lecture 5
... the “factories” in which the synthesis of proteins occurs. -The large ribosomal subunit catalyzes formation of the peptide bonds that link amino acid residues in a protein. -The small subunit binds mRNA and is responsible for the accuracy of translation by ensuring correct base-pairing between the c ...
... the “factories” in which the synthesis of proteins occurs. -The large ribosomal subunit catalyzes formation of the peptide bonds that link amino acid residues in a protein. -The small subunit binds mRNA and is responsible for the accuracy of translation by ensuring correct base-pairing between the c ...
Ch11_lecture - Dr Owen class material
... • The ribosome joins the amino acids together with peptide bonds to form a protein. • When a stop codon is reached, the finished protein is released from the ribosome. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education Inc. ...
... • The ribosome joins the amino acids together with peptide bonds to form a protein. • When a stop codon is reached, the finished protein is released from the ribosome. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education Inc. ...
Prokaryote Gene Expression Section 1 Overview of RNA
... All tRNAs have a common 3D fold Bind to three sites on ribosomes, which fit this common 3D structure Function to bind codons on mRNA bound to ribosome and bring amino acyl groups to the catalytic site on the ribosome Ribosomes to not differentiate tRNA structure or amino acylation. ...
... All tRNAs have a common 3D fold Bind to three sites on ribosomes, which fit this common 3D structure Function to bind codons on mRNA bound to ribosome and bring amino acyl groups to the catalytic site on the ribosome Ribosomes to not differentiate tRNA structure or amino acylation. ...
DNA technology
... to identify 2.) The DNA being tested will have its strands separated 3.) The strands are mixed with the probe, which will bind to specific part of the strand – DNA hybridisation 4.) The site the probe binds to is identified by the radioactivity or florescent that it emits. ...
... to identify 2.) The DNA being tested will have its strands separated 3.) The strands are mixed with the probe, which will bind to specific part of the strand – DNA hybridisation 4.) The site the probe binds to is identified by the radioactivity or florescent that it emits. ...
Review PowerPoint
... triphosphates used during DNA synthesis is that A. the nucleoside triphosphates have the sugar deoxyribose; ATP has the sugar ribose. B. the nucleoside triphosphates have two phosphate groups; ATP has three phosphate groups. C. ATP contains three high-energy bonds; the nucleoside triphosphates have ...
... triphosphates used during DNA synthesis is that A. the nucleoside triphosphates have the sugar deoxyribose; ATP has the sugar ribose. B. the nucleoside triphosphates have two phosphate groups; ATP has three phosphate groups. C. ATP contains three high-energy bonds; the nucleoside triphosphates have ...
CH 3
... manufacturers can control the precise composition of the margarine to create a particular 'mouth feel', melting range and stability. unlike the cis acids, which occur naturally, the trans acids are artificial and so cannot be metabolised in the human body as efficiently as their isomers. Over the pa ...
... manufacturers can control the precise composition of the margarine to create a particular 'mouth feel', melting range and stability. unlike the cis acids, which occur naturally, the trans acids are artificial and so cannot be metabolised in the human body as efficiently as their isomers. Over the pa ...
Document
... New base pair in the code for new amino acid • Implementation with isoC:isoG pair • UAG nonsense codon for iodotyrosine • Or the (iso-C)AG codon • Challenge: coupling of non-standard amino acids to nonstandard tRNAs by nonstandard synthetases ...
... New base pair in the code for new amino acid • Implementation with isoC:isoG pair • UAG nonsense codon for iodotyrosine • Or the (iso-C)AG codon • Challenge: coupling of non-standard amino acids to nonstandard tRNAs by nonstandard synthetases ...
2016 Energetics Protein Enzyme WS
... For the questions below, use the diagram above of a polypeptide chain. The heavy line represents the backbone of the chain. Selected R groups of amino acids are shown together with various bonds and interactions that stabilize the folding of the chain. Each bond or interaction is labeled with a rom ...
