
Why teach a course in bioinformatics?
... spots, each spot containing a different DNA oligomer. • Each oligomer in a DNA microarray can serve as a probe to detect a unique, complementary DNA or RNA molecule. ...
... spots, each spot containing a different DNA oligomer. • Each oligomer in a DNA microarray can serve as a probe to detect a unique, complementary DNA or RNA molecule. ...
Prokaryotic Gene Regulation
... ¾Bind activators and cause them to bind to DNA ¾Bind repressors and prevent them from binding to DNA - Inhibitors of transcription (2 types) ¾Corepressors bind to repressors and cause them to bind to DNA ¾Inhibitors bind to activators and prevent them from binding to DNA ...
... ¾Bind activators and cause them to bind to DNA ¾Bind repressors and prevent them from binding to DNA - Inhibitors of transcription (2 types) ¾Corepressors bind to repressors and cause them to bind to DNA ¾Inhibitors bind to activators and prevent them from binding to DNA ...
C2005/F2401 `07 -- Lecture 16 -- Last Edited
... with the chromosome. A single cut and rejoin event between two circles (such as the bacterial chromosome and a plasmid) generates one big circle. This type of recombination does occur, joining the two circles. The process can be reversed, regenerating the two individual circles. If mistakes are made ...
... with the chromosome. A single cut and rejoin event between two circles (such as the bacterial chromosome and a plasmid) generates one big circle. This type of recombination does occur, joining the two circles. The process can be reversed, regenerating the two individual circles. If mistakes are made ...
Genetic Update Conferences - 2002 - yhs
... Interactome - sum total of all the protein / protein interactions can be used in cancer prognosis Exome - sum total of all the Coding DNA sequences in all the human Exons Exome Sequencing to find mutations in rare Mendelian Syndromes 1.5% of genome Introme - sum total of all the Non-Coding DNA seque ...
... Interactome - sum total of all the protein / protein interactions can be used in cancer prognosis Exome - sum total of all the Coding DNA sequences in all the human Exons Exome Sequencing to find mutations in rare Mendelian Syndromes 1.5% of genome Introme - sum total of all the Non-Coding DNA seque ...
هيتايحلأءايميكلأ د دادعأ . باهولأدبع ناميأ
... Non protein nitrogen compound: They are non protein compounds however they have nitrogen group and formed from elimination of amine group from amino acid such as , urea, creatinin, uric acid , ammonia, etc--Transportation of ammonia: 1. The final de amination and production of ammonia is taking pla ...
... Non protein nitrogen compound: They are non protein compounds however they have nitrogen group and formed from elimination of amine group from amino acid such as , urea, creatinin, uric acid , ammonia, etc--Transportation of ammonia: 1. The final de amination and production of ammonia is taking pla ...
Chance and Necessity in the Selection of Nucleic Acid Catalysts
... 100-mers can fold into structures capable of specifically binding certain organic dyes.4 In the last few years a number of RNA and DNA aptamers for amino acids,5-9 drugs,10 and enzymatic cofactors8,11-15 have been isolated. Typical association constants, measured in aqueous buffers, are in the range ...
... 100-mers can fold into structures capable of specifically binding certain organic dyes.4 In the last few years a number of RNA and DNA aptamers for amino acids,5-9 drugs,10 and enzymatic cofactors8,11-15 have been isolated. Typical association constants, measured in aqueous buffers, are in the range ...
How to search the PDB
... The 2015 Nobel prize in Chemistry was awarded jointly to Tomas Lindahl, Paul Modrich and Aziz Sancar "for mechanistic studies of DNA repair". ...
... The 2015 Nobel prize in Chemistry was awarded jointly to Tomas Lindahl, Paul Modrich and Aziz Sancar "for mechanistic studies of DNA repair". ...
Bio101 Development Guide.pages
... This is function is to convert sub sequences to file by the following steps. 1. Get the sequences from a file. 2. Get the index of sub sequences and P, check the index by parity-check. Then, order the sub sequences by analyzing that starting with A or T and ending with C or G. 3. Check the sub seque ...
... This is function is to convert sub sequences to file by the following steps. 1. Get the sequences from a file. 2. Get the index of sub sequences and P, check the index by parity-check. Then, order the sub sequences by analyzing that starting with A or T and ending with C or G. 3. Check the sub seque ...
DNA Replication Lecture PowerPoint
... but... • Rarely leads to a protein having a novel property that improves ability of organism and its descendants to survive and reproduce. ...
... but... • Rarely leads to a protein having a novel property that improves ability of organism and its descendants to survive and reproduce. ...
Practical II - Faculty Websites
... necessary raw material, including all four dNTPs, what would be your two primers? ...
... necessary raw material, including all four dNTPs, what would be your two primers? ...
NUTRICALM A Formula Designed to Calm and Sooth NutriCalm
... NUTRICALM A Formula Designed to Calm and Sooth NutriCalm features pharmaceutical grade L-tryptophan, an essential amino acid which is converted to serotonin in the brain. In addition, the herbs ashwaganda, theanine and valerian root help soothe and relax naturally, effectively and safely. 1 Capsule ...
... NUTRICALM A Formula Designed to Calm and Sooth NutriCalm features pharmaceutical grade L-tryptophan, an essential amino acid which is converted to serotonin in the brain. In addition, the herbs ashwaganda, theanine and valerian root help soothe and relax naturally, effectively and safely. 1 Capsule ...
