BiomimeticsandGEPI-l..
... learning from our understanding of molecular biology. How can we build materials, like biological systems do, at the molecular level? ...
... learning from our understanding of molecular biology. How can we build materials, like biological systems do, at the molecular level? ...
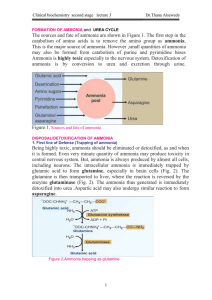
FORMATION OF AMMONIA
... A urea cycle disorder is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation that results in a deficiency of one of the enzymes in the urea cycle. These enzymes are responsible for removing ammonia from the blood stream. Severe deficiency or total absence of activity of any of the first four enzymes (CPS1, OTC, ...
... A urea cycle disorder is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation that results in a deficiency of one of the enzymes in the urea cycle. These enzymes are responsible for removing ammonia from the blood stream. Severe deficiency or total absence of activity of any of the first four enzymes (CPS1, OTC, ...
Leukaemia Section t(5;11)(q33;p13) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... occurs in mes-senger ribonucleoprotein particles that also contain RNA binding proteins; CAPRIN1/ G3BP1 comp-lexes occur in RNA granules called cytoplasmic stress granules, which form in stressed cells. CAPRIN1 induces phosphorylation of eIF-2alpha. CAPRIN1 selectively binds mRNA for c-MYC and CCND2 ...
... occurs in mes-senger ribonucleoprotein particles that also contain RNA binding proteins; CAPRIN1/ G3BP1 comp-lexes occur in RNA granules called cytoplasmic stress granules, which form in stressed cells. CAPRIN1 induces phosphorylation of eIF-2alpha. CAPRIN1 selectively binds mRNA for c-MYC and CCND2 ...
presentation
... Looking deeper at the rejected value test, all the 5 test values are rejected for n = 3 while n = 7 gives ZERO rejected values, the thing that emphasizes the truth of our hypothesis. ...
... Looking deeper at the rejected value test, all the 5 test values are rejected for n = 3 while n = 7 gives ZERO rejected values, the thing that emphasizes the truth of our hypothesis. ...
Excretion - Mocks.ie
... Urea and carbon dioxide are excretory products of the human body. In the case of each product name a substance from which it is derived. ...
... Urea and carbon dioxide are excretory products of the human body. In the case of each product name a substance from which it is derived. ...
LE 5-2 - MrBrock.com
... • Fats are constructed from two types of smaller molecules: glycerol and fatty acids • Glycerol is a three-carbon alcohol with a hydroxyl group attached to each carbon • A fatty acid consists of a carboxyl group attached to a long carbon skeleton ...
... • Fats are constructed from two types of smaller molecules: glycerol and fatty acids • Glycerol is a three-carbon alcohol with a hydroxyl group attached to each carbon • A fatty acid consists of a carboxyl group attached to a long carbon skeleton ...
Teaching metabolic pathways
... compounds. Stryer6 points out that in glycolysis, the C6 compounds are all derivatives of either glucose or fructose. The Ca compounds are all derivatives of either dihydroxyacetone, glyceraidehyde, glycerate or pyruvate. Furthermore, the substrates and products of each reaction are derivatives of e ...
... compounds. Stryer6 points out that in glycolysis, the C6 compounds are all derivatives of either glucose or fructose. The Ca compounds are all derivatives of either dihydroxyacetone, glyceraidehyde, glycerate or pyruvate. Furthermore, the substrates and products of each reaction are derivatives of e ...
Recognize and apply the definition of diffusion
... Identify the levels of organization in the biosphere including cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems, as well as organisms, populations, communities, and ecosystems Organisms: an individual living thing that is made of cells, uses energy, reproduces, responds to stimuli, grows and develops P ...
... Identify the levels of organization in the biosphere including cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems, as well as organisms, populations, communities, and ecosystems Organisms: an individual living thing that is made of cells, uses energy, reproduces, responds to stimuli, grows and develops P ...
