Amino acids catabolism
... building blocks and to the synthesis of variety of other biologically molecules. When a.acids deaminated (removed the αamino group), their C-keletons can be fed to TCA cycle. ...
... building blocks and to the synthesis of variety of other biologically molecules. When a.acids deaminated (removed the αamino group), their C-keletons can be fed to TCA cycle. ...
Unit 2 Study Guide
... so that new DNA can be “grown”. The second step of PCR is called annealing. The thermal cycler cools to 55 degrees C, and the DNA primers which were added to the DNA mixture early on with the bead are ready to do their job. Think of annealing as gluing. In this stage, the DNA primers (short sequence ...
... so that new DNA can be “grown”. The second step of PCR is called annealing. The thermal cycler cools to 55 degrees C, and the DNA primers which were added to the DNA mixture early on with the bead are ready to do their job. Think of annealing as gluing. In this stage, the DNA primers (short sequence ...
MI Unit 2 Cram Sheet
... Three “ingredients” are added to a sample of DNA so that copies can be made: Taq polymerase, DNA primers, and DNA nucleotides. The Taq polymerase and DNA nucleotides are included in a little pellet called a PCR bead, while the primer needed for the specific genes being tested for is added to it. Th ...
... Three “ingredients” are added to a sample of DNA so that copies can be made: Taq polymerase, DNA primers, and DNA nucleotides. The Taq polymerase and DNA nucleotides are included in a little pellet called a PCR bead, while the primer needed for the specific genes being tested for is added to it. Th ...
Rapid communication: Nucleotide sequence of the river buffalo beta
... primer and superscript II reverse transcriptase (GIBCOBRL, Grand Island, NY). PCR was performed using the above oligo d(T)17 as reverse primer and a forward primer (5′ GGAAAAAAGGAATTGAGAGCC 3′) designed on the basis of conserved regions, through a multiple alignment of bovine, ovine, caprine, and po ...
... primer and superscript II reverse transcriptase (GIBCOBRL, Grand Island, NY). PCR was performed using the above oligo d(T)17 as reverse primer and a forward primer (5′ GGAAAAAAGGAATTGAGAGCC 3′) designed on the basis of conserved regions, through a multiple alignment of bovine, ovine, caprine, and po ...
7.02 Fall 2001 Recombinant DNA methods Agenda
... with the 5’ end of the coding sequence next to the promoter, in order for the protein to be expressed. What would happen if the insert went in backwards? (Might get transcription of the non-coding strand and expression of a nonsense protein. More likely, nothing at all will be expressed.) ...
... with the 5’ end of the coding sequence next to the promoter, in order for the protein to be expressed. What would happen if the insert went in backwards? (Might get transcription of the non-coding strand and expression of a nonsense protein. More likely, nothing at all will be expressed.) ...
An endosperm enzyme catalyzes the formation of phosphotriester
... The broad presence of this enzyme in biological kingdom suggests that the enzyme is an evolution significant protein. A variety of short chain length nucleotides and poly nucleotides including polyU, polyC and polyA had been tested as substrates for demonstrating the catalysis of enzyme reaction. Ho ...
... The broad presence of this enzyme in biological kingdom suggests that the enzyme is an evolution significant protein. A variety of short chain length nucleotides and poly nucleotides including polyU, polyC and polyA had been tested as substrates for demonstrating the catalysis of enzyme reaction. Ho ...
ATP
... construct proteins; stored in DNA • Gene – segment of DNA that codes for one protein • Genome – complete set of genes • Genetic Code – method used to translate a ...
... construct proteins; stored in DNA • Gene – segment of DNA that codes for one protein • Genome – complete set of genes • Genetic Code – method used to translate a ...
Document
... 40 Vk x 5 Jk = 200 combinations 30 Vl x 4 Jl = 120 combinations = 320 different light chains If H and L chains pair randomly as H2L2 i.e. 10,530 x 320 = 3,369600 possibilities Due only to COMBINATORIAL diversity In practice, some H + L combinations do not occur as they are unstable Certain V and J g ...
... 40 Vk x 5 Jk = 200 combinations 30 Vl x 4 Jl = 120 combinations = 320 different light chains If H and L chains pair randomly as H2L2 i.e. 10,530 x 320 = 3,369600 possibilities Due only to COMBINATORIAL diversity In practice, some H + L combinations do not occur as they are unstable Certain V and J g ...
Import Settings
... C) constant pKs no matter what aqueous environment they are found in D) different pKs in peptides as compared to the free amino acids E) polar functional groups 19. Asx refers to A) a negatively charged aspartic acid B) a positively charged asparagine C) a dipeptide containing both aspartic acid and ...
... C) constant pKs no matter what aqueous environment they are found in D) different pKs in peptides as compared to the free amino acids E) polar functional groups 19. Asx refers to A) a negatively charged aspartic acid B) a positively charged asparagine C) a dipeptide containing both aspartic acid and ...
Poster
... • The cyclopropane ring is close to ParC residues on Ser79 and Asp83 • Resistance occurs with mutation of either residue • FQ resistance may be related to the octahedral coordination sphere • The most common mutations involve S79F and S79Y ...
... • The cyclopropane ring is close to ParC residues on Ser79 and Asp83 • Resistance occurs with mutation of either residue • FQ resistance may be related to the octahedral coordination sphere • The most common mutations involve S79F and S79Y ...
unit4geneticsandadvancesingeneticsnotes
... – Capable of replicating itself • one copy can pass from one bacterial cell to another, resulting in gene "sharing" among bacteria ...
... – Capable of replicating itself • one copy can pass from one bacterial cell to another, resulting in gene "sharing" among bacteria ...
