose. ...
CARBOHYDRATES: METABOLISM (cont.)
... • Ketones can be used by the liver or transported to other tissues to enter the CA cycle – Lipid anabolism consists of the synthesis of triglycerides, cholesterol, phospholipids, and prostaglandins • Made from glycerol and FA or excess glucose or aa • Most FA can be made by the body, but some must b ...
... • Ketones can be used by the liver or transported to other tissues to enter the CA cycle – Lipid anabolism consists of the synthesis of triglycerides, cholesterol, phospholipids, and prostaglandins • Made from glycerol and FA or excess glucose or aa • Most FA can be made by the body, but some must b ...
ppt
... hormon sensitive ratio ratio lipase glucagon / insulin insulin / glucagon (lipolysis in fatty catecholamines tissue) carnitin malonyl-Co A acyltransferase I ratio (transfer of fatty insulin / glucagon acids into mitochondria) ...
... hormon sensitive ratio ratio lipase glucagon / insulin insulin / glucagon (lipolysis in fatty catecholamines tissue) carnitin malonyl-Co A acyltransferase I ratio (transfer of fatty insulin / glucagon acids into mitochondria) ...