Honors Genetics: Senior Exam Review Chapter 1: Introduction to
... Describe the process of DNA replication as a semiconservative replication process. Understand the difference between conservative and dispersive replication. How did the Messelson-Stahl experiment prove semiconservative replication? Know why E. coli was used as the organism for experimentation. What ...
... Describe the process of DNA replication as a semiconservative replication process. Understand the difference between conservative and dispersive replication. How did the Messelson-Stahl experiment prove semiconservative replication? Know why E. coli was used as the organism for experimentation. What ...
Evolution of prokaryotic genomes
... DNA rearrangements and (4) acquisition of genetic information. Each of these categories again includes a variety of specific mechanisms. In addition, some of the observed processes may overlap with more than one of the listed categories. For example, intrinsic limits of structural stability of nucle ...
... DNA rearrangements and (4) acquisition of genetic information. Each of these categories again includes a variety of specific mechanisms. In addition, some of the observed processes may overlap with more than one of the listed categories. For example, intrinsic limits of structural stability of nucle ...
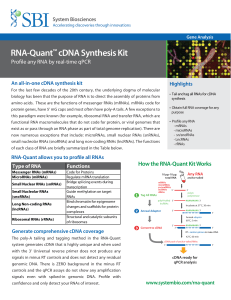
RNA-Quant™ cDNA Synthesis Kit
... Total RNA was harvested from human HT1080 cells using standard Trizol extraction protocols. The RNA-Quant kit was used to tail and tag all RNAs into quantifiable cDNA for qPCR analysis. Sample amplification plots and specificity tests using dissociation analyses are shown below. ...
... Total RNA was harvested from human HT1080 cells using standard Trizol extraction protocols. The RNA-Quant kit was used to tail and tag all RNAs into quantifiable cDNA for qPCR analysis. Sample amplification plots and specificity tests using dissociation analyses are shown below. ...
Text Book of Molecular Biology
... If the twisting of the DNA is in the same direction as that of the double helix (right-handed) that is the helix is twisted up before closure, then the supercoiling formed is positive (the left-handed positive supercoil). For example, when the piece of dsDNA with 200 helical turns is twisted up two ...
... If the twisting of the DNA is in the same direction as that of the double helix (right-handed) that is the helix is twisted up before closure, then the supercoiling formed is positive (the left-handed positive supercoil). For example, when the piece of dsDNA with 200 helical turns is twisted up two ...
Physical and Chemical Control of Microorganisms
... Forms _______________ free radicals (e.g. superoxides, hydroxyl radicals: see last lecture) which are toxic to all cells Also breaks down to H2O and O2, therefore is strongly effective against _____________. ...
... Forms _______________ free radicals (e.g. superoxides, hydroxyl radicals: see last lecture) which are toxic to all cells Also breaks down to H2O and O2, therefore is strongly effective against _____________. ...
pGLO Transformation Lab Introduction to Transformation In this lab
... transformation occurs when a cell takes up (takes inside) and expresses a new piece of genetic material— DNA. This new genetic information often provides the organism with a new trait which is identifiable after transformation. Genetic transformation literally means change caused by genes and involv ...
... transformation occurs when a cell takes up (takes inside) and expresses a new piece of genetic material— DNA. This new genetic information often provides the organism with a new trait which is identifiable after transformation. Genetic transformation literally means change caused by genes and involv ...
DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and Sequencing: the IGS
... tissues preserved in CTAB buffer, were placed in 2.0 ml microcentrifuge tubes with 4-5 3 mm glass beads and macerated using a Mini-BeadBeater-8 (BioSpec Products Inc., Bartlesville, OK) set at 3/4 speed for one minute (100 ml of 2X CTAB is 10 ml of a 1 M stock of TRIS-HCL pH 8.0, 28 ml of a 5 M stoc ...
... tissues preserved in CTAB buffer, were placed in 2.0 ml microcentrifuge tubes with 4-5 3 mm glass beads and macerated using a Mini-BeadBeater-8 (BioSpec Products Inc., Bartlesville, OK) set at 3/4 speed for one minute (100 ml of 2X CTAB is 10 ml of a 1 M stock of TRIS-HCL pH 8.0, 28 ml of a 5 M stoc ...
Experiment 8 - WordPress.com
... The transformed cells contain the genes for GFP (green fluorescent protein) which allows the bacteria to display green fluorescence in the presence of arabinose and a UV light. GFP can be switched on and off. Arabinose, a biological molecule, allows GFP to turn on and, therefore, fluoresce. The a ...
... The transformed cells contain the genes for GFP (green fluorescent protein) which allows the bacteria to display green fluorescence in the presence of arabinose and a UV light. GFP can be switched on and off. Arabinose, a biological molecule, allows GFP to turn on and, therefore, fluoresce. The a ...
Chapter 4
... 2. Charged, amino-acylated initiator tRNA binds to P site of ribosome and is based paired through tRNA anticodon to codon on mRNA 3. A second amino-acylated tRNA fills A site and anticodon Hbonds with second codon on mRNA 4. Amino acids in P and A site are joined by a peptide bond. tRNA in P site is ...
