Stem cells
... • A stem cell is a cell that can grow into any type of cell, it is not specialised • All animal cells originate from embryo stem cells. During the development of an embryo, most of these cells become specialised. They cannot later change to become a different type of cell. This process is called cel ...
... • A stem cell is a cell that can grow into any type of cell, it is not specialised • All animal cells originate from embryo stem cells. During the development of an embryo, most of these cells become specialised. They cannot later change to become a different type of cell. This process is called cel ...
Phylum Porifera
... Polyps can reproduce asexually by budding. In the Medusa form there is external fertilization. The male release sperm into the water and the female releases eggs into the water. ...
... Polyps can reproduce asexually by budding. In the Medusa form there is external fertilization. The male release sperm into the water and the female releases eggs into the water. ...
Document
... To be closely related means the amino acid composition should be almost the same, since that is what the DNA is coding. Between Q and T, only 4 levels are the same – Between R and S only 4 levels are the same – Between Q and S 5 of the levels are the same, but – Between Q and R 5 of the lev ...
... To be closely related means the amino acid composition should be almost the same, since that is what the DNA is coding. Between Q and T, only 4 levels are the same – Between R and S only 4 levels are the same – Between Q and S 5 of the levels are the same, but – Between Q and R 5 of the lev ...
Development of body cavities
... the Amniotic Sac, as shown here at the end of the third week. Cut edge of amniotic membrane The dashed line shows the approximate plane of section used for the cross sectional drawings on syllabus page 30. ...
... the Amniotic Sac, as shown here at the end of the third week. Cut edge of amniotic membrane The dashed line shows the approximate plane of section used for the cross sectional drawings on syllabus page 30. ...
Cells_and_Chemical_Changes_Background_Info_
... Cells and Chemical Changes Background Informataion Cells differentiate in both plants and animals. Although the groups of cells that form muscle tissue are different from the groups that form bone or blood, and cells that form roots of plants are different from those that form leaves. The protoplasm ...
... Cells and Chemical Changes Background Informataion Cells differentiate in both plants and animals. Although the groups of cells that form muscle tissue are different from the groups that form bone or blood, and cells that form roots of plants are different from those that form leaves. The protoplasm ...
Adult neural stem cells, which are commonly thought of as
... down very early during embryonic development. It’s almost as if the embryo is planning for the future.” The study was published on June 18 in Cell. Adult stem cells are found in organ systems throughout the body. Most are undifferentiated, meaning they have the potential to develop into several diff ...
... down very early during embryonic development. It’s almost as if the embryo is planning for the future.” The study was published on June 18 in Cell. Adult stem cells are found in organ systems throughout the body. Most are undifferentiated, meaning they have the potential to develop into several diff ...
File - Mr. Downing Science 10
... Put the letter S next to any part of the plant that is part of the shoot system, and R for the root system ...
... Put the letter S next to any part of the plant that is part of the shoot system, and R for the root system ...
Development of the Respiratory System
... The development of these structures will be discussed in a later. Trachea: The trachea develops caudal to the larynx. The epithelium develops from the endoderm and the tracheal cartilage and muscles develop from splanchnic mesoderm. Early in development the trachea bifurcates into the left and rig ...
... The development of these structures will be discussed in a later. Trachea: The trachea develops caudal to the larynx. The epithelium develops from the endoderm and the tracheal cartilage and muscles develop from splanchnic mesoderm. Early in development the trachea bifurcates into the left and rig ...
cours Kmita mars 2017
... Cells entering the blastocoel separate in two layers: - The deep layer joins the hypoblast along the midline. These cells give rise to all endodermal organs of the embryo as well as most of the extraembryonic membranes. - the second layer is formed of cells that are located between the endoderm and ...
... Cells entering the blastocoel separate in two layers: - The deep layer joins the hypoblast along the midline. These cells give rise to all endodermal organs of the embryo as well as most of the extraembryonic membranes. - the second layer is formed of cells that are located between the endoderm and ...
Foetal Membranes
... Monoamniotic pregnancy is when each embryo or fetus from one single zygote (monozygotic, commonly known as identical twins) is located within the same amnion which is itself in one chorion (monochorionic). ...
... Monoamniotic pregnancy is when each embryo or fetus from one single zygote (monozygotic, commonly known as identical twins) is located within the same amnion which is itself in one chorion (monochorionic). ...
