* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intermediate 1 Chemistry - Deans Community High School
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Liquid–liquid extraction wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Biological aspects of fluorine wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Alkaline earth metal wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Nitric acid wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Acid dissociation constant wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Acid strength wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
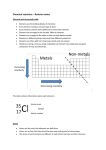
Intermediate 1 Chemistry S3 Revision Atoms and Elements Elements If a solid, liquid or gas is made up of only one type of atom we say it is an element. For example, consider a tripod made up of iron: These atoms are ALL iron – there’s nothing else in here The structure of the atom The Ancient Greeks used to believe that everything was made up of very small particles. I did some experiments in 1808 that proved this and called these particles ATOMS: Dalton NEUTRON – neutral, same mass as proton (“1”) PROTON – positive, same mass as neutron (“1”) ELECTRON – negative, mass nearly nothing Atoms and charges #1 Protons have a __________ charge Electrons have a ___________ charge Neutrons don’t have a charge So if an atom contains charged particles then why is the total charge on an atom always zero??????????? Atoms and Atomic number The atomic number of an element always tells us the number of _________ in the nucleus of each atom. We can find the atomic number on most _________ _________. As we go across a row from left to right the atomic number goes up by ______. Atoms and Atomic number #2 The atomic number for lithium is _____ The atomic number for carbon is _____ The atomic number for iodine is _____ The atomic number for copper is _____ The atomic number for tin is _____ A boron atom has ____ protons in its nucleus. A calcium atom has ____ protons in its nucleus. A gallium atom has ____ protons in its nucleus. A uranium atom has ____ protons in its nucleus. An oxygen atom has ____ protons in its nucleus. Periodic table The periodic table arranges all the elements in groups according to their properties. Vertical columns are called GROUPS Mendeleev Horizontal rows are called PERIODS The Periodic Table Fact 3: Most of the elements are metals: These elements are metals H e H Li B e B C N O F N e N a M g Al Si P S Cl Ar K C a Fe Ni C u Zn A g A This line divides Pt metals from non-u metals Br Kr I H g Xe These elements are non-metals The Periodic Table Fact 4: (Most important) All of the elements in the same group have similar PROPERTIES. H e H Li B e B C N O F N e N a M g Al Si P S Cl Ar K C a Fe Ni C u Zn Br Kr E.g. consider the group 1 metals. They all: A g 1) Are soft 2) Can be easily Pt cut 3) React with water A H with u ga I knife Xe Group 1 – The alkali metals Li Na K Rb Cs Fr Group 0 (or 8) – The Noble gases He Ne Ar Kr Xe Rn Group 0 – The Noble gases Some facts… 1) All of the noble gases have a full outer shell, so they are very _____________ 2) They all have low melting and boiling points 3) Helium is lighter then air and is used in balloons and airships (as well as for talking in a silly voice) 4) Argon is used in light bulbs (because it is so unreactive) and argon , krypton and neon are used in fancy lights Group 7 – The halogens F Cl Br I At Compounds Compounds Compounds are different to elements. They contain different types of atoms joined together. Here are some examples: Glucose Methane Sodium chloride (salt) Some simple compounds… Methane, CH4 Water, H2O Carbon dioxide, CO2 Key Hydrogen Ethyne, C2H2 Oxygen Sulphuric acid, H2SO4 Carbon Sulphur Covalent Compounds • Covalent bonds only appear in non-metal compounds like water (H2O) and Carbon dioxide(CO2) • The compounds are also known as molecules and the covalent bonds are very strong between the non-metal atoms. • Between all the molecules there is weak forces holding them together. Covalent Compounds • Covalent Water Molecules (H2O) weak bond O atom H H O H atom Strong covalent bond H atom O H H Ions in Compounds • Ions are charged particles which are contained in ionic compounds. • Ions can be either positively charged (+) or negatively charged (-) • Ions are attracted to each other and form very strong bonds. Ions in compounds • Ionic Compound ions Strong bonds Naming compounds Fill in the blanks below using the table on the previous slide to help you. Copper and chlorine will make ________ _________ Iron and sulphur will make ________ _________ Magnesium and oxygen will make ________ _________ Calcium and fluorine will make ________ _________ _________ and ________ will make barium nitride Naming compounds Fill in the blanks below using the previous slide to help you. Copper, carbon and oxygen will make ________ _________ Lithium, sulphur and oxygen will make ________ _________ Calcium, nitrogen and oxygen will make _______ _________ Potassium, carbon and oxygen will make _______ ________ _______, _______ and _______ will make silver nitrate Before Mixtures After Element, mixture or