Bacteriology Exam 1 Name_______________________ 1/31/06 1.
... The cell membrane functions to regulate entry to and exit from the cell. It is described as selectively permeable, meaning that the membrane functions to select what can enter a cell. This is possible because very little -- water and only a few other very small molecules -- can diffuse through the l ...
... The cell membrane functions to regulate entry to and exit from the cell. It is described as selectively permeable, meaning that the membrane functions to select what can enter a cell. This is possible because very little -- water and only a few other very small molecules -- can diffuse through the l ...
Chapter 7
... a way for a cell to get ATP fast! b. Aerobic RespirationThe remnants of glycolysis (pyruvates) and all other energy-providing nutrients, go through this process. This is a very complex series of reactions that occurs within MITOCHONDRIA. Mitochondria are isolated “rooms” in the cell where the enzyme ...
... a way for a cell to get ATP fast! b. Aerobic RespirationThe remnants of glycolysis (pyruvates) and all other energy-providing nutrients, go through this process. This is a very complex series of reactions that occurs within MITOCHONDRIA. Mitochondria are isolated “rooms” in the cell where the enzyme ...
Notes_Biochemistry_Short_Course
... a. When in plant tissues: called __________________ & used by humans for _______________ b. When in animal tissues: called ________________ - found in ________________ & _________________ and used for _______________________________________________ C. What has to happen to the disaccharides & polysa ...
... a. When in plant tissues: called __________________ & used by humans for _______________ b. When in animal tissues: called ________________ - found in ________________ & _________________ and used for _______________________________________________ C. What has to happen to the disaccharides & polysa ...
Aerobic organisms obtain energy from oxidation of food molecules
... generate energy for •synthesis of enzymes to degrade stored foods ...
... generate energy for •synthesis of enzymes to degrade stored foods ...
15_intro-to
... nonequilibrium process can perform work • The flux of intermediates in a pathway is set by the rate-determining step ...
... nonequilibrium process can perform work • The flux of intermediates in a pathway is set by the rate-determining step ...
Master Entrance Exam
... 10. 1000 bps DNA coding sequences can make protein roughly (A) 23 (B) 27 (C) 33 (D) 37 (E) 43 kilodalton II. 是非題 (每題 2 分) Yes or No for answer 1. Lipid components of membranes do not readily move from one side of a bilayer to the other. 2. In the Citrate-Pyruvate Cycle, the step that generates NADPH ...
... 10. 1000 bps DNA coding sequences can make protein roughly (A) 23 (B) 27 (C) 33 (D) 37 (E) 43 kilodalton II. 是非題 (每題 2 分) Yes or No for answer 1. Lipid components of membranes do not readily move from one side of a bilayer to the other. 2. In the Citrate-Pyruvate Cycle, the step that generates NADPH ...
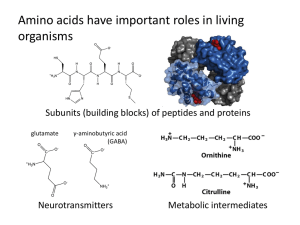
Amino acids have many roles in living organisms
... Vertical bonds point away from viewer (dashed wedges) ...
... Vertical bonds point away from viewer (dashed wedges) ...
Notes
... In the cytoplasm of a cell, the process of glycolysis breaks up __________________ into two molecules of pyruvate. You also get two____________ and free up two ______________ that are picked up by a carrier. The second part oxidates pyruvate inside the mitochondria. Each pyruvate loses a ___________ ...
... In the cytoplasm of a cell, the process of glycolysis breaks up __________________ into two molecules of pyruvate. You also get two____________ and free up two ______________ that are picked up by a carrier. The second part oxidates pyruvate inside the mitochondria. Each pyruvate loses a ___________ ...
Ch 19 - Chemistry Courses: About
... • Looks allosteric, but this is monomeric enzyme • May be due to conformational change upon product release— stays in active state at high concentration of glucose ...
... • Looks allosteric, but this is monomeric enzyme • May be due to conformational change upon product release— stays in active state at high concentration of glucose ...
河北交通职业技术学院教案 Lesion 5 Alcoholic Beverages (1) 课题引
... pathway involving carbon dioxide fixation by producing 2 moles glutamate per mole ...
... pathway involving carbon dioxide fixation by producing 2 moles glutamate per mole ...
TRICARBOXYLIC ACID CYCLE
... acid cycle) is a focal end point for the oxidation of carbohydrate, fat and amino acids via acetyl coenzyme A. • Pyruvate is converted to acetyl coenzyme A by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. • The reactions of the TCA cycle generate carbon dioxide, reduced NAD, reduced FAD and GTP • There are ne ...
