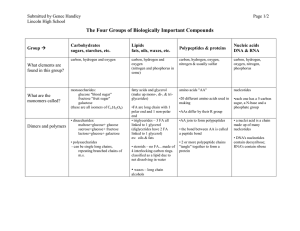
Organic Compound Notes
... __________________: Many monomers joined together to form a large compound ____________________________ ____________________________: The process of combining small compounds to form large compounds and water molecules. (Also known as Condensation Reaction) ...
... __________________: Many monomers joined together to form a large compound ____________________________ ____________________________: The process of combining small compounds to form large compounds and water molecules. (Also known as Condensation Reaction) ...
unit 2 - Biochem packet_hnrs
... __________________: Many monomers joined together to form a large compound ____________________________ ____________________________: The process of combining small compounds to form large compounds and water molecules. (Also known as Condensation Reaction) ...
... __________________: Many monomers joined together to form a large compound ____________________________ ____________________________: The process of combining small compounds to form large compounds and water molecules. (Also known as Condensation Reaction) ...
Metabolism - CSU, Chico
... ATP works by transferring the high energy phosphate to other molecules that use it for work There are three major types of work done by the high energy phosphate of ATP. In each case, the phosphate is transferred from one molecule to the next with the energy being used to do work. ...
... ATP works by transferring the high energy phosphate to other molecules that use it for work There are three major types of work done by the high energy phosphate of ATP. In each case, the phosphate is transferred from one molecule to the next with the energy being used to do work. ...
organic macromolecules webquest
... these questions: http://www.chem4kids.com/files/bio_carbos.html 1. Carbohydrates are made up of the following elements: a. b. c. 2. Give 4 examples of carbohydrates: o o o o 3. What carbohydrate is stored in plants? ...
... these questions: http://www.chem4kids.com/files/bio_carbos.html 1. Carbohydrates are made up of the following elements: a. b. c. 2. Give 4 examples of carbohydrates: o o o o 3. What carbohydrate is stored in plants? ...
Ch 8 Carbon Chem
... 1. Starch-complex carbs, bread, cereal, pasta, rice and potatoes. The energy released by breaking down starch allows the body to carry out its life functions. 2. Cellulose- (fiber) plant polymer. Body cannot breakdown and use for energy. ...
... 1. Starch-complex carbs, bread, cereal, pasta, rice and potatoes. The energy released by breaking down starch allows the body to carry out its life functions. 2. Cellulose- (fiber) plant polymer. Body cannot breakdown and use for energy. ...
Chemistry of Life Answers 1. Differentiate between an ionic and
... List the different types of lipids and state each of their functions. 1. Phospholipids & sterols: structural support 2. Triglycerides: stored energy, cushioning, insulation, padding 3. Waxes: protection (e.g., waxy cuticle on leaves) 4. Lipid hormones & fat soluble vitamins: chemical regulators 24. ...
... List the different types of lipids and state each of their functions. 1. Phospholipids & sterols: structural support 2. Triglycerides: stored energy, cushioning, insulation, padding 3. Waxes: protection (e.g., waxy cuticle on leaves) 4. Lipid hormones & fat soluble vitamins: chemical regulators 24. ...
Macromolecules Worksheet #2
... molecules. The sequence of amino acids in each protein is unique to that protein, so each protein has its own ...
... molecules. The sequence of amino acids in each protein is unique to that protein, so each protein has its own ...
Physiology of Digestive System
... 1. ‘Fasting’ – Starts after 4 hours till next meal 2. Main source of energy is absorbed carbohydrates 2. Main source of energy is fats by lipolysis 3. Net uptake of glucose by liver, promotes 3. Liver releases glucose by glycogenolysis glycogenesis /gluconeogenesis 4. Brain continues to use glucose ...
... 1. ‘Fasting’ – Starts after 4 hours till next meal 2. Main source of energy is absorbed carbohydrates 2. Main source of energy is fats by lipolysis 3. Net uptake of glucose by liver, promotes 3. Liver releases glucose by glycogenolysis glycogenesis /gluconeogenesis 4. Brain continues to use glucose ...
Slide 1
... the cysteine chains that are close together to form disulfide bridges. As a result, the hair will remain in the shape that it was held after the perm. This will last until the disulfide bridges naturally break down. If you have very curly hair, the protein in your hair contains a more cysteine than ...
... the cysteine chains that are close together to form disulfide bridges. As a result, the hair will remain in the shape that it was held after the perm. This will last until the disulfide bridges naturally break down. If you have very curly hair, the protein in your hair contains a more cysteine than ...
CH03_Lecture
... in Presentation Mode and playing each animation. Most animations will require the latest version of the Flash Player, which is available at http://get.adobe.com/flashplayer. ...
... in Presentation Mode and playing each animation. Most animations will require the latest version of the Flash Player, which is available at http://get.adobe.com/flashplayer. ...
Citric acid Cycle:
... generate 6 molecules of carbon dioxide? 7. How many grams of glucose is needed to elevate an object of 50 Kg to the height of 100 meters. Assume that all the energy released by ATP hydrolysis is used with 100% efficiency in this work, and G = - 50KJ/Mole in physiological condition. 8. Deficiency of ...
... generate 6 molecules of carbon dioxide? 7. How many grams of glucose is needed to elevate an object of 50 Kg to the height of 100 meters. Assume that all the energy released by ATP hydrolysis is used with 100% efficiency in this work, and G = - 50KJ/Mole in physiological condition. 8. Deficiency of ...