14: The Eukaryotic Genome and Its Expression
... • Different cells in multicellular organisms produce some proteins found in all cell types, but also some that are unique to each cell type. • With few exceptions, all cells in an organism have the same genes or DNA sequences, but they express genes differently. • For example, both brain and liver c ...
... • Different cells in multicellular organisms produce some proteins found in all cell types, but also some that are unique to each cell type. • With few exceptions, all cells in an organism have the same genes or DNA sequences, but they express genes differently. • For example, both brain and liver c ...
The Organic Chemistry of Drug Design and Drug Action by
... N-7 of guanine > N-3 of adenine > N-7 of adenine > N-3 of guanine > N-1 of adenine > N-1 of cytosine N-3 of cytosine, the O-6 of guanine, and phosphate ...
... N-7 of guanine > N-3 of adenine > N-7 of adenine > N-3 of guanine > N-1 of adenine > N-1 of cytosine N-3 of cytosine, the O-6 of guanine, and phosphate ...
JMT Coffee
... simplex infections, or cold sores. They are called essential amino acids not because they are more important than other amino acids but because it is essential that they are included in the daily diet since they are not produced naturally by the body. ...
... simplex infections, or cold sores. They are called essential amino acids not because they are more important than other amino acids but because it is essential that they are included in the daily diet since they are not produced naturally by the body. ...
Overview of Basic Genetic Concepts and Terminology
... The subunits are called nucleotides which contain the nitrogenous bases There are four different nitrogenous bases, called adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). ...
... The subunits are called nucleotides which contain the nitrogenous bases There are four different nitrogenous bases, called adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). ...
DNA - Gene - Website Staff UI
... Is the heritable changes in the genetic material. The term mutation refers to (1) change in the genetic material, (2) the process by which the change occurs. Mutation provides the raw material for evolution. Without mutation, all of genes would exist in only one form and alleles would not exis. Orga ...
... Is the heritable changes in the genetic material. The term mutation refers to (1) change in the genetic material, (2) the process by which the change occurs. Mutation provides the raw material for evolution. Without mutation, all of genes would exist in only one form and alleles would not exis. Orga ...
ap® biology 2012 scoring guidelines - AP Central
... This question asked students to describe information flow within cells and organisms — specifically, the regulation of, and the effects of mutations on, protein synthesis. Part (a) required students to describe the role of three normal cellular processes or factors in the regulation of protein synth ...
... This question asked students to describe information flow within cells and organisms — specifically, the regulation of, and the effects of mutations on, protein synthesis. Part (a) required students to describe the role of three normal cellular processes or factors in the regulation of protein synth ...
Phylogenetic DNA profiling : a tool for the investigation of poaching
... procedure. Reactions were performed in a total volume of 25 µl using 1-10 ng template DNA. The final concentration of the components in reaction mix was as follows; 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.3), 50 mM KCl, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 0.25 µM each primer, 200 µM dNTP’s, 1 unit Taq polymerase (Life Technologies, Austral ...
... procedure. Reactions were performed in a total volume of 25 µl using 1-10 ng template DNA. The final concentration of the components in reaction mix was as follows; 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.3), 50 mM KCl, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 0.25 µM each primer, 200 µM dNTP’s, 1 unit Taq polymerase (Life Technologies, Austral ...
Biology Curriculum Pacing Guide and Study Guide
... Autosomal inheritance patterns and characteristics of sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, and Huntington’s disease Solve and interpret co-dominant crosses involving multiple alleles. A, B, AB and O blood types (alleles: IA, IB, and i). Determine if parentage is possible based on blood types. Some t ...
... Autosomal inheritance patterns and characteristics of sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, and Huntington’s disease Solve and interpret co-dominant crosses involving multiple alleles. A, B, AB and O blood types (alleles: IA, IB, and i). Determine if parentage is possible based on blood types. Some t ...
Official pGLO GFP powerpoint Spring 2005
... • Serves entire class of 32 students (up to 4 students per group) • Cost-effective • Success in student’s hands • Safe • Striking results! ...
... • Serves entire class of 32 students (up to 4 students per group) • Cost-effective • Success in student’s hands • Safe • Striking results! ...
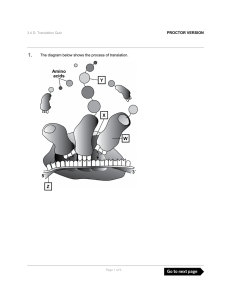
The diagram below shows the process of translation. PROCTOR
... that will be folded and moved to its final location in or out of the cell. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that polypeptides are synthesized based on the interaction of rRNA and tRNA molecules assembling specific amino acids into a chain, but does not understand ...
... that will be folded and moved to its final location in or out of the cell. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that polypeptides are synthesized based on the interaction of rRNA and tRNA molecules assembling specific amino acids into a chain, but does not understand ...
Aim #29: NYS Biodiversity Lab Review
... cuts between G and A State how many cuts will be made in the DNA sequences of each species when this enzyme is used. ...
... cuts between G and A State how many cuts will be made in the DNA sequences of each species when this enzyme is used. ...
Slide 1
... • A single strand of DNA whose sequence of bases is not known is placed in a test tube • DNA polymerase, the enzyme that copies DNA, and the four nucleotide bases, A, T, G, and C, are added to the test tube • As the enzyme goes to work, it uses the unknown strand as a template to make one new DNA st ...
... • A single strand of DNA whose sequence of bases is not known is placed in a test tube • DNA polymerase, the enzyme that copies DNA, and the four nucleotide bases, A, T, G, and C, are added to the test tube • As the enzyme goes to work, it uses the unknown strand as a template to make one new DNA st ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.