... For the questions below, use the diagram above of a polypeptide chain. The heavy line represents the backbone of the chain. Selected R groups of amino acids are shown together with various bonds and interactions that stabilize the folding of the chain. Each bond or interaction is labeled with a rom ...
Nucleic Acid Synthesis in the Neoplastic Cell
... Bromodeoxyuridine is incorporated in place of now classic proposal that DNA consists of two helical polynucleotide chains of opposite polarity thymine into the DNA of bacteria, bacteriophage, and animal cells (41, 92, 143, 253). It has been which are twined round one another. The two shown at the en ...
... Bromodeoxyuridine is incorporated in place of now classic proposal that DNA consists of two helical polynucleotide chains of opposite polarity thymine into the DNA of bacteria, bacteriophage, and animal cells (41, 92, 143, 253). It has been which are twined round one another. The two shown at the en ...
Sequences of the Nucleocapsid Genes from Two Strains of Avian
... Examination of the amino acid sequence shows that it predicts a polypeptide which is enriched in basic residues with an overall positive charge at neutral p H of 19 for Beaudette and 20 for M41. These basic residues are clustered in distinct regions; for example, in the Beaudette sequence the region ...
... Examination of the amino acid sequence shows that it predicts a polypeptide which is enriched in basic residues with an overall positive charge at neutral p H of 19 for Beaudette and 20 for M41. These basic residues are clustered in distinct regions; for example, in the Beaudette sequence the region ...
Diethyl pyrocarbonate (D5758) - Product Information - Sigma
... exposure to moisture. This product has a shelf-life of 2 years. If the product is exposed to even traces of moisture, it does hydrolyze somewhat. The carbon dioxide which is formed is more soluble in DEPC at 0-4°C than at room temperature, and as the product is brought to room temperature before ope ...
... exposure to moisture. This product has a shelf-life of 2 years. If the product is exposed to even traces of moisture, it does hydrolyze somewhat. The carbon dioxide which is formed is more soluble in DEPC at 0-4°C than at room temperature, and as the product is brought to room temperature before ope ...
Mutations & DNA Technology Worksheet
... Mutations are changes in DNA. Somatic mutations occur in non-reproductive cells and won't be passed onto offspring. Mutations that occur in reproductive cells like eggs and sperm (germ-line mutations) can be passed onto offspring. Effects of germ line mutations: A single germ line mutation can have ...
... Mutations are changes in DNA. Somatic mutations occur in non-reproductive cells and won't be passed onto offspring. Mutations that occur in reproductive cells like eggs and sperm (germ-line mutations) can be passed onto offspring. Effects of germ line mutations: A single germ line mutation can have ...
What are L-Amino Acids
... ingest the others in order to function. All amino acids that occur in proteins are of the “L” form (as opposed to “D” form). Essentially, these are mirror images of each other (like a pair of hands); they are very similar in appearance, but with important differences. L-amino acids are a key compone ...
... ingest the others in order to function. All amino acids that occur in proteins are of the “L” form (as opposed to “D” form). Essentially, these are mirror images of each other (like a pair of hands); they are very similar in appearance, but with important differences. L-amino acids are a key compone ...
DNA Isolation: plant materials
... The DNA in a cell is about 100,000 times as long as the cell itself. However, DNA only takes up about 10% of the cell's volume. This is because the highly convoluted (folded) DNA molecules are packed into chromosomes in the cell's nucleus. The walls of plant cells are made of cellulose, which is a p ...
... The DNA in a cell is about 100,000 times as long as the cell itself. However, DNA only takes up about 10% of the cell's volume. This is because the highly convoluted (folded) DNA molecules are packed into chromosomes in the cell's nucleus. The walls of plant cells are made of cellulose, which is a p ...
5 end
... reaches the A site of the ribosome The A site accepts a protein called a release factor The release factor adds a water molecule instead of an amino acid The polypeptide, the mRNA, and the two ribosomal subunits come apart and float off into the cytoplasm ...