2-2 Properties of Water
... glycogen. H. Plants store excess sugar as plant starch. I. Plants also make cellulose, a fiber that gives plants their strength and rigidity. Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound found on the Earth. IV. Lipids A. Lipid – macromolecule made mainly from carbon, hydrogen, ...
... glycogen. H. Plants store excess sugar as plant starch. I. Plants also make cellulose, a fiber that gives plants their strength and rigidity. Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound found on the Earth. IV. Lipids A. Lipid – macromolecule made mainly from carbon, hydrogen, ...
Figure 5-2
... b. Remove water to break bonds between monomer units. c. Add amine groups to monomer units. d. Remove carboxyl groups from monomer units. Figure 5-1 ...
... b. Remove water to break bonds between monomer units. c. Add amine groups to monomer units. d. Remove carboxyl groups from monomer units. Figure 5-1 ...
Elements and Molecules in Organisms
... 25. ____Peptide______ bonds form when water is removed to hold ____amino acids_____ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lip ...
... 25. ____Peptide______ bonds form when water is removed to hold ____amino acids_____ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lip ...
Notes - Organic Molecules of Life
... More than twice as much energy stored than carbohydrates: fats- 9 Cal/g; carbohydrates- 4 Cal/g In plants: stored in and around ______________ (Peanut oil, corn oil, olive oil) In animals: stored under the _____________ and around ________________ - insulation and shock absorber 2. Phospholipids - S ...
... More than twice as much energy stored than carbohydrates: fats- 9 Cal/g; carbohydrates- 4 Cal/g In plants: stored in and around ______________ (Peanut oil, corn oil, olive oil) In animals: stored under the _____________ and around ________________ - insulation and shock absorber 2. Phospholipids - S ...
Elements Found in Living Things - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... 25. ____Peptide______ bonds form when water is removed to hold ____amino acids_____ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lip ...
... 25. ____Peptide______ bonds form when water is removed to hold ____amino acids_____ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lip ...
Document
... mannose can enter glycolytic pathway after phosphorylation Galactose is modified before being transformed into glucose-6-P ...
... mannose can enter glycolytic pathway after phosphorylation Galactose is modified before being transformed into glucose-6-P ...
2013
... Phosphocarnitine serves as ‘stored ATP’ to regenerate ATP during bursts of heavy activity. The brain requires glucose as preferred energy source but can use ketone bodies and fatty acids when glucose is unavailable. Glucagon and insulin act in opposition, in some cases on the same target enzyme. Epi ...
... Phosphocarnitine serves as ‘stored ATP’ to regenerate ATP during bursts of heavy activity. The brain requires glucose as preferred energy source but can use ketone bodies and fatty acids when glucose is unavailable. Glucagon and insulin act in opposition, in some cases on the same target enzyme. Epi ...
organic molecules webquest
... questions: http://www.chem4kids.com/files/bio_nucleicacids.html 1. The __________________ are the building blocks of living organisms. 2. ________________ is just one type of nucleic acid. 3. List 4 types of nucleic acids (NA’s): o o o o Draw pictures of the four nucleic acids below: ...
... questions: http://www.chem4kids.com/files/bio_nucleicacids.html 1. The __________________ are the building blocks of living organisms. 2. ________________ is just one type of nucleic acid. 3. List 4 types of nucleic acids (NA’s): o o o o Draw pictures of the four nucleic acids below: ...
0c5168dab2ecd61778b5bb175973dab5 UNPDF
... 10. The significance of “directionality” of the monomers in a polymer is that when you put the monomers together in a certain sequence/order they have ______________________ a. The process of “putting monomers together” is called b. What is lost during the process ? c. What kind of bond is formed ge ...
... 10. The significance of “directionality” of the monomers in a polymer is that when you put the monomers together in a certain sequence/order they have ______________________ a. The process of “putting monomers together” is called b. What is lost during the process ? c. What kind of bond is formed ge ...
Biomolecules: lipids - e
... Glycerides: mono-, di-, tri-esters of fatty acids and glycerol Ceramides: esters of sphingosine and fatty acids Phospholipids: di-esters of glycerol-3-Phosphate or esters of sphingosine-phosphate Cerebrosides (glycolipids): esters of sphingosine with 1 FA and 1 sugar with 6-C (hexose) Gangliosides: ...
... Glycerides: mono-, di-, tri-esters of fatty acids and glycerol Ceramides: esters of sphingosine and fatty acids Phospholipids: di-esters of glycerol-3-Phosphate or esters of sphingosine-phosphate Cerebrosides (glycolipids): esters of sphingosine with 1 FA and 1 sugar with 6-C (hexose) Gangliosides: ...
Test 2
... lead to the increase in glucose synthesis and excretion by liver. One of these changes involves inhibition of glycolysis and stimulation of gluconeogenesis (i.e. the conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to glucose). Describe all the steps and intermediates involved in this stimulation, beginning with t ...
... lead to the increase in glucose synthesis and excretion by liver. One of these changes involves inhibition of glycolysis and stimulation of gluconeogenesis (i.e. the conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to glucose). Describe all the steps and intermediates involved in this stimulation, beginning with t ...
Macromolecules Worksheet
... pH scale_ 1. This measures the hydrogen ion level of a solution. acid_ 2. What kind of solution contains more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions? carbohydrate or polysaccharide_ 3. This is the name for a compound with many sugar subunits linked together. protons_ 4. What are the positively charged pa ...
... pH scale_ 1. This measures the hydrogen ion level of a solution. acid_ 2. What kind of solution contains more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions? carbohydrate or polysaccharide_ 3. This is the name for a compound with many sugar subunits linked together. protons_ 4. What are the positively charged pa ...