The Digestive System - Anoka-Hennepin School District 11
... Balancing glucose levels in blood depress appetite ...
... Balancing glucose levels in blood depress appetite ...
Digestion - My Teacher Pages
... • The process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use is called digestion. • Digestion occurs in the gastrointestinal tract, or digestive tract, which is a long tube which begins at the mouth and winds through the body to the anus. • Organs next to the digestive tract also aid in the d ...
... • The process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use is called digestion. • Digestion occurs in the gastrointestinal tract, or digestive tract, which is a long tube which begins at the mouth and winds through the body to the anus. • Organs next to the digestive tract also aid in the d ...
Document
... Glucose + 6 O2 + 38 ADP + 39 Phosphate = 6 CO2 + 6H2O + 38 ATP ANAEROBIC METABOLISM In anaerobic metabolism, pyruvate is converted to lactate. However, in the presence of sufficient oxygen, pyruvate can be oxidised for energy in the mitochondria (the energy factories of the cell). Glucose, a six car ...
... Glucose + 6 O2 + 38 ADP + 39 Phosphate = 6 CO2 + 6H2O + 38 ATP ANAEROBIC METABOLISM In anaerobic metabolism, pyruvate is converted to lactate. However, in the presence of sufficient oxygen, pyruvate can be oxidised for energy in the mitochondria (the energy factories of the cell). Glucose, a six car ...
3.3 teacher Notes
... • Cellulose is found in the cell walls of plants. • In a complex organism, cells recognize neighboring cells by the short, branched chains of varying sugar units on their outer surface. ...
... • Cellulose is found in the cell walls of plants. • In a complex organism, cells recognize neighboring cells by the short, branched chains of varying sugar units on their outer surface. ...
PowerPoint presentation file for this
... • Excess energy from the energyyielding nutrients is stored as fat. • The fat is first broken into fragments called fatty acids. • Fatty acids Basic units of fat composed of chains of carbon atoms with an acid group at one and and hydrogen atoms attached all ...
... • Excess energy from the energyyielding nutrients is stored as fat. • The fat is first broken into fragments called fatty acids. • Fatty acids Basic units of fat composed of chains of carbon atoms with an acid group at one and and hydrogen atoms attached all ...
BY 330 Summer 2015Mock Exam 2 Ten molecules of
... for this conversion, including all intermediates and energy production sites. (I won’t show the pathway for the conversion, but it is the process of glycolysis starting at G3P and ending at pyruvate. This will come straight from your notes. Make sure you show all of the carbon intermediates, where A ...
... for this conversion, including all intermediates and energy production sites. (I won’t show the pathway for the conversion, but it is the process of glycolysis starting at G3P and ending at pyruvate. This will come straight from your notes. Make sure you show all of the carbon intermediates, where A ...
Biochemistry 3300 More Quizzes Page:1/4 1) How many electrons
... 7) Germinating plant seeds can convert acetyl-CoA (from fatty acids stored as oils) into carbohydrates, whereas animals cannot convert fatty acids into glucose. This difference is due to the fact that: A) animals have glycogen and don’t need to make glucose from fatty acids. B) plants use the glyoxy ...
... 7) Germinating plant seeds can convert acetyl-CoA (from fatty acids stored as oils) into carbohydrates, whereas animals cannot convert fatty acids into glucose. This difference is due to the fact that: A) animals have glycogen and don’t need to make glucose from fatty acids. B) plants use the glyoxy ...
Fatty Acid Catabolism
... absorbed by the cells lining the small intestine. {Metabolism of the monosaccharides has already been discussed. The modified monosaccharides that are absorbed from the GI tract are transported to the liver, activated by coupling to UTP, and used in protein and/or sphingolipid biosynthesis.} The sho ...
... absorbed by the cells lining the small intestine. {Metabolism of the monosaccharides has already been discussed. The modified monosaccharides that are absorbed from the GI tract are transported to the liver, activated by coupling to UTP, and used in protein and/or sphingolipid biosynthesis.} The sho ...
Gluconeogenesis Precursors for Gluconeogenesis
... Local Regulation • Energy charge – ATP downregulates glycolysis – AMP, ADP downregulate GNG ...
... Local Regulation • Energy charge – ATP downregulates glycolysis – AMP, ADP downregulate GNG ...
Microbiology (Notes)
... between the neutral atoms. Because carbon requires four electrons to complete its outer shell (and the shell is thus half-filled), it can covalently bond with many other atoms in an order 4 rotationally symmetric way. Carbon thus exists as a convenient structural element in the formation of long com ...
... between the neutral atoms. Because carbon requires four electrons to complete its outer shell (and the shell is thus half-filled), it can covalently bond with many other atoms in an order 4 rotationally symmetric way. Carbon thus exists as a convenient structural element in the formation of long com ...
Biology 12 – Lesson 3 - Biological Molecules 1 http://nhscience
... A disaccharide is formed when 2 monosaccharides are joined by dehydration synthesis. During dehydration synthesis a bond between 2 monosaccharides is created when one monosaccharide loses a hydroxyl group (-OH) and another loses a hydrogen (-H) forming a water (dehydration) Disaccharides mus ...
... A disaccharide is formed when 2 monosaccharides are joined by dehydration synthesis. During dehydration synthesis a bond between 2 monosaccharides is created when one monosaccharide loses a hydroxyl group (-OH) and another loses a hydrogen (-H) forming a water (dehydration) Disaccharides mus ...