... 2. Charged, amino-acylated initiator tRNA binds to P site of ribosome and is based paired through tRNA anticodon to codon on mRNA 3. A second amino-acylated tRNA fills A site and anticodon Hbonds with second codon on mRNA 4. Amino acids in P and A site are joined by a peptide bond. tRNA in P site is ...
Nucleotides: Synthesis and Degradation
... 1DUD: Deoxyuridine-5'-Nucleotide Hydrolase in a complex with a bound substrate analog, Deoxyuridine-5'-Diphosphate (dUDP). Explore dUTPase as follows: • Find the substrate in its binding site • Find C5 on the Uracil group. Is there enough room to attach a methyl group to C5? • Locate the ribose 2’ C ...
... 1DUD: Deoxyuridine-5'-Nucleotide Hydrolase in a complex with a bound substrate analog, Deoxyuridine-5'-Diphosphate (dUDP). Explore dUTPase as follows: • Find the substrate in its binding site • Find C5 on the Uracil group. Is there enough room to attach a methyl group to C5? • Locate the ribose 2’ C ...
BIOLOGY IS THE STUDY OF LIFE
... neutral substances pass through membrane more easily 4. Presence of a carrier molecule for the entering molecule These carriers are enzymes or coenzymes. ...
... neutral substances pass through membrane more easily 4. Presence of a carrier molecule for the entering molecule These carriers are enzymes or coenzymes. ...
Study Guide for Exam 3
... State the nucleotides found in DNA and the ones in RNA. Be able to apply the base-pairing rules to predict the nucleotide structure of a complimentary strand of DNA or transcription into RNA. Show the compliment to a sequence of 9 nucleotides. 8. Explain where the different types of RNA are found: m ...
... State the nucleotides found in DNA and the ones in RNA. Be able to apply the base-pairing rules to predict the nucleotide structure of a complimentary strand of DNA or transcription into RNA. Show the compliment to a sequence of 9 nucleotides. 8. Explain where the different types of RNA are found: m ...
Document
... What is it, what can you do with it, etc Difference between it and genetic engineering Project Examples - iGEM ...
... What is it, what can you do with it, etc Difference between it and genetic engineering Project Examples - iGEM ...
Section E
... • Both leading and lagging strand primers are elongated by DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. This complex is a dimer, – One half synthesizes the leading strand; – The other synthesizes the lagging strand; – The two polymerases in a single complex ensures that both strands are synthesized at the same ra ...
... • Both leading and lagging strand primers are elongated by DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. This complex is a dimer, – One half synthesizes the leading strand; – The other synthesizes the lagging strand; – The two polymerases in a single complex ensures that both strands are synthesized at the same ra ...
Plant Biotechnology and GMOs
... •Activated virG turns on other vir genes, including vir D and E. •vir D cuts at a specific site in the Ti plasmid (tumor-inducing), the left border. The left border and a similar sequence, the right border, delineate the T-DNA, the DNA that will be transferred from the bacterium to the plant cell •S ...
... •Activated virG turns on other vir genes, including vir D and E. •vir D cuts at a specific site in the Ti plasmid (tumor-inducing), the left border. The left border and a similar sequence, the right border, delineate the T-DNA, the DNA that will be transferred from the bacterium to the plant cell •S ...
Translation
... codon (mRNA) and anticodon of (tRNA). Sites include regions of large and small subunits of ribosome. ...
... codon (mRNA) and anticodon of (tRNA). Sites include regions of large and small subunits of ribosome. ...
... i) Amino acid side chains are to proteins as nucleotide bases are to DNA. ii) The mainchain atoms in protein are represented by __________________ sugars in DNA. iii) The peptide bond in proteins is analogous to the __________________bond in DNA. iv) The amino acid phenylalanine has the same number ...
Darwin`s warm little pond revisited: from molecules to the origin of life
... light, heat, electricity etc. present, that a protein compound was chemically formed, ready to undergo still more complex changes at the present such matter would be instantly devoured, which would not have been the case before living creatures were formed. Charles Darwin (1809–1882) wrote these sen ...
... light, heat, electricity etc. present, that a protein compound was chemically formed, ready to undergo still more complex changes at the present such matter would be instantly devoured, which would not have been the case before living creatures were formed. Charles Darwin (1809–1882) wrote these sen ...
Technical Information - BIOLOG Life Science Institute
... Toxicity and Safety: Since cADPR seems to have tasks in every organism, it is not unlikely that it will interfere with many cell regulation processes in vivo. However, due to the rather small quantities to work with, no health hazards have been reported. Nevertheless please keep in mind, that the in ...
... Toxicity and Safety: Since cADPR seems to have tasks in every organism, it is not unlikely that it will interfere with many cell regulation processes in vivo. However, due to the rather small quantities to work with, no health hazards have been reported. Nevertheless please keep in mind, that the in ...
Chapter 2
... chains of amino acids (20 different kinds) Shape of protein is determined by how amino acids react with on another and with water Enzymes are proteins that promote chemical reactions Also important for structural functions and for the immune system ...
... chains of amino acids (20 different kinds) Shape of protein is determined by how amino acids react with on another and with water Enzymes are proteins that promote chemical reactions Also important for structural functions and for the immune system ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.