organic molecules : proteins - Mr. Lesiuk
... - The second or Secondary Structure takes place as the chains of amino acids get longer they begin to twist into a spiral. (called an alpha helix). ...
... - The second or Secondary Structure takes place as the chains of amino acids get longer they begin to twist into a spiral. (called an alpha helix). ...
The Chemistry of Carbon
... ◦ Different chemical properties ◦ Different biological functions It’s the same, but different ...
... ◦ Different chemical properties ◦ Different biological functions It’s the same, but different ...
Seminar compendium 2016/2017
... Describe the bonds keeping a cell membrane together and what is the importane of having fatty acid components with cis double bonds? In addition to phospholipids, what other components are common in membranes? ...
... Describe the bonds keeping a cell membrane together and what is the importane of having fatty acid components with cis double bonds? In addition to phospholipids, what other components are common in membranes? ...
Carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency: metabolic
... Glucose is the major source of energy for the fetus [1]. Immediately after birth free fatty acids are mobilized from adipose tissue stores. A rapid increase in the activity of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I and II and a rise in the capacity to oxidize fatty acids is found in liver [2] and in heart ...
... Glucose is the major source of energy for the fetus [1]. Immediately after birth free fatty acids are mobilized from adipose tissue stores. A rapid increase in the activity of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I and II and a rise in the capacity to oxidize fatty acids is found in liver [2] and in heart ...
FREE Sample Here
... Hydrogen bonds are attractions between adjacent molecules Inorganic compounds Water, an inorganic compound, is essential to plants Water’s polarity causes many of its properties Acids and bases Acids and bases dissociate when dissolved in water A solution’s acidity or alkalinity is expressed in term ...
... Hydrogen bonds are attractions between adjacent molecules Inorganic compounds Water, an inorganic compound, is essential to plants Water’s polarity causes many of its properties Acids and bases Acids and bases dissociate when dissolved in water A solution’s acidity or alkalinity is expressed in term ...
Unit 1 Practice Test
... 31. Which organic compound is correctly matched with the subunit that composes it? (a) maltose amino acid (b) starchglucose (c) proteinfatty acid (d) lipidsucrose 32. A chemical bond in which two atoms share a pair of electrons is referred to as (a) covalent (b) acidic (c) ionic (d) double 33. ...
... 31. Which organic compound is correctly matched with the subunit that composes it? (a) maltose amino acid (b) starchglucose (c) proteinfatty acid (d) lipidsucrose 32. A chemical bond in which two atoms share a pair of electrons is referred to as (a) covalent (b) acidic (c) ionic (d) double 33. ...
DOC
... important in biology. They may be used for biological structures or as nutrients. Some of the more important ones are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. CARBOHYDRATES Carbohydrates contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). The ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is 2:1 in carbohydrat ...
... important in biology. They may be used for biological structures or as nutrients. Some of the more important ones are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. CARBOHYDRATES Carbohydrates contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). The ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is 2:1 in carbohydrat ...
Amino Acids Worksheet - Newcastle University
... structure called? Why do you think this makes the melting points in solid amino acids 200-300oC? 3. What conditions do you think the amino acid (TRYPTC) is in to make its zwitterion structure to be in this form? 4. Open up the WebCSD in two separate tabs of your internet browser and arrange them so ...
... structure called? Why do you think this makes the melting points in solid amino acids 200-300oC? 3. What conditions do you think the amino acid (TRYPTC) is in to make its zwitterion structure to be in this form? 4. Open up the WebCSD in two separate tabs of your internet browser and arrange them so ...
Fatty Acid Oxid
... Human genetic diseases have been identified that involve mutations in: the plasma membrane fatty acid transporter CD36 Carnitine Palmitoyltransferases I & II (required for transfer of fatty acids into mitochondria) Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenases for various chain lengths of fatty acids Hydroxyacyl ...
... Human genetic diseases have been identified that involve mutations in: the plasma membrane fatty acid transporter CD36 Carnitine Palmitoyltransferases I & II (required for transfer of fatty acids into mitochondria) Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenases for various chain lengths of fatty acids Hydroxyacyl ...
Energy Transfer and Glycolysis Cellular Respiration • Remember
... Remember that there are four stages that occur in three different places within the cell 1. Glycolysis: occurs in the cytoplasm 2. Pyruvate Oxidation: occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion 3. Kreb Cycle: occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion 4. Electron Transport and Chemiosmosis: occur on ...
... Remember that there are four stages that occur in three different places within the cell 1. Glycolysis: occurs in the cytoplasm 2. Pyruvate Oxidation: occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion 3. Kreb Cycle: occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion 4. Electron Transport and Chemiosmosis: occur on ...
The Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
... cycle of reactions called the Krebs cycle. The common pathway to completely oxidize fuel molecules which mostly is acetyl CoA ,the product from the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate It enters the cycle and passes ten steps of reactions that yield energy and CO2 These reactions can only occ ...
... cycle of reactions called the Krebs cycle. The common pathway to completely oxidize fuel molecules which mostly is acetyl CoA ,the product from the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate It enters the cycle and passes ten steps of reactions that yield energy and CO2 These reactions can only occ ...
Biomolecules Discussion
... Shmoop Editorial Team. (November 11, 2008).Biomolecules and the Chemistry of Life. Retrieved April 6, 2013, from http://www.shmoop.com/biomolecules/ Shmoop Editorial Team. (November 11, 2008).Organic vs. Inorganic Molecules Shmoop Biology. Retrieved April 6, 2013, from http://www.shmoop.com/biomolec ...