compound? Salty water Hydrogen Hydrochloric acid Air Diamond Sodium chloride (salt) Elements, compounds or mixture Decide whether each of the samples is an element, mixture or compound. Salt water = _____________ Hydrogen = _____________ Hydrochloric acid = _____________ Air = _____________ Diamond = _____________ Salt = _____________ Solutions and separating Dissolving things – some meanings If a substance CAN be dissolved it is __________ If a substance CANNOT be dissolved it is _________ Words – soluble, solute, solvent, solution, insoluble Distillation - separating liquids Distillation can be used to separate water and ethanol because they have different _______ ______. The ______ will boil first, then turn back into a _______ in the condenser and collect in the _______. The water will stay in the round flask, as long as the _______ does not go above ______OC. Distillation is used to separate crude _______ into useful fuels like petrol. Words – 100, temperature, oil, boiling points, ethanol, beaker, liquid Separating mixtures summary 1) A mixture containing a solid and a liquid can be separated using __________ 2) A mixture of liquids with different boiling points can be separated using _________ 3) A mixture of different inks can be separated using _______ 4) Water can be removed from a solution by ___________ 5) Separation methods are _____ chemical reactions because a _____ substance is not being made. Distillation, not, chromatography, new, evaporation or filtration Saturated solutions Consider our previous work on solutions: Clearly, there is only so much solute a solution can take… A mixture that cannot take any more solute is called a “saturated solution” Solubility words Draw lines to match up the words to their meanings. One has already been done for you. Something that CAN dissolve is described as being… Solute How much of something that can be dissolved is called… Solution Something that CANNOT be dissolved is described as being… Solvent A solution that CAN’T dissolve anything else is… Soluble The solid that will be dissolved is the… The mixture of solute and solvent is called the… The liquid that the solute will be dissolved into is the… Insoluble Saturated Solubility Chemical Reactions Testing for oxygen Oxygen will make a glowing splint _______ Testing for hydrogen Hydrogen makes a ___________ splint go _______. “POP” Testing for carbon dioxide Carbon dioxide Gas Limewater Carbon dixoide makes ___________ go __________ Adding acids to metals Some metals react with acids to produce ________ gas. The gas will make the mixture _______ and the metal will eventually be _______ _____. Some metals, like _______ and _______, are so unreactive that nothing will happen. Words – gold, hydrogen, bubble, copper, used up Adding acid to carbonates Carbonates are compounds that react with acids to make _________ __________ gas. This makes the mixture _________. When all of the carbonate is used up the _________ will stop. Limewater goes cloudy Carbonates used to be used as building materials but aren’t any more because acid rain would eventually ________ the building. Words – dissolve, bubble, carbon dioxide, bubbles Acids and Alkalis Name_____________________ Universal Indicator and the pH scale Universal Indicator changes colour depending on whether it is in an acid, alkali or neutral solution. 1 2 3 Stomach acid 4 5 6 Lemon juice 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Water Soap Baking powder Oven cleaner Below 7 is _____ Above 7 is _________ Exactly 7 is _________ Quiz on acids and alkalis Acid, alkali or both??? 1) This has pH of less than 7 ____________ 2) This is often used in cleaners or soap __________ 3) This would turn Universal Indicator red ________ 4) Sodium hydroxide is an ____________ 5) This would feel soapy on your skin _________ 6) This could burn your skin _________ 7) This will turn universal indicator purple _________ 8) Lemon juice and vinegar are examples of weak _______ 9) limewater (calcium hydroxide) is an example of this__________ Neutralisation An acid and alkali will cancel each other out (neutralise) each other if the correct amounts are used Acid + alkali Salt + water E.g. hydrochloric acid + sodium hydroxide sodium chloride + water This reaction is called ________________ because the acid is used up and _________ is made. Choose your answers from the list below: combustion respiration neutralisation hydrogen water oxygen Complete the blank spaces Adding sodium hydroxide to hydrochloric acid will make water and a salt called sodium _________. Adding sodium hydroxide to nitric acid will make water and a salt called sodium _________. Adding potassium hydroxide to sulphuric acid will make water and a salt called _________ _________. Adding magnesium hydroxide to hydrochloric acid will make water and a salt called _________ _________. Adding lithium hydroxide to sulphuric acid will make water and a salt called _________ _________. Adding acid to carbonates Carbonates are compounds containing carbon and oxygen. When an acid and a carbonate are added together, the mixture starts to fizz. A gas called _________ _________ is produced. The limewater will go __________ Complete the blanks spaces Adding sodium carbonate to hydrochloric acid will make carbon dioxide, water and a salt called _________ _________. Adding sodium carbonate to nitric acid will make carbon dioxide, water and a salt called __________ _________. Adding potassium carbonate to sulphuric acid will make carbon dioxide, water and a salt called ___________ _________. Adding magnesium carbonate to hydrochloric acid will make carbon dioxide, water and a salt called ___________ _________. Adding copper carbonate to sulphuric acid will make carbon dioxide, water and a salt called _________ _________. Reactions of metals with acids When a metal reacts with an acid a gas called ______________ is made. A salt is also made at the same time. METAL + ACID SALT + ____________ The name of the salt depends on the metal and the acid. e.g. magnesium + hydrochloric acid magnesium chloride + hydrogen Complete the following reactions: Calcium + hydrochloric acid _________ ________ + __________ Zinc + hydrochloric acid _________ ________ + __________ Iron + nitric acid _________ ________ + __________ Lithium + sulphuric acid _________ ________ + __________ These reactions are not neutralisation because _________ is not being made. Useful acid-alkali reactions 1) Hydrochloric acid is used in the stomach to help digest food. If we eat too many “rich” foods our stomachs make too much ______. This is called _____________. Indigestion tablets take away this pain because they ______________ the acid. 2) Soil is often acidic, mainly due to acid ____. This can have bad effects on ______ and vegetable growth. ________ is an alkali that farmers and gardners add to soil to _________ the acid. Words – plant, indigestion, neutralise, rain, acid, neutralise, lime Uses of acid reactions When acids react new chemicals called salts are made. These salts have many uses. Sodium chloride is the chemical name for table salt that we put on our chips. Salts that are made from nitric acid contain nitrate. Nitrates are needed by plants to help them grow. Chemical companies use nitric acid to make nitrate salts for farmers to use as fertilisers for their crops. Nitrate salts are also used in explosives. Acid gases The names of three acid gases are: _________ _________ _________ _________ _________ _________ When fossil fuels like coal, _____ or natural _____ are burned in power stations, the carbon contained in them reacts with oxygen to form ___________ dioxide gas. Carbon dioxide also comes out of car exhausts. A car engine needs a spark to set the petrol on fire. The energy from the spark makes nitrogen and oxygen join together to make the acid gas called__________ dioxide gas. Some fossil fuels contain sulphur. When the fuel burns, the acid gas called _________dioxide is made. Problems with acid gases The acid gases called _________ dioxide, _________ dioxide and _______ dioxide dissolve in cloud droplets and fall as _____ ______. The acid rain gets into rivers and streams and kills ______. It can kill ______ when it falls onto their leaves. Acid rain can also damage stone buildings and metal structures because it reacts and eats them away. The reactivity series of metals Metals with oxygen When a metal is heated with oxygen it will glow and turn into a METAL OXIDE. . The colour and brightness of the glow can tell us about how reactive the metal is. Metal Magnesium Observation Very bright white glow Copper Dull red glow Iron Bright red glow The order of reactivity most to least is ____________ then ____________ then ____________. Order of reactivity To work out which metals were more reactive than others the number of bubbles made in one minute were counted. Magnesium made 28 bubbles in one minute Tin made 10 bubbles in one minute Zinc made 17 bubbles in one minute Copper made 0 bubbles in one minute Calcium made 34 bubbles in one minute Aluminium made 23 bubbles in one minute Iron made 13 bubbles in one minute Reactivity series so far A reactivity series of a list of metals in order of how _________ they are. The ________ reactive metal goes at the top of the list. Most ____________ Put these lithium reactive metals in magnesium order of reactivity: copper iron ____________ ____________ ____________ calcium ____________ tin ____________ sodium ____________ aluminium ____________ potassium ____________ zinc Least ____________ reactive Reactions of Metals You need to know 3 reactions of metals: METAL + OXYGEN eg magnesium + oxygen METAL + WATER eg calcium + water METAL OXIDE magnesium oxide METAL HYDROXIDE + HYDROGEN calcium hydroxide + hydrogen METAL + ACID e.g. magnesium + hydrochloric acid SALT + HYDROGEN magnesium chloride + hydrogen Complete the following reactions: 1) Lithium + water _______ _______ + _________ 2) Lithium + hydrochloric acid _______ _______ + _________ 3) Silver + oxygen _______ _______ 4) tin + hydrochloric acid _______ _______ + _________ 5) Potassium + oxygen _______ _______ 6) Aluminium + oxygen _______ _______ 7) Magnesium + water _______ _______ + _________ 8) zinc + hydrochloric acid _______ _______ + _________ 9) Lithium + oxygen _______ _______ 10) calcium + hydrochloric acid _______ _______ + _________