Review Sheet Answers
... 2. A group of different species that live in the same habitat and interact with each other 3. A group of organisms of the same species that live in a specific area and can interbreed 4. Environmental factor that is associated with or results from activities of living things 5. The part of the Earth ...
... 2. A group of different species that live in the same habitat and interact with each other 3. A group of organisms of the same species that live in a specific area and can interbreed 4. Environmental factor that is associated with or results from activities of living things 5. The part of the Earth ...
APES Fall Midterm (Chapters 1-5)
... 13. A species of bird had an original range covering the entire eastern half of the United States from New England down to Florida, west to the Rocky Mountains. During a period of glaciation, the eastern part of the range was cut off from the western part for 2000 years. Then the glaciers melted ...
... 13. A species of bird had an original range covering the entire eastern half of the United States from New England down to Florida, west to the Rocky Mountains. During a period of glaciation, the eastern part of the range was cut off from the western part for 2000 years. Then the glaciers melted ...
Ch. 4 Ecology
... Define key ecological concepts • Left side – make a list of biotic and abiotic factors that might impact a rainforest ecosystem. Read the story a hike through the rainforest. Pick one living thing from the story and describe it’s niche, and habitat, describe what other organisms it might be in compe ...
... Define key ecological concepts • Left side – make a list of biotic and abiotic factors that might impact a rainforest ecosystem. Read the story a hike through the rainforest. Pick one living thing from the story and describe it’s niche, and habitat, describe what other organisms it might be in compe ...
Species Related Terms and Concepts
... Grasshopper (Locust), Pink Bullworm, Brown Planthoppers, Aphids. ...
... Grasshopper (Locust), Pink Bullworm, Brown Planthoppers, Aphids. ...
Section: 2.4 Name: Section Title: Ecology
... a) close to the equator. c) far from the equator. b) with small islands. d) with low community stability. Match the types of species reactions with their characteristics in Numbers 21-25. 4) _____Similar to predation, but does not result in immediate death of host. 5) _____Relationship where one spe ...
... a) close to the equator. c) far from the equator. b) with small islands. d) with low community stability. Match the types of species reactions with their characteristics in Numbers 21-25. 4) _____Similar to predation, but does not result in immediate death of host. 5) _____Relationship where one spe ...
APES Alec Humphries Chapter 8 Guided Reading 1: Explain how
... 1: Define and give an example of each of the following: * Convergent Evolution The independent evolution of similar features in species of different lineages. Ex: wings, birds have different kinds of them but some cannot fly. * Divergent Evolution The accumulation of differences between groups which ...
... 1: Define and give an example of each of the following: * Convergent Evolution The independent evolution of similar features in species of different lineages. Ex: wings, birds have different kinds of them but some cannot fly. * Divergent Evolution The accumulation of differences between groups which ...
Ecology
... behavioral mechanisms of organisms to understand their ecological relationships • Animals in nature coexist with others of the same species as reproductive units are called populations – Population has properties that cannot be discovered by studying individuals alone • Populations of many species l ...
... behavioral mechanisms of organisms to understand their ecological relationships • Animals in nature coexist with others of the same species as reproductive units are called populations – Population has properties that cannot be discovered by studying individuals alone • Populations of many species l ...
Population Ecology - Verona Public Schools
... Species: Genetically similar organisms that can reproduce and produce fertile offspring Members of a species may not all live in the same place. Field mice in Maine will not interact with field mice in Texas. However, each organism lives as part of a population. Populations are groups of organisms o ...
... Species: Genetically similar organisms that can reproduce and produce fertile offspring Members of a species may not all live in the same place. Field mice in Maine will not interact with field mice in Texas. However, each organism lives as part of a population. Populations are groups of organisms o ...
Community Ecology
... • I can evaluate the claims, evidence and reasoning that the complex interactions in ecosystems maintain relatively consistent numbers and types of organisms in stable conditions, but changing conditions may result in a new ecosystem. ...
