PP Notes DNA continued
... 5. What are the main differences between DNA and RNA. DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose; DNA has 2 strands, RNA has one strand; DNA has thymine, RNA has uracil. 6. Using the chart on page 303, identify the amino acids coded for by these codons: UGGCAGUGC tryptophan-glutamine-cysteine ...
... 5. What are the main differences between DNA and RNA. DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose; DNA has 2 strands, RNA has one strand; DNA has thymine, RNA has uracil. 6. Using the chart on page 303, identify the amino acids coded for by these codons: UGGCAGUGC tryptophan-glutamine-cysteine ...
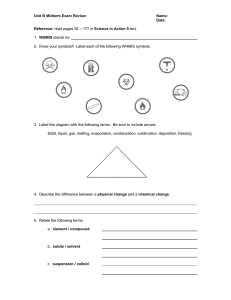
Molar Heat of Reaction
... dissolving one mole of solute in the solvent (which is usually water) Expressed in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) of dissolved solute In this reaction heat can be either released or absorbed ...
... dissolving one mole of solute in the solvent (which is usually water) Expressed in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) of dissolved solute In this reaction heat can be either released or absorbed ...
Chemistry Unit Review
... 16. Write chemical formula equations for the following. a. zinc and hydrochloric acid are added together to produce hydrogen gas and zinc chloride ...
... 16. Write chemical formula equations for the following. a. zinc and hydrochloric acid are added together to produce hydrogen gas and zinc chloride ...
Lecture 6, Exam III Worksheet Answers
... 2. Missense mutation- usually causes only minimal damage. These usually change one amino acid into another amino acid; the new a.a. may have properties similar to the first or it may not affect the total protein structure. 3. Nonsense mutation- often lethal. This mutation changes a base pair that re ...
... 2. Missense mutation- usually causes only minimal damage. These usually change one amino acid into another amino acid; the new a.a. may have properties similar to the first or it may not affect the total protein structure. 3. Nonsense mutation- often lethal. This mutation changes a base pair that re ...
Biol 1406 Ch 5
... vii) Know the differences structurally, and functionally, of lipids. Are there also ...
... vii) Know the differences structurally, and functionally, of lipids. Are there also ...
Lecture 5 & 6 Metabolism S11 Chpt. 6 for HO
... 12 pairs of electrons (snatched by electron carriers) Glucose →→→→→→→6 CO2 ...
... 12 pairs of electrons (snatched by electron carriers) Glucose →→→→→→→6 CO2 ...
Syllabus of the International Chemistry Olympiad
... unravelled, how aspects of green chemistry can be treated more quantitatively, how detergents aggregate to give micelles, how a hard coating can be made, and how fuel cells can produce electricity. In the practical problems microscale equipment will be used. The synthesis of some organic compounds, ...
... unravelled, how aspects of green chemistry can be treated more quantitatively, how detergents aggregate to give micelles, how a hard coating can be made, and how fuel cells can produce electricity. In the practical problems microscale equipment will be used. The synthesis of some organic compounds, ...
Chemistry Notes with Blanks
... The combination of carbon and water contains the same _________ as sugar. Elements: can’t be broken into _________ substances (atoms.) (Carbon is an element) Sugar + water…would you drink this? Ash + water…would you drink this? Why? They contain the same elements don’t they? Why don’t you get sugar ...
... The combination of carbon and water contains the same _________ as sugar. Elements: can’t be broken into _________ substances (atoms.) (Carbon is an element) Sugar + water…would you drink this? Ash + water…would you drink this? Why? They contain the same elements don’t they? Why don’t you get sugar ...
Enzymologie. Jak pracují enzymy
... 2) Alcoholic substrate changes OH- coupled with Zn2+ reorganisation of bonds and E-NADH- aldehyd complex formations ...
... 2) Alcoholic substrate changes OH- coupled with Zn2+ reorganisation of bonds and E-NADH- aldehyd complex formations ...
Lecture6
... LIPIDS METABOLISM Series of reactions that occurs in the body are called pathways. They are processes by which the cell regulates itself, various myriad of enzymes that catalyse chemical reactions that take place in living celsl are referred to as metabolism. ...
... LIPIDS METABOLISM Series of reactions that occurs in the body are called pathways. They are processes by which the cell regulates itself, various myriad of enzymes that catalyse chemical reactions that take place in living celsl are referred to as metabolism. ...
Cq4 INVESTIGATOR Name Elisabeth Knust Address Max
... Freund’s complete, final boost: Freund’s incomplete ...
... Freund’s complete, final boost: Freund’s incomplete ...
Ch 8-10 Review Topics - Wahconah Science Department
... Stages of Cellular Respiration: Know where each stage occurs, what the reactants and products are for each. 1. Glycolysis You need to be able to 2. Pyruvate Oxidation and the Citric Acid Cycle (Kreb’s Cycle) identify the major 3. Oxidative Phosphorylation: ETC (chemiosmosis) components of each Ferme ...