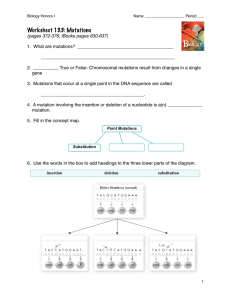
Worksheet 13.3
... 2. __________ True or False: Chromosomal mutations result from changes in a single gene 3. Mutations that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence are called ...
... 2. __________ True or False: Chromosomal mutations result from changes in a single gene 3. Mutations that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence are called ...
How to search the PDB
... Last week Nobel prize in Chemistry 2015 was awarded jointly to Tomas Lindahl, Paul Modrich and Aziz Sancar "for mechanistic studies of DNA repair". ...
... Last week Nobel prize in Chemistry 2015 was awarded jointly to Tomas Lindahl, Paul Modrich and Aziz Sancar "for mechanistic studies of DNA repair". ...
fall break, take home exam
... Perform a BLASTN with this sequence against GenBank for an initial likely identification of the genome (mitochondrial or nuclear), and the organism. Perform A BLASTX with the correct genetic code to identify the name of the gene represented by this sequence: Genome (1 point): Organism (1 point): Gen ...
... Perform a BLASTN with this sequence against GenBank for an initial likely identification of the genome (mitochondrial or nuclear), and the organism. Perform A BLASTX with the correct genetic code to identify the name of the gene represented by this sequence: Genome (1 point): Organism (1 point): Gen ...
Part 1
... organisms to transmit their genetic material from one generation to the next. Two copies of nucleic acid are synthesized from one parent molecule during the process of cell division such that each daughter cell obtains one copy of the genetic material. The process can be inhibited by novobiocin, nal ...
... organisms to transmit their genetic material from one generation to the next. Two copies of nucleic acid are synthesized from one parent molecule during the process of cell division such that each daughter cell obtains one copy of the genetic material. The process can be inhibited by novobiocin, nal ...
Proteins perform most functions in the cell [1].
... 5. If a chain of amino acids is actually a polypeptide and not a protein as was first mentioned in this section. Explain the relationship between amino acids, polypeptides, and proteins. [1] ...
... 5. If a chain of amino acids is actually a polypeptide and not a protein as was first mentioned in this section. Explain the relationship between amino acids, polypeptides, and proteins. [1] ...
Evidence of Common Ancestry
... how did monomers become polymers, such as proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. In the 1980s, American scientist Thomas Cech and his colleagues discovered that RNA (ribonucleic acid) can act as a catalyst, helping to drive the chemical reactions necessary for many processes in an organism. Ribosomal ...
... how did monomers become polymers, such as proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. In the 1980s, American scientist Thomas Cech and his colleagues discovered that RNA (ribonucleic acid) can act as a catalyst, helping to drive the chemical reactions necessary for many processes in an organism. Ribosomal ...
AP Biology Summer Assignment Chapter 3 Quiz 2016-17
... with both labeled bases. After five hours of incubation, the biologist extracted polynucleotides from the cells and separated them into three groups, each containing a range of different polynucleotide lengths. The first group contained the shortest polynucleotides. The second group contained polynu ...
... with both labeled bases. After five hours of incubation, the biologist extracted polynucleotides from the cells and separated them into three groups, each containing a range of different polynucleotide lengths. The first group contained the shortest polynucleotides. The second group contained polynu ...
powerpoint 24 Aug
... bridges, and non-polar/non-polar interactions. In order for amylase to break down starch it must bind the starch. It can only bind starch because its tertiary structure results in the formation of a binding site. Quaternary structure would be more than one peptide chain associated with each other ...
... bridges, and non-polar/non-polar interactions. In order for amylase to break down starch it must bind the starch. It can only bind starch because its tertiary structure results in the formation of a binding site. Quaternary structure would be more than one peptide chain associated with each other ...
Chapter 4 Stoichiometry Power Point
... We use the term Ionization in order to describe the separation of acids and bases into ions. In order to determine whether or not you have a strong acid or base, you see whether the acid or base dissociates completely in water. If it does completely ionize in water, then it is considered to be a str ...
... We use the term Ionization in order to describe the separation of acids and bases into ions. In order to determine whether or not you have a strong acid or base, you see whether the acid or base dissociates completely in water. If it does completely ionize in water, then it is considered to be a str ...
lecture 5
... the “factories” in which the synthesis of proteins occurs. -The large ribosomal subunit catalyzes formation of the peptide bonds that link amino acid residues in a protein. -The small subunit binds mRNA and is responsible for the accuracy of translation by ensuring correct base-pairing between the c ...
... the “factories” in which the synthesis of proteins occurs. -The large ribosomal subunit catalyzes formation of the peptide bonds that link amino acid residues in a protein. -The small subunit binds mRNA and is responsible for the accuracy of translation by ensuring correct base-pairing between the c ...
Ch11_lecture - Dr Owen class material
... • The ribosome joins the amino acids together with peptide bonds to form a protein. • When a stop codon is reached, the finished protein is released from the ribosome. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education Inc. ...
... • The ribosome joins the amino acids together with peptide bonds to form a protein. • When a stop codon is reached, the finished protein is released from the ribosome. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education Inc. ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.
















![Proteins perform most functions in the cell [1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014430699_1-2242d98249553cc613e120034bd15855-300x300.png)





