The Chemistry of Life
... • Lipids may consist of fatty acids alone, or they may contain other molecules as well. – some lipids contain alcohol or phosphate groups. They include 1. triglycerides: the main form of stored energy in animals 2. phospholipids: the major components of cell membranes 3. steroids: serve as chemical ...
... • Lipids may consist of fatty acids alone, or they may contain other molecules as well. – some lipids contain alcohol or phosphate groups. They include 1. triglycerides: the main form of stored energy in animals 2. phospholipids: the major components of cell membranes 3. steroids: serve as chemical ...
Milk Composition
... - complex mixture of lipids - triglycerides are the major type - major energy source of young - extremely variable between species and within a species ...
... - complex mixture of lipids - triglycerides are the major type - major energy source of young - extremely variable between species and within a species ...
Macromolecules
... A Chemical reaction is a process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals. Chemical reactions always involve the breaking of bonds in reactants and the formation of bonds in products. ...
... A Chemical reaction is a process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals. Chemical reactions always involve the breaking of bonds in reactants and the formation of bonds in products. ...
Regulation of gene expression by polyunsaturated fatty acids
... into the cell (1) and are rapidly converted to acyl coenzyme A (CoA) by acyl CoA synthetase (ACS) (2). The acyl CoA can be oxidized (3) or can be esterified into complex lipids (4) such as triglycerides (TG), phospholipids (PL), or diacylglycerols (DAG). These complex lipids can also replenish the c ...
... into the cell (1) and are rapidly converted to acyl coenzyme A (CoA) by acyl CoA synthetase (ACS) (2). The acyl CoA can be oxidized (3) or can be esterified into complex lipids (4) such as triglycerides (TG), phospholipids (PL), or diacylglycerols (DAG). These complex lipids can also replenish the c ...
Protein
... As a result, they are able to dissolve in both type of solvents as well. They are important for living things because they form the borders of all cells (cell membranes) and also participate in forming many cell organelles. ...
... As a result, they are able to dissolve in both type of solvents as well. They are important for living things because they form the borders of all cells (cell membranes) and also participate in forming many cell organelles. ...
Biochemistry Chp 3
... Monomer Single unit of a macromolecule Can be linked together to form polymers ...
... Monomer Single unit of a macromolecule Can be linked together to form polymers ...
Mouth - Net Start Class
... Digestion of the cracker begins here. Teeth physically (mechanically) crush and chop the food while the tongue mashes the food around. Saliva which is excreted by salivary glands, contains water, mucus, and the enzyme amalyse which chemically breaks large starch molecules, also called polysaccarides ...
... Digestion of the cracker begins here. Teeth physically (mechanically) crush and chop the food while the tongue mashes the food around. Saliva which is excreted by salivary glands, contains water, mucus, and the enzyme amalyse which chemically breaks large starch molecules, also called polysaccarides ...
Lorem Ipsum - Tri-County Technical College
... Obligate anaerobe is organism that cannot use oxygen and is poisoned by it Facultative anaerobe is organism that uses oxygen if available (in fact, prefers it) but can switch to alternate pathway if oxygen is unavailable ...
... Obligate anaerobe is organism that cannot use oxygen and is poisoned by it Facultative anaerobe is organism that uses oxygen if available (in fact, prefers it) but can switch to alternate pathway if oxygen is unavailable ...
Organic Compounds
... waxes – Neutral fats: most abundant type of lipid 3 Fatty Acids + glycerol • Simplest lipid = fatty acid ...
... waxes – Neutral fats: most abundant type of lipid 3 Fatty Acids + glycerol • Simplest lipid = fatty acid ...
This is Most of an Old Exam
... uses glycogen as a source of new glucose molecules to maintain blood glucose. C. can make new glucose molecules from the direct reversal of the glycolytic pathway. D. is only activated when adipose depots of triglycerides are low. Write brief, but complete to questions 1-3. Then choose two questions ...
... uses glycogen as a source of new glucose molecules to maintain blood glucose. C. can make new glucose molecules from the direct reversal of the glycolytic pathway. D. is only activated when adipose depots of triglycerides are low. Write brief, but complete to questions 1-3. Then choose two questions ...
