chapter 4 types of chemical reactions and solution stoichiometry
... a. The species reduced is the element that gains electrons. The reducing agent causes reducduction to occur by itself being oxidized. The reducing agent generally refers to the entire formula of the compound/ion that contains the element oxidized. b. The species oxidized is the element that loses el ...
... a. The species reduced is the element that gains electrons. The reducing agent causes reducduction to occur by itself being oxidized. The reducing agent generally refers to the entire formula of the compound/ion that contains the element oxidized. b. The species oxidized is the element that loses el ...
chapter 4 types of chemical reactions and solution stoichiometry
... a. The species reduced is the element that gains electrons. The reducing agent causes reduction to occur by itself being oxidized. The reducing agent generally refers to the entire formula of the compound/ion that contains the element oxidized. b. The species oxidized is the element that loses elect ...
... a. The species reduced is the element that gains electrons. The reducing agent causes reduction to occur by itself being oxidized. The reducing agent generally refers to the entire formula of the compound/ion that contains the element oxidized. b. The species oxidized is the element that loses elect ...
as a PDF
... eight elements within its compass (S.A. Cotton and F.A. Hart, The Heavy Transition Elements, Macmillan, 1975). This volume shares the same aim of covering the descriptive chemistry of silver, gold and the six platinum metals in some detail at a level suitable for advanced undergraduate and postgradu ...
... eight elements within its compass (S.A. Cotton and F.A. Hart, The Heavy Transition Elements, Macmillan, 1975). This volume shares the same aim of covering the descriptive chemistry of silver, gold and the six platinum metals in some detail at a level suitable for advanced undergraduate and postgradu ...
CHAPTER 4 SOLUTION STOICHIOMETRY 1 CHAPTER FOUR
... The best way to identify a redox reaction is to assign oxidation states to all elements in the reaction. If elements show a change in oxidation states when going from reactants to products, then the reaction is a redox reaction. No change in oxidation states indicates the reaction is not a redox rea ...
... The best way to identify a redox reaction is to assign oxidation states to all elements in the reaction. If elements show a change in oxidation states when going from reactants to products, then the reaction is a redox reaction. No change in oxidation states indicates the reaction is not a redox rea ...
Chapter 4
... The best way to identify a redox reaction is to assign oxidation states to all elements in the reaction. If elements show a change in oxidation states when going from reactants to products, then the reaction is a redox reaction. No change in oxidation states indicates the reaction is not a redox rea ...
... The best way to identify a redox reaction is to assign oxidation states to all elements in the reaction. If elements show a change in oxidation states when going from reactants to products, then the reaction is a redox reaction. No change in oxidation states indicates the reaction is not a redox rea ...
Study Guide Chapter 10: An Introduction to Chemistry
... 7. For some chemical reactions, chemists want to mix reactants in amounts that are as close as possible to the ratio that would lead to the complete reaction of each. This ratio is sometimes called the stoichiometric ratio. 9. Sometimes one product is more important than others are, and the amounts ...
... 7. For some chemical reactions, chemists want to mix reactants in amounts that are as close as possible to the ratio that would lead to the complete reaction of each. This ratio is sometimes called the stoichiometric ratio. 9. Sometimes one product is more important than others are, and the amounts ...
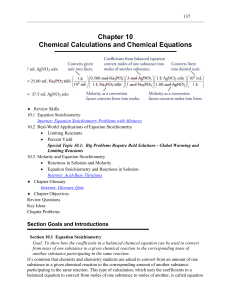
Chapter 10 Chemical Calculations and Chemical Equations
... 7. For some chemical reactions, chemists want to mix reactants in amounts that are as close as possible to the ratio that would lead to the complete reaction of each. This ratio is sometimes called the stoichiometric ratio. 9. Sometimes one product is more important than others are, and the amounts ...
... 7. For some chemical reactions, chemists want to mix reactants in amounts that are as close as possible to the ratio that would lead to the complete reaction of each. This ratio is sometimes called the stoichiometric ratio. 9. Sometimes one product is more important than others are, and the amounts ...
Quantitative Chemical Analysis
... Nuclear fission is far less polluting than burning oil, but difficult problems of waste containment are unsolved. Much coal remains, but coal creates carbon dioxide and more air pollution than any major energy source. There is a public misconception that hydrogen is a source of energy. Hydrogen requ ...