... acid cycle) is a focal end point for the oxidation of carbohydrate, fat and amino acids via acetyl coenzyme A. • Pyruvate is converted to acetyl coenzyme A by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. • The reactions of the TCA cycle generate carbon dioxide, reduced NAD, reduced FAD and GTP • There are ne ...
see previous week 3 link
... • The carbon backbones of amino acids can also enter the reactions of cellular respiration to provide energy. • The amino acid first undergoes deamination, or the removal of the amino group in the liver; the amino group becomes ammonia (NH3) and is excreted as urea. • Where the carbon portion of the ...
... • The carbon backbones of amino acids can also enter the reactions of cellular respiration to provide energy. • The amino acid first undergoes deamination, or the removal of the amino group in the liver; the amino group becomes ammonia (NH3) and is excreted as urea. • Where the carbon portion of the ...
Zhang Yufeng - USD Biology
... high • Lipids contain more energy compare to other substrate • Other organs use lipids as fuel • Fatty acid metabolism has a role in neurodevelopment, neurotransmission, and repair processes ...
... high • Lipids contain more energy compare to other substrate • Other organs use lipids as fuel • Fatty acid metabolism has a role in neurodevelopment, neurotransmission, and repair processes ...
Gluconeogenesis
... - Include all intermediates of glycolysis and citric acid cycle, glycerol, lactate and the α-keto acids obtained from deamination of glucogenic amino acids. -Glycerol: obtained from the hydrolysis of the triglycerides in adipose tissue, travels to liver which is phosphorylated and metabolized - Lact ...
... - Include all intermediates of glycolysis and citric acid cycle, glycerol, lactate and the α-keto acids obtained from deamination of glucogenic amino acids. -Glycerol: obtained from the hydrolysis of the triglycerides in adipose tissue, travels to liver which is phosphorylated and metabolized - Lact ...
Overview of Metaboli.. - Frozen Crocus Productions
... Getting back to the ATP thing, these are some of the major metabolic pathways for metabolism: Glycolysis: produces pyruvate for acetyl CoA production in mitochondria, produces NADH (electrons) for ETC in mitochondria, anaerobic production of ATP MK & CPK: anaerobic production of ATP TCA: accepts ac ...
... Getting back to the ATP thing, these are some of the major metabolic pathways for metabolism: Glycolysis: produces pyruvate for acetyl CoA production in mitochondria, produces NADH (electrons) for ETC in mitochondria, anaerobic production of ATP MK & CPK: anaerobic production of ATP TCA: accepts ac ...
Pentose Phosphate Pathway (aka Hexose monophosphate shunt)
... A second transketolase catalyzes the transfer of C2 from Xu-5-P to E-4-P forming a second F-6-P and GAP. Requires TPP as cofactor Goes through a TPP-Xu5-P adduct as intermediate ...
... A second transketolase catalyzes the transfer of C2 from Xu-5-P to E-4-P forming a second F-6-P and GAP. Requires TPP as cofactor Goes through a TPP-Xu5-P adduct as intermediate ...
The Lower Alimentary Organs
... abdominal cavity • Secretes pancreatic juices into duodenum • digestive enzymes • Bicarbonate (alkaline)- increase pH level after chyme has left acidic stomach • Secretes hormones insulin and glucagon to regulate glucose levels in the ...
... abdominal cavity • Secretes pancreatic juices into duodenum • digestive enzymes • Bicarbonate (alkaline)- increase pH level after chyme has left acidic stomach • Secretes hormones insulin and glucagon to regulate glucose levels in the ...
25_Metabolism of lipids digestion, absorption, resynthesis
... • two lipoproteins — apo B-100 and apo E • the main transport form of TGs synthesized in the organism (liver) • deliver the TGs from liver to peripheral tissue (muscle for energy, adipose for storage) • bind to membrane-bound lipoprotein lipases (triacylglycerols are again degraded into free fatty a ...
... • two lipoproteins — apo B-100 and apo E • the main transport form of TGs synthesized in the organism (liver) • deliver the TGs from liver to peripheral tissue (muscle for energy, adipose for storage) • bind to membrane-bound lipoprotein lipases (triacylglycerols are again degraded into free fatty a ...
lecture5
... kinase A, which activates the lipases by phosphorylating them. Thus, epinephrine, norepinephrine, glucagon, and adrenocorticotropic hormone induce lipolysis (Figure 22.6). In contrast, insulin inhibits lipolysis. The released fatty acids are not soluble in blood plasma, and so, on release, serum alb ...
... kinase A, which activates the lipases by phosphorylating them. Thus, epinephrine, norepinephrine, glucagon, and adrenocorticotropic hormone induce lipolysis (Figure 22.6). In contrast, insulin inhibits lipolysis. The released fatty acids are not soluble in blood plasma, and so, on release, serum alb ...