Basic Strategies of Cell Metabolism
... The relationships between catabolism and anabolism occur not only at the common intermediates. Certain pathways play dual roles, as they function in both anabolism and catabolism. For instance, the tricarboxylic acid cycle, as will be demonstrated later, is involved not only in the oxidation of pyru ...
... The relationships between catabolism and anabolism occur not only at the common intermediates. Certain pathways play dual roles, as they function in both anabolism and catabolism. For instance, the tricarboxylic acid cycle, as will be demonstrated later, is involved not only in the oxidation of pyru ...
L24_Krebs
... • Krebs cycle activity is controlled early on – At isocitrate dehydrogenase (ICDH) – alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (aKGDH) ...
... • Krebs cycle activity is controlled early on – At isocitrate dehydrogenase (ICDH) – alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (aKGDH) ...
H &
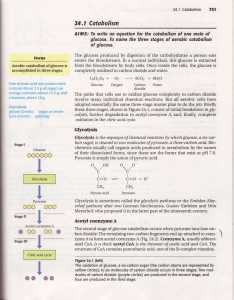
... The glucose produced by digestion of the carbohydrate.sa person eats enters the bloodstream. In a normal individual, this glucose is extracted from the bloodstream by body cells. Once inside the cells, the glucoseis completely oxidized to carbon dioxide and water. c6H12o6+ 02 + Glucose oxygen ...
... The glucose produced by digestion of the carbohydrate.sa person eats enters the bloodstream. In a normal individual, this glucose is extracted from the bloodstream by body cells. Once inside the cells, the glucoseis completely oxidized to carbon dioxide and water. c6H12o6+ 02 + Glucose oxygen ...
Reading - Science with Ms. Wang
... through peptide bonds. The type of protein, and thus its function, is determined by the kind of amino acids joined together and the order in which those amino acids are arranged. Some proteins are very large molecules, containing hundreds of amino acids. Often these long proteins are bent and folded ...
... through peptide bonds. The type of protein, and thus its function, is determined by the kind of amino acids joined together and the order in which those amino acids are arranged. Some proteins are very large molecules, containing hundreds of amino acids. Often these long proteins are bent and folded ...
Fatty Acid Synthesis
... • Classify lipoproteins according to their densities – The densities are related to the relative amounts of lipid and protein – Proteins have densities of about 1.3 to ...
... • Classify lipoproteins according to their densities – The densities are related to the relative amounts of lipid and protein – Proteins have densities of about 1.3 to ...
Chapter 5: What are the major types of organic molecules?
... formed when the equivalent of a water molecule is removed from the two monosaccharides an oxygen atom is bound to a carbon from each momomer typically, the linkage is between carbon 1 of one and 4 of the other maltose, sucrose, and lactose are common disaccharides maltose (malt sugar): has ...
... formed when the equivalent of a water molecule is removed from the two monosaccharides an oxygen atom is bound to a carbon from each momomer typically, the linkage is between carbon 1 of one and 4 of the other maltose, sucrose, and lactose are common disaccharides maltose (malt sugar): has ...
b) How many electrons are in carbons 2nd energy
... 20 of 20) Grab bag: Behind the President and Vice-President, what position in American government is 3rd in the chain of command? ...
... 20 of 20) Grab bag: Behind the President and Vice-President, what position in American government is 3rd in the chain of command? ...
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... Advantageous to animals that have to move around – unlike plants that can have unlimited bulk without concern for mobility. Cells that store fat – adipose cells ...
... Advantageous to animals that have to move around – unlike plants that can have unlimited bulk without concern for mobility. Cells that store fat – adipose cells ...
1 - VCOMcc
... c. provide starting material for protein synthesis and the synthesis of nitrogencontaining compounds. d. all of the above. ...
... c. provide starting material for protein synthesis and the synthesis of nitrogencontaining compounds. d. all of the above. ...
Basic Biochemistry Powerpoint
... Monosaccharides - simple sugars, single chain or single ring structures Most important in the body are the pentose and hexose sugars ...
... Monosaccharides - simple sugars, single chain or single ring structures Most important in the body are the pentose and hexose sugars ...
ppt
... derivatives in which one fatty acid has been replaced by a phosphate group and one of several nitrogencontaining molecules. an important part of the cell membrane (phospholipid bilayer) ...
... derivatives in which one fatty acid has been replaced by a phosphate group and one of several nitrogencontaining molecules. an important part of the cell membrane (phospholipid bilayer) ...