Methylation
... allowed to bind protein. Bound and unbound populations are separated, and strands are cleaved at the modified bases. Bases critical for protein binding will not appear as bands in the bound population. Methylation and uracil interference techniques differ in the base(s) targeted, and in the method u ...
... allowed to bind protein. Bound and unbound populations are separated, and strands are cleaved at the modified bases. Bases critical for protein binding will not appear as bands in the bound population. Methylation and uracil interference techniques differ in the base(s) targeted, and in the method u ...
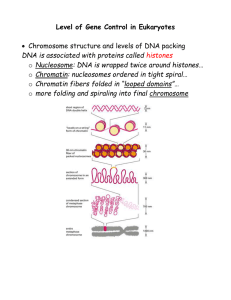
Genetic Controls in Eukaryotes
... o Controlled by regulatory proteins specific to each cell type o Consequence = a single gene can code for more than one polypeptide = alternative RNA splicing o Humans can have fewer genes than proteins that are made. - mRNA degradation o How long mRNA stays in cytoplasm will determine how much prot ...
... o Controlled by regulatory proteins specific to each cell type o Consequence = a single gene can code for more than one polypeptide = alternative RNA splicing o Humans can have fewer genes than proteins that are made. - mRNA degradation o How long mRNA stays in cytoplasm will determine how much prot ...
PCR applications in diagnosis of parasitic diseases
... But it is usful in the epidemiological studies to collect data on the prevalence of E. histolytica and E. dispar which is more advantageous than the ELISA by: ...
... But it is usful in the epidemiological studies to collect data on the prevalence of E. histolytica and E. dispar which is more advantageous than the ELISA by: ...
Epigenetics of Coeliac Disease
... • It may translate the effects of risk factors in terms of molecular events. • It is feasable with the recent development of micro arrays/Si RNA knowledge. • There is no data published to date on this topic (pubmed June 2012). ...
... • It may translate the effects of risk factors in terms of molecular events. • It is feasable with the recent development of micro arrays/Si RNA knowledge. • There is no data published to date on this topic (pubmed June 2012). ...
The subject of the offer are unique sequences of single
... Prokaryotic and eukaryotic expression systems for the production of recombinant proteins are used on a large scale in scientific research. The genetically engineered fusion tags, e.g. histidine tag (His‐Tag) are used for fast and efficient purification of the desired recombinant ...
... Prokaryotic and eukaryotic expression systems for the production of recombinant proteins are used on a large scale in scientific research. The genetically engineered fusion tags, e.g. histidine tag (His‐Tag) are used for fast and efficient purification of the desired recombinant ...
AG-BAs-02.471-05.4p c-Biotechnology_Larry_Stine
... are used to feed on oil slicks and spills Bacteria are being developed to decompose or deactivate ...
... are used to feed on oil slicks and spills Bacteria are being developed to decompose or deactivate ...
pH Properties of Buffer Solutions
... aqueous chemistry. Make it a challenge! Identify the ratios and concentrations at each pH that will have the highest capacity with respect to added acid or added base. Hint: They are not the same! ...
... aqueous chemistry. Make it a challenge! Identify the ratios and concentrations at each pH that will have the highest capacity with respect to added acid or added base. Hint: They are not the same! ...
Translation
... Two major stages involved: • The first stage is called transcription – The 2 strands of the DNA molecule unwind and mRNA copies the genetic code (letters A, C, G and T) from DNA, the master molecule. ...
... Two major stages involved: • The first stage is called transcription – The 2 strands of the DNA molecule unwind and mRNA copies the genetic code (letters A, C, G and T) from DNA, the master molecule. ...
Hypercholesterolemia Questions KEY
... 5. What does RFLP stand for and what are they? Restriction enzymes are first used to cut the DNA segment into pieces (fragments); each fragment will be a different size based on where the DNA is cut. We call these fragments Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs). These fragments will be s ...
... 5. What does RFLP stand for and what are they? Restriction enzymes are first used to cut the DNA segment into pieces (fragments); each fragment will be a different size based on where the DNA is cut. We call these fragments Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLPs). These fragments will be s ...
Evolution of cells
... urea,lactic acid,acetic acid,formic acid. The other step in evolution was the formation of macromolecules. In the cells there are two informational maromolecules present(nucleic acids and proteins) ...
... urea,lactic acid,acetic acid,formic acid. The other step in evolution was the formation of macromolecules. In the cells there are two informational maromolecules present(nucleic acids and proteins) ...
PDF
... The homeodomain is a DNA binding domain about 60 amino acids in length that occurs in many developmental regulatory proteins. Based on their degree of relatedness, homeodomain sequences have been grouped into 10 different families plus some unclassified sequences (1). Using a set of degenerate oligo ...
... The homeodomain is a DNA binding domain about 60 amino acids in length that occurs in many developmental regulatory proteins. Based on their degree of relatedness, homeodomain sequences have been grouped into 10 different families plus some unclassified sequences (1). Using a set of degenerate oligo ...
