1. Given the following metabolic pathway (as it occurs in the cell): a
... of the organism under anaerobic and aerobic conditions, using glucose as the food source. a. How would lysine → arginine mutations affect the function of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex E2? Explain in 25 words or fewer. b. If your hypothesis is correct, how will the organism’s growth differ from norm ...
... of the organism under anaerobic and aerobic conditions, using glucose as the food source. a. How would lysine → arginine mutations affect the function of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex E2? Explain in 25 words or fewer. b. If your hypothesis is correct, how will the organism’s growth differ from norm ...
Molecular Evolution
... • Or almost the whole protein – Histone 4 – Almost all in contact with DNA or other proteins ...
... • Or almost the whole protein – Histone 4 – Almost all in contact with DNA or other proteins ...
The citric acid cycle is the
... • In 1935 in Hungary, Albert SzentGyörgyi was studying the oxidation of similar organic substrates by pigeon breast muscle. • he observed that addition of any of three four-carbon dicarboxylic acids— fumarate, succinate, or malate—caused the consumption of much more oxygen than was required for the ...
... • In 1935 in Hungary, Albert SzentGyörgyi was studying the oxidation of similar organic substrates by pigeon breast muscle. • he observed that addition of any of three four-carbon dicarboxylic acids— fumarate, succinate, or malate—caused the consumption of much more oxygen than was required for the ...
Q1. Lysozyme is an enzyme consisting of a single polypeptide chain
... In an investigation, a culture of Chlamydomonas was treated in a way that caused them to lose their flagella without any other damage to the cells. The flagella grew back to their original length in 60 minutes. How many amino acid molecules would be incorporated into each growing flagellum per minut ...
... In an investigation, a culture of Chlamydomonas was treated in a way that caused them to lose their flagella without any other damage to the cells. The flagella grew back to their original length in 60 minutes. How many amino acid molecules would be incorporated into each growing flagellum per minut ...
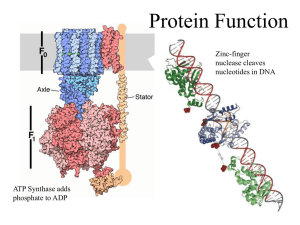
Protein Function - Gleason Chemistry
... Redox reaction: electron transfer Functional group transfer Hydrolysis (breaking) of various covalent bonds using water Cleavage or formation of double bonds without water ...
... Redox reaction: electron transfer Functional group transfer Hydrolysis (breaking) of various covalent bonds using water Cleavage or formation of double bonds without water ...
intermediary metabolism
... is controlled by the needs of the cell for energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. Thus cells conserve just enough nutrients to meet the energy utilization at any given time. Similarly the rate of biosynthesis of building block molecules and of cell macromolecules is also adjusted to immediate needs. M ...
... is controlled by the needs of the cell for energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. Thus cells conserve just enough nutrients to meet the energy utilization at any given time. Similarly the rate of biosynthesis of building block molecules and of cell macromolecules is also adjusted to immediate needs. M ...
8 Introduction to Metabolism Notes
... spontaneously, it must increase the entropy of the universe. C. Living systems create ordered structures from less ordered starting materials. For example, amino acids are ordered into polypeptide chains, and the structure of a multicellular body is organized and complex. ...
... spontaneously, it must increase the entropy of the universe. C. Living systems create ordered structures from less ordered starting materials. For example, amino acids are ordered into polypeptide chains, and the structure of a multicellular body is organized and complex. ...
File
... ways that do not normally occur in nature __________ selection: intentional reproduction of individuals in a population with a desired trait ...
... ways that do not normally occur in nature __________ selection: intentional reproduction of individuals in a population with a desired trait ...
Unit 3: Cellular Energetics
... Frogs of three different species were weighed and the amount of oxygen consumed by each species was determined by placing them in a respirometer for 1 hour. The results of this experiment are shown on the right. ...
... Frogs of three different species were weighed and the amount of oxygen consumed by each species was determined by placing them in a respirometer for 1 hour. The results of this experiment are shown on the right. ...
