* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Lower Alimentary Organs
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
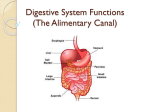
The Lower Alimentary Organs Lower Alimentary/Organs • Small Intestine- continuing on the pathway through the gi • All food absorption takes place here • Begins at the pyloric sphincter and ends at the ileocecal valve • Longest part of alimentary canal (13-23 feet!) • Duodenum- first section • Final digestion (food breakdown) • Bile & pancreatic enzymes • Jejunum-Middle section • Ileum-final section Dogs Just Itch Small Intestine • Microvilli / Villi / Circular Folds • Structures that help to increase surface area to help in absorption of nutrients into bloodstream Liver, pancreas, gallbladder • Responsible for chemical digestion within the duodenum- first segment of small intestine; site of final food breakdown (digestion) • Liver- large multifunctional organ in upper right abdominal cavity (our 2nd largest organ!) • Produces bile (a chemical that breaks down fats)-emulsifier • Maintains homeostasis by regulating blood levels of: • Glucose, lipids, and amino acids • Converts molecules such as carbs to lipids or amino acids to glucose! • Creates and stores glycogen, converts glycogen back to glucose • Also helps to filter out and breakdown toxins that we ingest (how??? All the blood vessels that allow for nutrient absorption lead to the liver first!!!!) Liver, pancreas, gallbladder • Gallbladder-small organ sits behind the liver • Stores/secretes bile into duodenum • Can live without a gallbladder, and it is prone to problems • Pancreas-multifunctional organ under the stomach in upper left abdominal cavity • Secretes pancreatic juices into duodenum • digestive enzymes • Bicarbonate (alkaline)- increase pH level after chyme has left acidic stomach • Secretes hormones insulin and glucagon to regulate glucose levels in the blood. These hormones act on the liver to remove excess glucose from blood or convert glycogen to glucose to increase blood glucose levels. *** We will learn more about the role the pancreas plays with metabolism in the endocrine system! Large Intestines • Responsible for propulsion and elimination of waste as well as final absorption of water, vitamins and electrolytes • Only about 5 feet long! But wider in diameter than the small intestine we could call them the long and short ☺ • Bacteria live in the large intestine to our benefit • Vitamins B and K synthesis • Ferment indigestible carbohydrates • Create gases- flatulus… Large Intestines • Ileocecal valve • Valve that separates the small & large intestines • Cecum- pouch-like area where appendix resides (bacteria collect in this area)- appendicitis occurs with bacterial infection • Colon • • • • Ascending colon-ascends right side abdominal cavity Transverse colon-transverses abdominal cavity Descending colon-descends left side Sigmoid colon-final section of colon- S shaped – curves to form rectum Large Intestine • Rectum-short segment that holds any remaining material after all absorption is done and needing to be eliminated • Anal Canal/Anus- opening to outside of the body • Internal involuntary anal sphincter usually constricted, relaxes when waste reaches the rectum • External voluntary anal sphincter allows for defecation. Goblet Cells • Large Intestines do not need villi – no absorption of nutrients happens here! • However, it does contain goblet cells • Produce mucus to help with the passage of dried-out feces These blobs should look familiar they were all over your microscope slides of simple columnar tissue!!