Chem331 Krebs Cycle
... The Krebs cycle is a central pathway for recovering energy from three major metabolites: carbohydrates, fatty acids, and amino acids. Most enter the cycle through Acetyl~CoA. The two carbons entered at this step are lost as CO2 (the reason you breath out CO 2). The carbon atoms that enter by A-CoA l ...
... The Krebs cycle is a central pathway for recovering energy from three major metabolites: carbohydrates, fatty acids, and amino acids. Most enter the cycle through Acetyl~CoA. The two carbons entered at this step are lost as CO2 (the reason you breath out CO 2). The carbon atoms that enter by A-CoA l ...
1 - BrainMass
... Diagram and explain the dependence of Phosphofructokinase reaction rate on [fructose-6phosphate], at low and high [ATP]. Explain the value to a cell of the effect of high [ATP] on Phosphofructokinase. 4. a. List substrates and products for the reaction catalyzed by Hexokinase. b. How does the liver ...
... Diagram and explain the dependence of Phosphofructokinase reaction rate on [fructose-6phosphate], at low and high [ATP]. Explain the value to a cell of the effect of high [ATP] on Phosphofructokinase. 4. a. List substrates and products for the reaction catalyzed by Hexokinase. b. How does the liver ...
Fat - Food a fact of life
... There are many health problems linked with too much saturated fat in the diet, e.g. coronary heart disease, and strokes. ...
... There are many health problems linked with too much saturated fat in the diet, e.g. coronary heart disease, and strokes. ...
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Chapter
... b. kidneys. c. small intestines. d. large intestines. ____________ 22. Each kidney is connected to the urinary bladder by a(an) a. urethra. b. renal artery. c. villus. d. ureter. ____________ 23. The saclike organ where liquid wastes are stored before excretion is the a. urethra. b. urinary bladder. ...
... b. kidneys. c. small intestines. d. large intestines. ____________ 22. Each kidney is connected to the urinary bladder by a(an) a. urethra. b. renal artery. c. villus. d. ureter. ____________ 23. The saclike organ where liquid wastes are stored before excretion is the a. urethra. b. urinary bladder. ...
Biol 1107 Biomolecules Lab Fall 2003
... a substance changes form a solid to a liquid. Molecules in a solid state are packed together in an orderly fashion with very much movement, while molecules in a liquid state are moving around in a random pattern termed Brownian motion. Therefore, the melting point is affected by anything that affect ...
... a substance changes form a solid to a liquid. Molecules in a solid state are packed together in an orderly fashion with very much movement, while molecules in a liquid state are moving around in a random pattern termed Brownian motion. Therefore, the melting point is affected by anything that affect ...
Unit 3 Review Sheet – Biochemistry
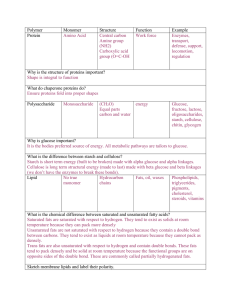
... Monosaccharide is a single sugar, disaccharide is made of two monosaccharides and a polysaccharide is made of many monosaccharides What are some examples of each of the 4 macromolecules? 1. Carbohydrate Glucose, fructose (mono); sucrose (di); starch, glycogen (poly) ...
... Monosaccharide is a single sugar, disaccharide is made of two monosaccharides and a polysaccharide is made of many monosaccharides What are some examples of each of the 4 macromolecules? 1. Carbohydrate Glucose, fructose (mono); sucrose (di); starch, glycogen (poly) ...
Formative Assesments
... surface area for ansorption Submucosa: second layer that contains blood vessels to provide nutrients, nerve endings, lymph nodules, and vessels. Muscularis externa: two layers of muscle one circular and one longitudinal that alternate contraction to create a wave of motion Serosa: outer most layer t ...
... surface area for ansorption Submucosa: second layer that contains blood vessels to provide nutrients, nerve endings, lymph nodules, and vessels. Muscularis externa: two layers of muscle one circular and one longitudinal that alternate contraction to create a wave of motion Serosa: outer most layer t ...
Energy For Movement
... • Decreased potassium needed for nerve transmission along the sarcolemma • Calcium retention within the sarcoplasmic reticulum. – fatigue may be psychological and therefore terminate exercise before the muscles are physiologically exhausted ...
... • Decreased potassium needed for nerve transmission along the sarcolemma • Calcium retention within the sarcoplasmic reticulum. – fatigue may be psychological and therefore terminate exercise before the muscles are physiologically exhausted ...
Q14to17
... B. Fatty acids can be converted into glucose big NO!!! C. Muscle glycogen is the major carbohydrate reserve for the brainalthough lots of glycogen in muscle, can’t access D. The total amount of glycogen stored in muscle is less than the total amount stored in liver no 250g vs 100g E. There is no spe ...
... B. Fatty acids can be converted into glucose big NO!!! C. Muscle glycogen is the major carbohydrate reserve for the brainalthough lots of glycogen in muscle, can’t access D. The total amount of glycogen stored in muscle is less than the total amount stored in liver no 250g vs 100g E. There is no spe ...
Chapter 23
... - Acetyl CoA combine together to produce ketone bodies. - They are produced in liver. ...
... - Acetyl CoA combine together to produce ketone bodies. - They are produced in liver. ...