... Nuclear fission is far less polluting than burning oil, but difficult problems of waste containment are unsolved. Much coal remains, but coal creates carbon dioxide and more air pollution than any major energy source. There is a public misconception that hydrogen is a source of energy. Hydrogen requ ...
Chapter 4 - Chemistry
... Solution: CH3COOH is a weak acid. It will be shown as a molecule in the ionic equation. KOH is a strong base. It completely ionizes to K and OH ions. Since CH3COOH is an acid, it donates an H to the base, OH, producing water. The other product is the salt, CH3COOK, which is soluble and remains i ...
... Solution: CH3COOH is a weak acid. It will be shown as a molecule in the ionic equation. KOH is a strong base. It completely ionizes to K and OH ions. Since CH3COOH is an acid, it donates an H to the base, OH, producing water. The other product is the salt, CH3COOK, which is soluble and remains i ...
CHAPTER 1 - THE MOLE SECTION 1
... then connected to a battery. The current causes the water to split apart into hydrogen and oxygen. The positive hydrogen ions go to the negative electrode where they combine to form hydrogen gas. The negative oxygen ions move to the positive electrode and form oxygen gas. If the apparatus has been f ...
... then connected to a battery. The current causes the water to split apart into hydrogen and oxygen. The positive hydrogen ions go to the negative electrode where they combine to form hydrogen gas. The negative oxygen ions move to the positive electrode and form oxygen gas. If the apparatus has been f ...
preview as pdf
... Types of Electrolytes Electrolytes can be further classified as strong electrolytes or weak electrolytes. For a strong electrolyte, such as sodium chloride 1NaCl2, there is 100% dissociation of the solute into ions. When the electrodes from the light bulb apparatus are placed in the NaCl solution, t ...
... Types of Electrolytes Electrolytes can be further classified as strong electrolytes or weak electrolytes. For a strong electrolyte, such as sodium chloride 1NaCl2, there is 100% dissociation of the solute into ions. When the electrodes from the light bulb apparatus are placed in the NaCl solution, t ...
COMPETITION PTOBLEMS 1
... This publication contains the competition problems from the first twenty International Chemistry Olympiads (ICHO) organized in the years 1968 – 1988. It has been published by the ICHO International Information Centre in Bratislava (Slovakia) on the occasion of the 40th anniversary of this internatio ...
... This publication contains the competition problems from the first twenty International Chemistry Olympiads (ICHO) organized in the years 1968 – 1988. It has been published by the ICHO International Information Centre in Bratislava (Slovakia) on the occasion of the 40th anniversary of this internatio ...
Moles Workbook
... Examples: Calculation of Molar Mass from Relative Atomic Mass data Before you start any of these questions make sure you read the Section 4 of this booklet (The mole on page 27). When you carry out experiments you will weigh chemicals in grams. Molar mass has the same numerical value as the Relativ ...
... Examples: Calculation of Molar Mass from Relative Atomic Mass data Before you start any of these questions make sure you read the Section 4 of this booklet (The mole on page 27). When you carry out experiments you will weigh chemicals in grams. Molar mass has the same numerical value as the Relativ ...
Copyright 2010 Scott R
... example of a fifteen-coordinate atom of any kind. As determined by both single crystal X-ray and single crystal neutron diffraction studies, the eight boron atoms describe an approximate D2d dodecahedral structure in which seven of the Th···B distances lie between 2.88 and 2.95 Å, but the eighth is ...
... example of a fifteen-coordinate atom of any kind. As determined by both single crystal X-ray and single crystal neutron diffraction studies, the eight boron atoms describe an approximate D2d dodecahedral structure in which seven of the Th···B distances lie between 2.88 and 2.95 Å, but the eighth is ...
Support Material
... Q.43. Non-stoichiometric cuprous oxide can be prepared in the laboratory. In this oxide, copper to oxygen ratio is slightly less than 2 : 1. Can you account for the fact that the substance is a p-type semiconductor ? Q.44. The unit cell of an element of atomic mass 50 u has edge length 290 pm. Calcu ...
... Q.43. Non-stoichiometric cuprous oxide can be prepared in the laboratory. In this oxide, copper to oxygen ratio is slightly less than 2 : 1. Can you account for the fact that the substance is a p-type semiconductor ? Q.44. The unit cell of an element of atomic mass 50 u has edge length 290 pm. Calcu ...