... Shmoop Editorial Team. (November 11, 2008).Biomolecules and the Chemistry of Life. Retrieved April 6, 2013, from http://www.shmoop.com/biomolecules/ Shmoop Editorial Team. (November 11, 2008).Organic vs. Inorganic Molecules Shmoop Biology. Retrieved April 6, 2013, from http://www.shmoop.com/biomolec ...
Question 2: Multiple-Choice Standard: Chemistry of Life
... surfaces. This coating reduces water loss because it is not water-permeable. This waxy coating is which of the following types of organic molecule? A. carbohydrate B. lipid C. nucleic acid D. protein ...
... surfaces. This coating reduces water loss because it is not water-permeable. This waxy coating is which of the following types of organic molecule? A. carbohydrate B. lipid C. nucleic acid D. protein ...
Samples Ch 10 to 12.tst
... 16) In the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA what molecule along with CO2 is formed? A) NADH ...
... 16) In the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA what molecule along with CO2 is formed? A) NADH ...
File
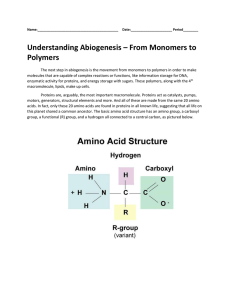
... The next step in abiogenesis is the movement from monomers to polymers in order to make molecules that are capable of complex reactions or functions, like information storage for DNA, enzymatic activity for proteins, and energy storage with sugars. These polymers, along with the 4th macromolecule, l ...
... The next step in abiogenesis is the movement from monomers to polymers in order to make molecules that are capable of complex reactions or functions, like information storage for DNA, enzymatic activity for proteins, and energy storage with sugars. These polymers, along with the 4th macromolecule, l ...
Glossary Protein
... fatty acid oxidation the metabolic breakdown of fatty acids to acetyl CoA; also called beta oxidation. fuel compounds that cells can use for energy. glycolysis the metabolic breakdown of glucose to pyruvate. keto acid an organic acid that contains a carbonyl group (C=O). lactate a 3-carbon compound ...
... fatty acid oxidation the metabolic breakdown of fatty acids to acetyl CoA; also called beta oxidation. fuel compounds that cells can use for energy. glycolysis the metabolic breakdown of glucose to pyruvate. keto acid an organic acid that contains a carbonyl group (C=O). lactate a 3-carbon compound ...
Lec. # 2
... ý They undergo 100% dissociation in water with equilibrium shifted completely to the right side. ý Many different organic functional groups behave as acids or bases, and these are listed in table 1 and 2 respectively. ý Organic functional groups that cannot give up or accept a proton are considered ...
... ý They undergo 100% dissociation in water with equilibrium shifted completely to the right side. ý Many different organic functional groups behave as acids or bases, and these are listed in table 1 and 2 respectively. ý Organic functional groups that cannot give up or accept a proton are considered ...
Digestion and Substances Involved in Digestion
... Digestion of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and most absorption of nutrients ...
... Digestion of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and most absorption of nutrients ...
Lecture 5: Powerpoint
... Hydrophobic interactions among hydrophobic R groups. Disulphide bridges that form strong, stable bonds between parts of the molecule ...
... Hydrophobic interactions among hydrophobic R groups. Disulphide bridges that form strong, stable bonds between parts of the molecule ...
Citric Acid Cycle
... nuclear weapons production decades ago. The bacteria's cleaning power comes from their ability to "inhale" toxic metals and "exhale" them in a non-toxic form, explains team member Brian Lower, assistant professor in the School of Environment and Natural Resources at Ohio State University. Using a un ...
... nuclear weapons production decades ago. The bacteria's cleaning power comes from their ability to "inhale" toxic metals and "exhale" them in a non-toxic form, explains team member Brian Lower, assistant professor in the School of Environment and Natural Resources at Ohio State University. Using a un ...
File
... 10. Although many proteins are enzymes, there are many other types of proteins in our bodies. Give 4 other types of proteins (HEATS: acronym to remember types) and their role in living things. 11. Draw the structural formula of a typical amino acid. Circle the amino group, acid group and remainder. ...
... 10. Although many proteins are enzymes, there are many other types of proteins in our bodies. Give 4 other types of proteins (HEATS: acronym to remember types) and their role in living things. 11. Draw the structural formula of a typical amino acid. Circle the amino group, acid group and remainder. ...
Biochemistry
... Lipids do not dissolve in water but do dissolve in oils Candy, red meats, fried foods, dairy products ...
... Lipids do not dissolve in water but do dissolve in oils Candy, red meats, fried foods, dairy products ...
2.3 and 2.4 Notes
... How is a tulip bulb able to sprout in the spring and then come back again each year? ...
... How is a tulip bulb able to sprout in the spring and then come back again each year? ...
Vitamin В 1
... -pyruvate dehydrogenase and alphaketoglutarate complexes -succinate dehydrogenase (Krebs cycle) -fatty acids oxidation (acyl CoA dehydrogenase) -uric acid formation (xanthine oxidase) -electron transport in respiration chain ...
... -pyruvate dehydrogenase and alphaketoglutarate complexes -succinate dehydrogenase (Krebs cycle) -fatty acids oxidation (acyl CoA dehydrogenase) -uric acid formation (xanthine oxidase) -electron transport in respiration chain ...