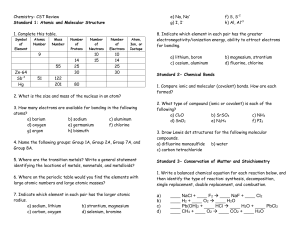
Chemistry- CST Review
... 8. If a sample of gas occupies 6.55 L at 300 °C, what will be its volume at 25 °C if the pressure does not change? 9. A gas at 790 mm Hg and 25 °C occupies a container with an initial volume of 1.20 L. By changing the volume, the pressure of the gas increases to 1500 mm Hg as the temperature is rais ...
... 8. If a sample of gas occupies 6.55 L at 300 °C, what will be its volume at 25 °C if the pressure does not change? 9. A gas at 790 mm Hg and 25 °C occupies a container with an initial volume of 1.20 L. By changing the volume, the pressure of the gas increases to 1500 mm Hg as the temperature is rais ...
Protein Synthesis Overview
... packaged) 1. Introns (interrupting sequences) removed 2. Exons spliced together 3. G3 Cap and PolyA Tail attached ...
... packaged) 1. Introns (interrupting sequences) removed 2. Exons spliced together 3. G3 Cap and PolyA Tail attached ...
Proteins
... phosphorus, and trace metals), proteins (which include all the essential amino acids), carbohydrates (chiefly lactose), and lipids. • The only important elements in which milk is seriously deficient are iron and Vitamin C. • Infants are usually born with a storage supply of iron large enough to meet ...
... phosphorus, and trace metals), proteins (which include all the essential amino acids), carbohydrates (chiefly lactose), and lipids. • The only important elements in which milk is seriously deficient are iron and Vitamin C. • Infants are usually born with a storage supply of iron large enough to meet ...
05. Metabolism of carbohydrates 1
... enzyme lactase, which cleaves lactose into glucose and galactose. Microorganisms in the colon ferment undigested lactose to lactic acid generating methane (CH4) and hydrogen gas (H2). The gas produced creates the uncomfortable feeling of gut distention and the annoying problem of flatulence. The lac ...
... enzyme lactase, which cleaves lactose into glucose and galactose. Microorganisms in the colon ferment undigested lactose to lactic acid generating methane (CH4) and hydrogen gas (H2). The gas produced creates the uncomfortable feeling of gut distention and the annoying problem of flatulence. The lac ...
Introduction to Metabolism Notes
... spontaneously, it must increase the entropy of the universe. C. Living systems create ordered structures from less ordered starting materials. For example, amino acids are ordered into polypeptide chains, and the structure of a multicellular body is organized and complex. ...
... spontaneously, it must increase the entropy of the universe. C. Living systems create ordered structures from less ordered starting materials. For example, amino acids are ordered into polypeptide chains, and the structure of a multicellular body is organized and complex. ...
Classification of Microorganisms
... • Not part of either domains • Not composed of cells • Use anabolic machinery within host cell to multiply • Viral genome can direct biosynthesis inside a cell • Some can be incorporated into the host’s genome • Virus is more closely related to its host than to other virus • Viral species- morpholog ...
... • Not part of either domains • Not composed of cells • Use anabolic machinery within host cell to multiply • Viral genome can direct biosynthesis inside a cell • Some can be incorporated into the host’s genome • Virus is more closely related to its host than to other virus • Viral species- morpholog ...
Poster - Department of Computer Science
... Figure 5: Process flow of the design and development of 3DIGARS3.0 energy function. ...
... Figure 5: Process flow of the design and development of 3DIGARS3.0 energy function. ...
Free Energy and Enzymes (Chapter 6) Outline Growing Old With
... substances can bind to alter enzyme activity; if this control substance is the end product in the enzyme's metabolic pathway, feedback inhibition occurs. ...
... substances can bind to alter enzyme activity; if this control substance is the end product in the enzyme's metabolic pathway, feedback inhibition occurs. ...
What is RNA? - Biology for Life
... Four processes were needed for the spontaneous origin of life on Earth: 1. Non-living synthesis of simple organic molecules 2. Assembly of these molecules into polymers 3. Origin of self replicating molecules that made inheritance possible 4. Packaging of these molecules into membranes with an inter ...
... Four processes were needed for the spontaneous origin of life on Earth: 1. Non-living synthesis of simple organic molecules 2. Assembly of these molecules into polymers 3. Origin of self replicating molecules that made inheritance possible 4. Packaging of these molecules into membranes with an inter ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.