Chapter 4 - Chemistry
... H2PO4 can either accept a proton, H, to become H3PO4 and thus behaves as a Brønsted base, or can donate a proton in water to yield H and HPO42, thus behaving as a Brønsted acid. HSO4 can either accept a proton, H, to become H2SO4 and thus behaves as a Brønsted base, or can donate a proton in w ...
... H2PO4 can either accept a proton, H, to become H3PO4 and thus behaves as a Brønsted base, or can donate a proton in water to yield H and HPO42, thus behaving as a Brønsted acid. HSO4 can either accept a proton, H, to become H2SO4 and thus behaves as a Brønsted base, or can donate a proton in w ...
AQA Science GCSE Chemistry
... AQA recognizes the importance of good-quality teaching, learning and assessment resources to accompany their specification. That's why they've chosen to work exclusively with nelson Thornes. With AQA examiners providing content and quality control, you can be confident that this course is as closely ...
... AQA recognizes the importance of good-quality teaching, learning and assessment resources to accompany their specification. That's why they've chosen to work exclusively with nelson Thornes. With AQA examiners providing content and quality control, you can be confident that this course is as closely ...
SCH3U: Final Exam Review Note: These questions a
... 43. 65 mL of a 2.5 mol/L solution of silver nitrate is added to an excess of calcium chloride. Identify the precipitate, and calculate the mass of this precipitate that is formed. 44. An excess of sodium carbonate solution is added to 75.0 mL of calcium chloride solution. 7.50 g of precipitate is fo ...
... 43. 65 mL of a 2.5 mol/L solution of silver nitrate is added to an excess of calcium chloride. Identify the precipitate, and calculate the mass of this precipitate that is formed. 44. An excess of sodium carbonate solution is added to 75.0 mL of calcium chloride solution. 7.50 g of precipitate is fo ...
questions based on high order thinking skill
... What happens when a Ferromagnetic or Ferrimagnetic solid is heated ? The ions of MgO and NaF all have the same number of electrons and intermolecular distance are about the same (235 & 215 pm). Why are the melting points are so different (2642 °C & 992 °C ? ...
... What happens when a Ferromagnetic or Ferrimagnetic solid is heated ? The ions of MgO and NaF all have the same number of electrons and intermolecular distance are about the same (235 & 215 pm). Why are the melting points are so different (2642 °C & 992 °C ? ...
questions based on high order thinking skill - Entrance
... What happens when a Ferromagnetic or Ferrimagnetic solid is heated ? The ions of MgO and NaF all have the same number of electrons and intermolecular distance are about the same (235 & 215 pm). Why are the melting points are so different (2642 °C & 992 °C ? ...
... What happens when a Ferromagnetic or Ferrimagnetic solid is heated ? The ions of MgO and NaF all have the same number of electrons and intermolecular distance are about the same (235 & 215 pm). Why are the melting points are so different (2642 °C & 992 °C ? ...
1 – Introduction
... 5% of global natural gas consumption, which is somewhat under 2% of world energy production. Natural gas is overwhelmingly used for the production of ammonia, but other energy sources, together with a hydrogen source, can be used for the production of nitrogen compounds suitable for fertilizers. The ...
... 5% of global natural gas consumption, which is somewhat under 2% of world energy production. Natural gas is overwhelmingly used for the production of ammonia, but other energy sources, together with a hydrogen source, can be used for the production of nitrogen compounds suitable for fertilizers. The ...
Hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, a ligand, a nucleophile and a catalyst. The hydroxide ion forms salts, some of which dissociate in aqueous solution, liberating solvated hydroxide ions. Sodium hydroxide is a multi-million-ton per annum commodity chemical. A hydroxide attached to a strongly electropositive center may itself ionize, liberating a hydrogen cation (H+), making the parent compound an acid.The corresponding electrically neutral compound •HO is the hydroxyl radical. The corresponding covalently-bound group -OH of atoms is the hydroxyl group.Hydroxide ion and hydroxyl group are nucleophiles and can act as a catalyst in organic chemistry.Many inorganic substances which bear the word ""hydroxide"" in their names are not ionic compounds of the hydroxide ion, but covalent compounds which contain hydroxyl groups.