Biological importance of Uronic Acid Pathway
... Substrate level phosphorylation from succinyl-CoA gives 2 ATP. Oxidation of succinate to fumarate gives 2 FADH2, thus 4 ATP. Oxidation of malate to oxaloacetate gives 2 NADH.H+, i.e., 6 ATP. Thus, for each mole of glucose oxidized by oxidative decarboxylation followed by Krebs' cycle 30 ATP are ...
... Substrate level phosphorylation from succinyl-CoA gives 2 ATP. Oxidation of succinate to fumarate gives 2 FADH2, thus 4 ATP. Oxidation of malate to oxaloacetate gives 2 NADH.H+, i.e., 6 ATP. Thus, for each mole of glucose oxidized by oxidative decarboxylation followed by Krebs' cycle 30 ATP are ...
Biochemical Aspects of Digestion of Lipids
... Phospholipase A2 & from the Cholesteryl ester and we are left with Lysophospholipase each removes 1 free cholesterol fatty acid ...
... Phospholipase A2 & from the Cholesteryl ester and we are left with Lysophospholipase each removes 1 free cholesterol fatty acid ...
Multiple Choice: Choose the one best answer to each question
... 18) a)True/b)False: Gap junctions create passages that allow sodium entering a cardiac cell to directly pass into the cytosol of a second cell causing it to depolarize. 19) ________hormones are produced locally and only act on cells in a close proximity to the origin. a) Autocrine b) Paracrine c) En ...
... 18) a)True/b)False: Gap junctions create passages that allow sodium entering a cardiac cell to directly pass into the cytosol of a second cell causing it to depolarize. 19) ________hormones are produced locally and only act on cells in a close proximity to the origin. a) Autocrine b) Paracrine c) En ...
III B.Sc. (CHEMISTRY) MODEL CURRICULUM FOR
... definition of isoelectric point. Chemical properties: General reactions due to amino and carboxyl groups – lactams from gamma and delta amino acids by heating peptide bond (amide linkage). Structure and nomenclature of peptides and proteins.(Elementary treatment only) Unit-III (physical chemistry- V ...
... definition of isoelectric point. Chemical properties: General reactions due to amino and carboxyl groups – lactams from gamma and delta amino acids by heating peptide bond (amide linkage). Structure and nomenclature of peptides and proteins.(Elementary treatment only) Unit-III (physical chemistry- V ...
File - Biology withMrs. Ellsworth
... 53. What is the monomer for lipids called? Glycerol Head and Fatty Acid Chain 54. Do lipids have polymers? ...
... 53. What is the monomer for lipids called? Glycerol Head and Fatty Acid Chain 54. Do lipids have polymers? ...
Secretin - Dental Decks
... • Stimulates the secretion of bile from the gallbladder • Cholecystokinin plays a key role in facilitating digestion within the small intestine. Cholecystokinin is secreted by the “I” cells in the mucosa of the duodenum and jejunum mainly in response to digestive products of fat, fatty acids, and mo ...
... • Stimulates the secretion of bile from the gallbladder • Cholecystokinin plays a key role in facilitating digestion within the small intestine. Cholecystokinin is secreted by the “I” cells in the mucosa of the duodenum and jejunum mainly in response to digestive products of fat, fatty acids, and mo ...
acetyl CoA
... • Also called the Krebs cycle (after the German-British researcher Hans Krebs, who worked out much of this pathway in the 1930s) • completes the oxidation of organic molecules • generates many NADH and FADH2 molecules. • the two-carbon group of acetyl CoA is added to a ...
... • Also called the Krebs cycle (after the German-British researcher Hans Krebs, who worked out much of this pathway in the 1930s) • completes the oxidation of organic molecules • generates many NADH and FADH2 molecules. • the two-carbon group of acetyl CoA is added to a ...
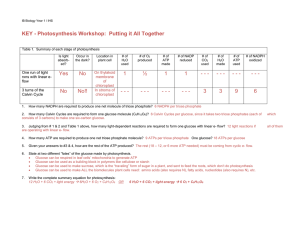
KEY - Photosynthesis Workshop: Putting it All Together
... 2. How many Calvin Cycles are required to form one glucose molecule (C6H12O6)? 6 Calvin Cycles per glucose, since it takes two triose phosphates (each of consists of 3 carbons) to make one six-carbon glucose. ...
... 2. How many Calvin Cycles are required to form one glucose molecule (C6H12O6)? 6 Calvin Cycles per glucose, since it takes two triose phosphates (each of consists of 3 carbons) to make one six-carbon glucose. ...
Integration and regulation of fuel metabolism in maintaining
... appears to be skewed toward providing the organism with an energy source that can be easily stored (fat), thereby proving times when food is not readily available. ...
... appears to be skewed toward providing the organism with an energy source that can be easily stored (fat), thereby proving times when food is not readily available. ...
What you need to Know for Chapter 1 Quiz
... o Explain general structural features of triglycerides, phospholipids, waxes, and sterols (steroids) o Compare fats to oils (saturated versus unsaturated – how do they differ? Review Protein note: o Key definitions: amino acids, essential amino acid, peptide bond o What are the functions of polypept ...
... o Explain general structural features of triglycerides, phospholipids, waxes, and sterols (steroids) o Compare fats to oils (saturated versus unsaturated – how do they differ? Review Protein note: o Key definitions: amino acids, essential amino acid, peptide bond o What are the functions of polypept ...