... Stages of Cellular Respiration: Know where each stage occurs, what the reactants and products are for each. 1. Glycolysis You need to be able to 2. Pyruvate Oxidation and the Citric Acid Cycle (Kreb’s Cycle) identify the major 3. Oxidative Phosphorylation: ETC (chemiosmosis) components of each Ferme ...
Molecules of Life - Morgan Community College
... • Fats are constructed from two types of smaller molecules: glycerol and fatty acids • Glycerol is a three-carbon alcohol with a hydroxyl group attached to each carbon • A fatty acid consists of a carboxyl group attached to a long carbon skeleton ...
... • Fats are constructed from two types of smaller molecules: glycerol and fatty acids • Glycerol is a three-carbon alcohol with a hydroxyl group attached to each carbon • A fatty acid consists of a carboxyl group attached to a long carbon skeleton ...
Vicia species belonging to the subgenus Cracca are
... Adams & Crooks, 2002; Jang, Jun, Rue, Han, Park & Kim 2002). ...
... Adams & Crooks, 2002; Jang, Jun, Rue, Han, Park & Kim 2002). ...
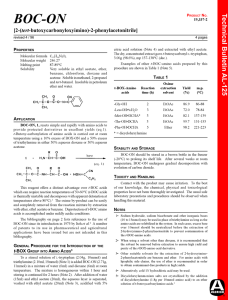
BOC-ON - Sigma
... This reagent offers a distinct advantage over t-BOC azide which can require reaction temperatures of 50-60°C (t-BOC azide is thermally unstable and decomposes with apparent detonation at temperatures above 80°C).1 The oxime by-product can be easily and completely removed from the reaction mixture by ...
... This reagent offers a distinct advantage over t-BOC azide which can require reaction temperatures of 50-60°C (t-BOC azide is thermally unstable and decomposes with apparent detonation at temperatures above 80°C).1 The oxime by-product can be easily and completely removed from the reaction mixture by ...
BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES
... The advanced course on Biological Macromolecules is an introduction to various aspects of structure and function of proteins, nucleic acids, and their complexes. The topics addressed are a selection of modern biophysical methods applied to current questions in macromolecular biochemistry. In particu ...
... The advanced course on Biological Macromolecules is an introduction to various aspects of structure and function of proteins, nucleic acids, and their complexes. The topics addressed are a selection of modern biophysical methods applied to current questions in macromolecular biochemistry. In particu ...
Discussion in Advanced Chemical Biology II
... excuse him/herself from the class before lecture starts, he/she has to provide a proof to the TA to explain his/her absence to the class.) Date ...
... excuse him/herself from the class before lecture starts, he/she has to provide a proof to the TA to explain his/her absence to the class.) Date ...
peran serta masyarakat dalam plh
... – Example: NAD+, NADP+, tetrahydrofolic acid dan thyamin pyrophosphate ...
... – Example: NAD+, NADP+, tetrahydrofolic acid dan thyamin pyrophosphate ...
Lecture 4 POWERPOINT here
... Saturated fats raise total blood cholesterol as well as LDL cholesterol (the bad cholesterol). Saturated fats are mainly found in animal products such as meat, dairy, eggs and seafood. Some plant foods are also high in saturated fats such as coconut oil, palm oil and palm kernel oil. ...
... Saturated fats raise total blood cholesterol as well as LDL cholesterol (the bad cholesterol). Saturated fats are mainly found in animal products such as meat, dairy, eggs and seafood. Some plant foods are also high in saturated fats such as coconut oil, palm oil and palm kernel oil. ...
File - Ms. Kenyon`s Class
... work so organisms cannot get much energy! (this is why humans & other organisms need O2!) ...
... work so organisms cannot get much energy! (this is why humans & other organisms need O2!) ...
August 19, 2002 - People
... (Alanine, Cysteine, …, Tyrosine) • Three bases --- a codon --- suffice to encode an amino acid, according to the genetic code. • There are also START and STOP codons. August 19, 2002 ...
... (Alanine, Cysteine, …, Tyrosine) • Three bases --- a codon --- suffice to encode an amino acid, according to the genetic code. • There are also START and STOP codons. August 19, 2002 ...
Relationship between Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... H+ ions must move back from a higher lower concentration Only return to inner compartment through ATP synthases, “gates of the dam” As they move through, activate ATP synthase to make ATP from ADP + Pi This process is called Chemiosmosis (ATP production linked to H+ gradient) ...
... H+ ions must move back from a higher lower concentration Only return to inner compartment through ATP synthases, “gates of the dam” As they move through, activate ATP synthase to make ATP from ADP + Pi This process is called Chemiosmosis (ATP production linked to H+ gradient) ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.