* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Amino Acids Worksheet - Newcastle University
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
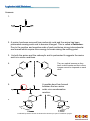
1. Draw out the general structure of an amino acid. 2. What is different about this amino acid (SIMPEJ) compared to the general structure you have just drawn? What is the structure called? Why do you think this makes the melting points in solid amino acids 200-300oC? 3. What conditions do you think the amino acid (TRYPTC) is in to make its zwitterion structure to be in this form? 4. Open up the WebCSD in two separate tabs of your internet browser and arrange them so you can see the 3D structure on the screen at the same time. In one tab search for the refcode LTYROS10 in the other FAZHET. Rotate the molecule so the hydrogen atom on the central carbon is pointing away from the screen. Draw the 2 molecules showing their mirror images and explain why they are optical isomers. 5. What do you notice about the two amino acids in the refcode (ALALHC)? What type of reaction has taken place? Draw out the molecule and highlight the new bond. 6. (Extension Question) Using the refcodes in question for can you explain with the aid of a diagram which is L and which is D? Produced by Steven Carman at Newcastle University as part of a MChem project. Answers: 1. 2. A proton has been removed from carboxylic acid and the amine has been protonated causing each end to become charged. This is called a Zwitterion. Due to the positive and negative ends of each zwitterion strong intermolecular are formed which require more energy to break raising the melting point. 3. As both the amine and the carboxylic acid is protonated it suggests the amino acid is in acidic conditions. 4. 5. They are optical isomers as they have a chiral centre and their mirror images cannot be imposed on each other. A peptide bond has formed between the two amino acids via a condensation reaction. 6. Produced by Steven Carman at Newcastle University as part of a MChem project.