Figures from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology
... different proteins varies tremendously. • Proteins with short life-spans, that are misfolded, or that become oxidized must be destroyed and recycled by the cell. Enzymes that degrade proteins are called proteases. They are hydrolytic enzymes. Most large cytosolic proteins in eukaryotes are degraded ...
... different proteins varies tremendously. • Proteins with short life-spans, that are misfolded, or that become oxidized must be destroyed and recycled by the cell. Enzymes that degrade proteins are called proteases. They are hydrolytic enzymes. Most large cytosolic proteins in eukaryotes are degraded ...
Introduction to Carbohydrates
... synthesized by transfer of an amino group to the α-keto acids pyruvate, oxaloacetate, and αketoglutarate, respectively. • These transamination reactions (Figure 20.12, and see p. 250) are the most direct of the biosynthetic pathways. • Glutamate is unusual in that it can also be synthesized by the r ...
... synthesized by transfer of an amino group to the α-keto acids pyruvate, oxaloacetate, and αketoglutarate, respectively. • These transamination reactions (Figure 20.12, and see p. 250) are the most direct of the biosynthetic pathways. • Glutamate is unusual in that it can also be synthesized by the r ...
Chapter 8
... Translation [of mRNA codons to protein] Experiments during the 1960s demonstrated that the DNA code was a three-base code. The three-base code in DNA or mRNA is called a codon. ...
... Translation [of mRNA codons to protein] Experiments during the 1960s demonstrated that the DNA code was a three-base code. The three-base code in DNA or mRNA is called a codon. ...
You Light Up My Life
... fatty acids • Glycerol is converted to PGAL, an intermediate of glycolysis • Fatty acids are broken down and converted to acetyl-CoA, which enters Krebs cycle ...
... fatty acids • Glycerol is converted to PGAL, an intermediate of glycolysis • Fatty acids are broken down and converted to acetyl-CoA, which enters Krebs cycle ...
6.3 Defense against infectious disease
... after digestion, polysaccharides are broken down into monosaccharides, polypeptides are broken down into amino acids, and lipids are broken down into glycerol and fatty acids monomers, such as monosaccharides, amino acids, glycerol, and fatty acids are small enough to be absorbed by small intest ...
... after digestion, polysaccharides are broken down into monosaccharides, polypeptides are broken down into amino acids, and lipids are broken down into glycerol and fatty acids monomers, such as monosaccharides, amino acids, glycerol, and fatty acids are small enough to be absorbed by small intest ...
Supplement 2
... SDS-PAGE analysis showed that the plasmids expressed corresponding sizes of recombinant proteins (SFig. 2a). SFig. 2b illustrates the amino acid sequences of the 4 recombinant fragments deduced from DNA sequencing after cloning into the vectors. 3. Discussion and Conclusion By successfully cloning a ...
... SDS-PAGE analysis showed that the plasmids expressed corresponding sizes of recombinant proteins (SFig. 2a). SFig. 2b illustrates the amino acid sequences of the 4 recombinant fragments deduced from DNA sequencing after cloning into the vectors. 3. Discussion and Conclusion By successfully cloning a ...
8/27/08 Transcript I
... acid, which in never found inside cells, because it is furnished into another fatty acid and then others, finally into C16 which will diffuse ...
... acid, which in never found inside cells, because it is furnished into another fatty acid and then others, finally into C16 which will diffuse ...
Unit 1 PPT 3 (2biii-iv Binding and conformation)
... Think • How is protein production controlled? • Why is it important that protein production is controlled? • Why is protein structure important in relation to its function? ...
... Think • How is protein production controlled? • Why is it important that protein production is controlled? • Why is protein structure important in relation to its function? ...
Exam2key - Biology Courses Server
... 15. (6 pts) tRNA translates the sequences of ribonucleotides in _mRNA________ into the sequence of __amino acids_______ ________ in proteins. tRNA binds both the large and small subunit of the _ribosome__________. The two most important regions of the tRNA are the _acceptor____________ stem at the _ ...
... 15. (6 pts) tRNA translates the sequences of ribonucleotides in _mRNA________ into the sequence of __amino acids_______ ________ in proteins. tRNA binds both the large and small subunit of the _ribosome__________. The two most important regions of the tRNA are the _acceptor____________ stem at the _ ...
Nature of Molecules and Water
... • Form when atoms share 2 or more valence electrons • Strength of covalent bond depends on the number of shared electrons • Many biological compounds are composed of more than 2 atoms – may share electrons with 2 or more atoms ...
... • Form when atoms share 2 or more valence electrons • Strength of covalent bond depends on the number of shared electrons • Many biological compounds are composed of more than 2 atoms – may share electrons with 2 or more atoms ...
metabole = change
... -increase the stability of the system Nonpontaneous change/reaction: -can occur only if energy is added to the system -decrease the stability of the system ...
... -increase the stability of the system Nonpontaneous change/reaction: -can occur only if energy is added to the system -decrease the stability of the system ...