... • I can evaluate the claims, evidence and reasoning that the complex interactions in ecosystems maintain relatively consistent numbers and types of organisms in stable conditions, but changing conditions may result in a new ecosystem. ...
Introduction to Population Dynamics
... 2. Density-independent limiting factors control population size regardless of whether a population is large or small. a. examples: natural causes such as geothermal activity, extreme ...
... 2. Density-independent limiting factors control population size regardless of whether a population is large or small. a. examples: natural causes such as geothermal activity, extreme ...
Prelecture Chapter 53 - Seattle Central College
... a. only a single species of herbivore feeds on each plant species. b. local extinction of a species causes extinction of the other species in its food chain. c. most of the energy in a trophic level is lost as it passes to the next higher level. d. predator species tend to be less diverse and less a ...
... a. only a single species of herbivore feeds on each plant species. b. local extinction of a species causes extinction of the other species in its food chain. c. most of the energy in a trophic level is lost as it passes to the next higher level. d. predator species tend to be less diverse and less a ...
Populations: Extinctions and Explosions
... • A freak storm could kill most of the healthy females in a small population. • The next year most or all of the offspring could be males. • Alleles could be lost through genetic drift. • These effects would not be likely in a larger population ...
... • A freak storm could kill most of the healthy females in a small population. • The next year most or all of the offspring could be males. • Alleles could be lost through genetic drift. • These effects would not be likely in a larger population ...
Earth as a Living System
... 1: Plants and algae make their own food and are called primary producers. 2: Herbivores eat plants and are called primary consumers. 3: Carnivores which eat herbivores are called secondary consumers. 4: Carnivores which eat other carnivores are called tertiary consumers. 5: Apex predators which have ...
... 1: Plants and algae make their own food and are called primary producers. 2: Herbivores eat plants and are called primary consumers. 3: Carnivores which eat herbivores are called secondary consumers. 4: Carnivores which eat other carnivores are called tertiary consumers. 5: Apex predators which have ...
Plant Ecology 101 in 5 minutes - Rutgers Environmental Stewards
... The set of parameters or environmental conditions a species need to live or the conditions outside of which it cannot survive. Typically temperature, water, food, reproductive needs, etc. Specialists and Generalists Generalists is the term given to species whose evolution has adapted them to survive ...
... The set of parameters or environmental conditions a species need to live or the conditions outside of which it cannot survive. Typically temperature, water, food, reproductive needs, etc. Specialists and Generalists Generalists is the term given to species whose evolution has adapted them to survive ...
Human Ecology Lecture 1
... leaving only 10% of it to be incorporated by the next trophic level. ...
... leaving only 10% of it to be incorporated by the next trophic level. ...
Understanding populations
... • Simply put: a population that grows at a fixed percentage each year. • = constant rate ...
... • Simply put: a population that grows at a fixed percentage each year. • = constant rate ...
Unit 5
... Ecology is basically the study of their interactions between organisms and their environment, when in the other hand evolution relates to the changes that have transformed life on earth. 3. Explain the importance of temperature, water, light, soil, and wind to living organisms. These are abiotic org ...
... Ecology is basically the study of their interactions between organisms and their environment, when in the other hand evolution relates to the changes that have transformed life on earth. 3. Explain the importance of temperature, water, light, soil, and wind to living organisms. These are abiotic org ...
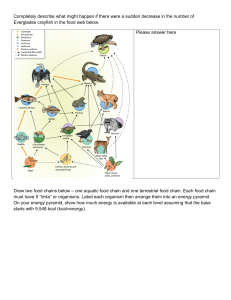
Completely describe what might happen if there were a sudden
... 2. The lowest level of environmental complexity that includes living and nonliving factors is the a. biome. b. community. c. ecosystem. d. biosphere. ...
... 2. The lowest level of environmental complexity that includes living and nonliving factors is the a. biome. b. community. c. ecosystem. d. biosphere. ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.