... reaches the A site of the ribosome The A site accepts a protein called a release factor The release factor adds a water molecule instead of an amino acid The polypeptide, the mRNA, and the two ribosomal subunits come apart and float off into the cytoplasm ...
Gene Sequencing
... the Sanger Method. • Two of the most widely-used NGS methods include 454Roche Pyrosequencing and Illumina Bridge Sequencing. • Others include Ion-Torrent Sequencing and Nanopore ...
... the Sanger Method. • Two of the most widely-used NGS methods include 454Roche Pyrosequencing and Illumina Bridge Sequencing. • Others include Ion-Torrent Sequencing and Nanopore ...
Non-coding RNAs - Structural Biology Labs
... • Some ncRNAs can bind directly to proteins, altering their structure, enzymatic activities or ligand binding • Targets of such ncRNAs often are proteins, involved in transcription, for example nuclear receptors or general transcription factors ...
... • Some ncRNAs can bind directly to proteins, altering their structure, enzymatic activities or ligand binding • Targets of such ncRNAs often are proteins, involved in transcription, for example nuclear receptors or general transcription factors ...
XRCC1 (X-Ray Repair Cross Complementing
... XRCC1 (X-Ray Repair Cross Complementing Protein1) Ab-1 (Clone 33-2-5) ...
... XRCC1 (X-Ray Repair Cross Complementing Protein1) Ab-1 (Clone 33-2-5) ...
magnetic waves enable cell communication.
... fields in a nuclear spin resonance spectrometer induce ring currents. The four bases of the double helix also use such a ring structure, except that two carbon atoms are replaced with nitrogen atoms. One of these nitrogen atoms forms the hydrogen bond to its partner on the other side of the helix (F ...
... fields in a nuclear spin resonance spectrometer induce ring currents. The four bases of the double helix also use such a ring structure, except that two carbon atoms are replaced with nitrogen atoms. One of these nitrogen atoms forms the hydrogen bond to its partner on the other side of the helix (F ...
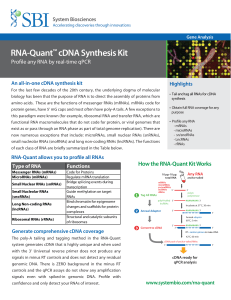
RNA-Quant™ cDNA Synthesis Kit
... Total RNA was harvested from human HT1080 cells using standard Trizol extraction protocols. The RNA-Quant kit was used to tail and tag all RNAs into quantifiable cDNA for qPCR analysis. Sample amplification plots and specificity tests using dissociation analyses are shown below. ...
... Total RNA was harvested from human HT1080 cells using standard Trizol extraction protocols. The RNA-Quant kit was used to tail and tag all RNAs into quantifiable cDNA for qPCR analysis. Sample amplification plots and specificity tests using dissociation analyses are shown below. ...
Honors Genetics: Senior Exam Review Chapter 1: Introduction to
... Describe the process of DNA replication as a semiconservative replication process. Understand the difference between conservative and dispersive replication. How did the Messelson-Stahl experiment prove semiconservative replication? Know why E. coli was used as the organism for experimentation. What ...
... Describe the process of DNA replication as a semiconservative replication process. Understand the difference between conservative and dispersive replication. How did the Messelson-Stahl experiment prove semiconservative replication? Know why E. coli was used as the organism for experimentation. What ...
pGLO Transformation Lab Introduction to Transformation In this lab
... transformation occurs when a cell takes up (takes inside) and expresses a new piece of genetic material— DNA. This new genetic information often provides the organism with a new trait which is identifiable after transformation. Genetic transformation literally means change caused by genes and involv ...
... transformation occurs when a cell takes up (takes inside) and expresses a new piece of genetic material— DNA. This new genetic information often provides the organism with a new trait which is identifiable after transformation. Genetic transformation literally means change caused by genes and involv ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.