Digital Processing and Molecular Logic Gates
... • Experimental procedures to join molecular components with structural control at the picometer level are available. A multitude of synthetic schemes to encourage the formation of chemical bonds between selected atoms in reacting molecules have been developed. • Furthermore, the tremendous progress ...
... • Experimental procedures to join molecular components with structural control at the picometer level are available. A multitude of synthetic schemes to encourage the formation of chemical bonds between selected atoms in reacting molecules have been developed. • Furthermore, the tremendous progress ...
Protein engineering of aldolase: Directed evolution
... Four billion years of natural evolution has created an enormous array of enzymes that can potentially be used as biocatalysts for the clean synthesis of complex medicinal and industrial compounds. Naturally occurring enzymes have, however, evolved for use in the living cell, and often do not exhibit ...
... Four billion years of natural evolution has created an enormous array of enzymes that can potentially be used as biocatalysts for the clean synthesis of complex medicinal and industrial compounds. Naturally occurring enzymes have, however, evolved for use in the living cell, and often do not exhibit ...
Proteins in Solution and in Membrane
... different from that of the unfolded polypeptides in chemical, physical and biological properties • Native protein can diffuse and rotate due to their compactness • Proteases cleave peptide bonds between domains or in mobile surface loops • Functional groups are held in proximity by the folded confor ...
... different from that of the unfolded polypeptides in chemical, physical and biological properties • Native protein can diffuse and rotate due to their compactness • Proteases cleave peptide bonds between domains or in mobile surface loops • Functional groups are held in proximity by the folded confor ...
Gel Electrophoresis - Institute of Tropical Disease
... We are now using biotechnology to study the basic processes of life, diagnose illnesses, and develop new treatments for diseases. Some of the tools of biotechnology are natural components of cells. Restriction enzymes are made by bacteria to protect themselves from viruses. They inactive the vir ...
... We are now using biotechnology to study the basic processes of life, diagnose illnesses, and develop new treatments for diseases. Some of the tools of biotechnology are natural components of cells. Restriction enzymes are made by bacteria to protect themselves from viruses. They inactive the vir ...
Protein folding: mechanisms and role in disease - Max
... shapes. Incorrect folding and clumping together of proteins is being recognized as the cause for a growing number of age-related diseases, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease as well as other neurodegenerative disorders. Definition of topic: Most biological functions in living cells are pe ...
... shapes. Incorrect folding and clumping together of proteins is being recognized as the cause for a growing number of age-related diseases, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease as well as other neurodegenerative disorders. Definition of topic: Most biological functions in living cells are pe ...
NoB1ch05QUICKcheck-ed
... Cows do not produce any enzymes that can digest cellulose to its glucose sub-units. Instead, cows (and other foregut-fermenting herbivores) depend on fermentation by bacteria in their stomach to digest cellulose. Cows have large four-chambered stomachs that can accommodate large volumes of bacteria ...
... Cows do not produce any enzymes that can digest cellulose to its glucose sub-units. Instead, cows (and other foregut-fermenting herbivores) depend on fermentation by bacteria in their stomach to digest cellulose. Cows have large four-chambered stomachs that can accommodate large volumes of bacteria ...
Citric Acid Cycle
... Oxidation of 2 isocitrate (2NADH) 6 ATP Oxidation of 2 -ketoglutarate (2NADH) 6 ATP 2 Direct substrate phosphorylations (2GTP) 2 ATP Oxidation of 2 succinate (2FADH2) 4 ATP Oxidation of 2 malate (2NADH) 6 ATP 24 ATP Summary: 2Acetyl CoA + 24 ADP + 24 Pi 4CO2 + 2H2O + 24 ATP + 2 CoASH ...
... Oxidation of 2 isocitrate (2NADH) 6 ATP Oxidation of 2 -ketoglutarate (2NADH) 6 ATP 2 Direct substrate phosphorylations (2GTP) 2 ATP Oxidation of 2 succinate (2FADH2) 4 ATP Oxidation of 2 malate (2NADH) 6 ATP 24 ATP Summary: 2Acetyl CoA + 24 ADP + 24 Pi 4CO2 + 2H2O + 24 ATP + 2 CoASH ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.