AP Biology Final Exam Topics 2015
... Classification – (D-KPhCOFGS), Domains and Kingdoms: Basic Characteristics of Each 1) Define heterozygous. Using the letter “T”, how would I represent an organism that is heterozygous? 2) Define homozygous. Using the letter “T”, how would I represent an organism that is heterozygous? 3) What are the ...
... Classification – (D-KPhCOFGS), Domains and Kingdoms: Basic Characteristics of Each 1) Define heterozygous. Using the letter “T”, how would I represent an organism that is heterozygous? 2) Define homozygous. Using the letter “T”, how would I represent an organism that is heterozygous? 3) What are the ...
Molecular Genetics DNA Functions Replication Molecular Genetics
... Single strands are templates for creation of new double strands. Nucleotides added by DNA polymerase in precise sequence: G-C and A-T. New DNA molecule consists of one strand from original molecule and another built using that parental strand as a template = semi-conservative replication. ...
... Single strands are templates for creation of new double strands. Nucleotides added by DNA polymerase in precise sequence: G-C and A-T. New DNA molecule consists of one strand from original molecule and another built using that parental strand as a template = semi-conservative replication. ...
...the story of making proteins continued… After transcription occurs
... then joined together this is called a ________________________________. Both tRNA’s shift down a seat and the next tRNA comes into the ribosome with it’s matching anticodon and amino acid. This third amino acid gets bonded to the other two a chain is starting to form! This keeps continuing unti ...
... then joined together this is called a ________________________________. Both tRNA’s shift down a seat and the next tRNA comes into the ribosome with it’s matching anticodon and amino acid. This third amino acid gets bonded to the other two a chain is starting to form! This keeps continuing unti ...
Lecture #7 Date ______ - Phillips Scientific Methods
... through enzymes that catalyze specific chem rxns. This led to “one gene/ one enzyme” theory • Studied a rare genetic disorder: Alkaptonuria • Thought to be a recessive disorder • Tyrosine is not broken down properly into carbon dioxide and water. • An Intermediate substance: Alkapton (aka “Homogenti ...
... through enzymes that catalyze specific chem rxns. This led to “one gene/ one enzyme” theory • Studied a rare genetic disorder: Alkaptonuria • Thought to be a recessive disorder • Tyrosine is not broken down properly into carbon dioxide and water. • An Intermediate substance: Alkapton (aka “Homogenti ...
Gene!
... acid (RNA) of the virus with nitrous acid. In the rarer cases where two amino-acids are altered (owing presumably to ! two separate deammations by the nitrous acid on one piece of RNA), the altered amino-acids ars not in adjacent positions in the polypeptide chain. Brsnnera had previously shown that ...
... acid (RNA) of the virus with nitrous acid. In the rarer cases where two amino-acids are altered (owing presumably to ! two separate deammations by the nitrous acid on one piece of RNA), the altered amino-acids ars not in adjacent positions in the polypeptide chain. Brsnnera had previously shown that ...
cell drinking
... • Ribosomes are on outside surfce of rough ER • Ribosomes are composed of rRNA and protein ...
... • Ribosomes are on outside surfce of rough ER • Ribosomes are composed of rRNA and protein ...
How can recombinant DNA be used?
... frost to form •Pesticide resistant plants- pesticides will kills pests (weeds, insects, etc.) but not plants •Oncomous – mouse with a gene for cancer (for research) •Pharming- inserting genes into livestock so they produce pharmaceutical products (like insulin in milk) •AquaAdvantage© Salmon – grow ...
... frost to form •Pesticide resistant plants- pesticides will kills pests (weeds, insects, etc.) but not plants •Oncomous – mouse with a gene for cancer (for research) •Pharming- inserting genes into livestock so they produce pharmaceutical products (like insulin in milk) •AquaAdvantage© Salmon – grow ...
14 - Lab Times
... was “deep red and turbid”. It also contained be essential. In 2004, Rosario Gil from the satellites. Fegley’s research indicates that the a newly synthesised mixture of amino acids University of Valencia estimated that the gases escaping from chondritic material suband amines! “core of a minimal bac ...
... was “deep red and turbid”. It also contained be essential. In 2004, Rosario Gil from the satellites. Fegley’s research indicates that the a newly synthesised mixture of amino acids University of Valencia estimated that the gases escaping from chondritic material suband amines! “core of a minimal bac ...
Week 1 Pre-Lecture Slides
... Imagine two massive proteins composed of 10,000 atoms. At the end of one protein is a hydroxyl group, while the other protein has a phosphate group in the same place. How are these massive molecules similar or different? Does it matter? ...
... Imagine two massive proteins composed of 10,000 atoms. At the end of one protein is a hydroxyl group, while the other protein has a phosphate group in the same place. How are these massive molecules similar or different? Does it matter? ...
Transcription and the Central Dogma
... from many genes averages out to this. – The closer these 2 regions actually are to the consensus sequences, the “stronger” the promoter, meaning the more likely RNA polymerase binding and transcription will occur. ...
... from many genes averages out to this. – The closer these 2 regions actually are to the consensus sequences, the “stronger” the promoter, meaning the more likely RNA polymerase binding and transcription will occur. ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.