Diffusion and Osmosis in plant and animal cells
... • Name the method by which water passes into and out of cells. • Explain what a selectively permeable membrane is. • Explain what is meant by a concentration gradient. • Define osmosis using the terms selectively permeable membrane and concentration gradient. • Identify water concentration gradients ...
... • Name the method by which water passes into and out of cells. • Explain what a selectively permeable membrane is. • Explain what is meant by a concentration gradient. • Define osmosis using the terms selectively permeable membrane and concentration gradient. • Identify water concentration gradients ...
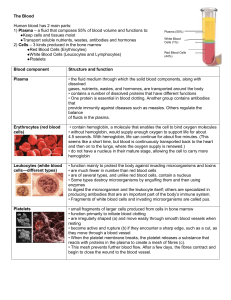
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
... 4.5 seconds. With hemoglobin, life can continue for about five minutes. (This seems like a short time, but blood is continuously transported back to the heart and then on to the lungs, where the oxygen supply is renewed.) • do not have a nucleus in their mature stage, allowing the cell to carry more ...
... 4.5 seconds. With hemoglobin, life can continue for about five minutes. (This seems like a short time, but blood is continuously transported back to the heart and then on to the lungs, where the oxygen supply is renewed.) • do not have a nucleus in their mature stage, allowing the cell to carry more ...
Biology Quiz Review – Science 8 Introduction to Cells, Tissues
... 3. What is cell theory? The idea that cells are the basic unit of structure of every living thing. (All living things are made of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure and function, and all cells come from existing cells). 4. What is a cell? Cells are the smallest independent units of life, a ...
... 3. What is cell theory? The idea that cells are the basic unit of structure of every living thing. (All living things are made of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure and function, and all cells come from existing cells). 4. What is a cell? Cells are the smallest independent units of life, a ...
body cavity
... which muscles can work. 3. The present of the cavity enables the internal organs to grow and move independently of the outer body wall. ...
... which muscles can work. 3. The present of the cavity enables the internal organs to grow and move independently of the outer body wall. ...
CHAPTER 3
... B. Tissues-groups of similar cells that do same sort of work—nerve tissue C. Organ-structure made up of different types of tissues –heart, lungs ...
... B. Tissues-groups of similar cells that do same sort of work—nerve tissue C. Organ-structure made up of different types of tissues –heart, lungs ...
Chapter 4 - Living Systems: Human Systems
... Chapter 4 - Living Systems: Human Systems Life Science Standards: 5, 6 1. The numbered drawings below show the organization within a multicellular organism from simple to complex. ...
... Chapter 4 - Living Systems: Human Systems Life Science Standards: 5, 6 1. The numbered drawings below show the organization within a multicellular organism from simple to complex. ...
Classification and Introduction to Animals Chapter 18 & 34
... •Haploid stage characterized by sperm and eggs produced by meiotic division •In most animal species, a small flagellated sperm fertilizes a larger non-motile egg, forming a zygote ...
... •Haploid stage characterized by sperm and eggs produced by meiotic division •In most animal species, a small flagellated sperm fertilizes a larger non-motile egg, forming a zygote ...
Chapter 3b
... As you see with the cilia actions being diminished, mucous starts to build up in the small airways making it harder for the smoker to breathe and causing the characteristic smokers cough in order to clear out the airways. Eventually though, the ciliated columnar cells are totally displaced. As can b ...
... As you see with the cilia actions being diminished, mucous starts to build up in the small airways making it harder for the smoker to breathe and causing the characteristic smokers cough in order to clear out the airways. Eventually though, the ciliated columnar cells are totally displaced. As can b ...
COMPARING INVERTEBRATES
... that extend throughout the body. The blood stays within these blood vessels. Materials reach body tissues by diffusing across the walls of the blood vessels. Blood circulates more efficiently in a closed ...
... that extend throughout the body. The blood stays within these blood vessels. Materials reach body tissues by diffusing across the walls of the blood vessels. Blood circulates more efficiently in a closed ...
Document
... region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration called pumps? A. They require energy to move substances against a concentration gradient. B. They open and close to allow substances to diffuse across the plasma membrane. C. They help with the osmosis of water through the plasma memb ...
... region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration called pumps? A. They require energy to move substances against a concentration gradient. B. They open and close to allow substances to diffuse across the plasma membrane. C. They help with the osmosis of water through the plasma memb ...
Illnesses of the Female Reproductive System
... __________________________ (oviduct) – located next to each ovary ...
... __________________________ (oviduct) – located next to each ovary ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.