(CH2) 2 - CHM152-SP10
... The three amino acids that Mr. Griffin taught us about for the purpose of the last quiz as well as the exam were Glycine, Alanine, and Phenylalanine. For Glycine (gly), R = H For Alanine (ala), R = CH3 For Phenylalanine (Phe), R = CH2— These three amino acids can be linked together in any possible o ...
... The three amino acids that Mr. Griffin taught us about for the purpose of the last quiz as well as the exam were Glycine, Alanine, and Phenylalanine. For Glycine (gly), R = H For Alanine (ala), R = CH3 For Phenylalanine (Phe), R = CH2— These three amino acids can be linked together in any possible o ...
7. Metabolism
... energy, amino acids to a lesser extent. • Glucose is made from all carbohydrates, most amino acids and the glycerol portion of fat. • Protein is made from amino acids. • Glucose can be made into nonessential amino acids if nitrogen is present ...
... energy, amino acids to a lesser extent. • Glucose is made from all carbohydrates, most amino acids and the glycerol portion of fat. • Protein is made from amino acids. • Glucose can be made into nonessential amino acids if nitrogen is present ...
2106lecture 3a-powerpoint
... amylase (alpha-amylase), minimally in stomach via hydrochloric acid and mostly by pancreatic amylase in small intestine -maltose units ultimately produced followed by maltase digestion ...
... amylase (alpha-amylase), minimally in stomach via hydrochloric acid and mostly by pancreatic amylase in small intestine -maltose units ultimately produced followed by maltase digestion ...
Chapter 3 Overview - Greensburg.k12.in.us
... form polymers during a process called dehydration synthesis (condensation reaction). During dehydration synthesis, a hydroxyl (OH) group is removed from one monomer and a hydrogen is removed from the other to join them together to form a polymer. During this process, water is produced (see left). ...
... form polymers during a process called dehydration synthesis (condensation reaction). During dehydration synthesis, a hydroxyl (OH) group is removed from one monomer and a hydrogen is removed from the other to join them together to form a polymer. During this process, water is produced (see left). ...
Chapter 12 - eduBuzz.org
... The pancreas, liver, and gallbladder are accessory organs of digestion; their secretions assist digestion. Accessory organs are not part of the digestive tube but produce enzymes and other substances that assist digestion. These three accessory organs send secretions to the duodenum via ducts. ...
... The pancreas, liver, and gallbladder are accessory organs of digestion; their secretions assist digestion. Accessory organs are not part of the digestive tube but produce enzymes and other substances that assist digestion. These three accessory organs send secretions to the duodenum via ducts. ...
Cellular respiration
... Partial oxidation of glucose to form pyruvic acid. A small amount of ATP is made. Some NAD is reduced to form NADH. The major glycolytic pathway in cells is the ...
... Partial oxidation of glucose to form pyruvic acid. A small amount of ATP is made. Some NAD is reduced to form NADH. The major glycolytic pathway in cells is the ...
Lecture DONE exam 1A MP
... A) Golgi apparatus, rough ER, lysosome B) Lysosome, Golgi apparatus, plasma membrane C) Plasma membrane, vesicle, lysosome D) Rough ER, cytoplasm, plasma-membrane E) Rough ER, Golgi apparatus, vesicle, plasma-membrane 25. What is attached to the 5´-carbon of ribose in RNA? A) Adenine B) Ribose C) Ur ...
... A) Golgi apparatus, rough ER, lysosome B) Lysosome, Golgi apparatus, plasma membrane C) Plasma membrane, vesicle, lysosome D) Rough ER, cytoplasm, plasma-membrane E) Rough ER, Golgi apparatus, vesicle, plasma-membrane 25. What is attached to the 5´-carbon of ribose in RNA? A) Adenine B) Ribose C) Ur ...
fat facts
... Dolly: Oh! It means three alcohols. Now what are fatty acids? I know if a –COOH, carboxyl, group is present it’s an acid. Mom: Good Dolly. Fatty acids are long chains of carbon that end with that –COOH group. In nature, these long chains usually have only an even number of carbon atoms, typically be ...
... Dolly: Oh! It means three alcohols. Now what are fatty acids? I know if a –COOH, carboxyl, group is present it’s an acid. Mom: Good Dolly. Fatty acids are long chains of carbon that end with that –COOH group. In nature, these long chains usually have only an even number of carbon atoms, typically be ...
Lipidomics in Cell Regulation
... Is the basis for energy metabolism – proton-gradients Ensure a stable cellular environment Provides a 2-D space for efficient chemical reaction The lipids creates an optimal environment for protein function in the membrane More than 300 lipid species are found in the plasma membrane ...
... Is the basis for energy metabolism – proton-gradients Ensure a stable cellular environment Provides a 2-D space for efficient chemical reaction The lipids creates an optimal environment for protein function in the membrane More than 300 lipid species are found in the plasma membrane ...
Ch. 2- BIOCHEMISTRY Macromolecules
... _______________ (polar) molecules - have polar covalent bonds; _______________ in water; dissociate easily; Ex: glucose, amino acids _______________ (nonpolar) molecules - mainly nonpolar covalent bonds; do _____ dissolve in water; have few charges; Ex: Lipids (fats) Ionic Bonds-electrons ____ ...
... _______________ (polar) molecules - have polar covalent bonds; _______________ in water; dissociate easily; Ex: glucose, amino acids _______________ (nonpolar) molecules - mainly nonpolar covalent bonds; do _____ dissolve in water; have few charges; Ex: Lipids (fats) Ionic Bonds-electrons ____ ...