Project Presentation
... 2. Generate lipid membrane, position protein on membrane 3. Solvate (immerse in water) the protein 4. Create batch files that tell supercomputer what to do ...
... 2. Generate lipid membrane, position protein on membrane 3. Solvate (immerse in water) the protein 4. Create batch files that tell supercomputer what to do ...
Introduction to Chemical Equations
... • You may NOT change any subscripts in any of the reactant’s or product’s formulas ...
... • You may NOT change any subscripts in any of the reactant’s or product’s formulas ...
Complete amino acid sequence of bovine colostrum lowM r cysteine
... The complete amino acid sequence of bovine colostrum cysteine proteinase inhibitor was determined by sequencing native inhibitor and peptides obtained by cyanogen bromide degradation, Achromobacter lysylendopeptidase digestion and partial acid hydrolysis of reduced and S-carboxymethylated protein. A ...
... The complete amino acid sequence of bovine colostrum cysteine proteinase inhibitor was determined by sequencing native inhibitor and peptides obtained by cyanogen bromide degradation, Achromobacter lysylendopeptidase digestion and partial acid hydrolysis of reduced and S-carboxymethylated protein. A ...
Slide 1
... form of starch. Oxygen is released in this process. Equation of photosynthesis :Sunlight 6CO2 + 12H2O C6H12O6 + 6H2O + 6O2 Chlorophyll Process of photosynthesis :Photosynthesis takes place in three main steps. They are :i) Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll. ii) Conversion of light energy int ...
... form of starch. Oxygen is released in this process. Equation of photosynthesis :Sunlight 6CO2 + 12H2O C6H12O6 + 6H2O + 6O2 Chlorophyll Process of photosynthesis :Photosynthesis takes place in three main steps. They are :i) Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll. ii) Conversion of light energy int ...
3. Machinery of a factory: The cell
... 3.6.2 ATP is needed for cell division. DNA is in the nucleus. During growth, each of our chromosomes containing DNA gets replicated and the cell divides to make a new cell. Many cells and proteins are as old as we are. The proteins that are in the center of your eye lens are as old as you are. Some ...
... 3.6.2 ATP is needed for cell division. DNA is in the nucleus. During growth, each of our chromosomes containing DNA gets replicated and the cell divides to make a new cell. Many cells and proteins are as old as we are. The proteins that are in the center of your eye lens are as old as you are. Some ...
Intermediate 1 Chemistry - Deans Community High School
... Fill in the blanks below using the previous slide to help you. Copper, carbon and oxygen will make ________ _________ Lithium, sulphur and oxygen will make ________ _________ ...
... Fill in the blanks below using the previous slide to help you. Copper, carbon and oxygen will make ________ _________ Lithium, sulphur and oxygen will make ________ _________ ...
Chapter 6 Microbial Genetics
... binds to the second code word on mRNA. A peptide bond forms between the two amino acids. The first tRNA leaves, and the enzyme translocase moves the ribosome down one code word of mRNA at a time. This repeats ~ 300X. ...
... binds to the second code word on mRNA. A peptide bond forms between the two amino acids. The first tRNA leaves, and the enzyme translocase moves the ribosome down one code word of mRNA at a time. This repeats ~ 300X. ...
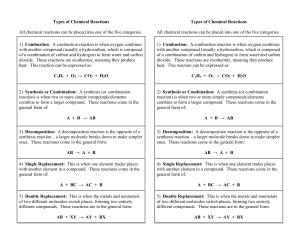
Types of Chemical Reactions
... of a combination of carbon and hydrogen) to form water and carbon dioxide. These reactions are exothermic, meaning they produce heat. This reaction can be expressed as: ...
... of a combination of carbon and hydrogen) to form water and carbon dioxide. These reactions are exothermic, meaning they produce heat. This reaction can be expressed as: ...
Notes from Dr
... breakdown products of the first two stages and passes them to one molecule after another. At the end of the chain, the electrons are combined with molecular oxygen and hydrogen ions where they form water. The energy released at each step of the chain is stored in a form the mitochondrion can use to ...
... breakdown products of the first two stages and passes them to one molecule after another. At the end of the chain, the electrons are combined with molecular oxygen and hydrogen ions where they form water. The energy released at each step of the chain is stored in a form the mitochondrion can use to ...
CRACKING THE GENETIC CODE
... After binding of the mRNA and the amino-acylated tRNA to the ribosome, a peptide bond forms between the amino acids, beginning protein synthesis. The nascent protein chain is elongated by the subsequent binding of additional tRNAs and formation of a peptide bond between the incoming amino acid and t ...
... After binding of the mRNA and the amino-acylated tRNA to the ribosome, a peptide bond forms between the amino acids, beginning protein synthesis. The nascent protein chain is elongated by the subsequent binding of additional tRNAs and formation of a peptide bond between the incoming amino acid and t ...
The respiratory system
... The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells. ...
... The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells. ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.