* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Foetal Membranes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
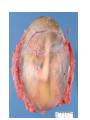
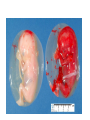
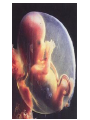
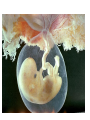
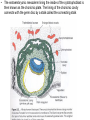
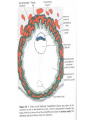
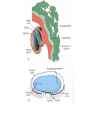
Foetal Membranes • Second month : the tropho blast develops secondary and tertiary villi • Villi are anchored to the mesoderm of the chorionic plate and peripherally attached to the maternal decidua by cytotrophoblast Amnion Definition : • The thin, transparent inner membrane (the chorion is the outer layer) that constitutes the amniotic membranes. • contain the amniotic fluid • A protective layer for the baby insulating him/her from bacteria in the vagina. Rupture of this sac exposes the child to bacteria in the vagina and increases the risk of infection if the infant is not delivered within about 18 hours. • Labor usually starts shortly after of before rupture of the amniotic membranes. • Amniotic fluid - watery liquid surrounding and cushioning a growing fetus within the amnion. It allows the fetus to move freely without the walls of the uterus being too tight against its body. • The amnion grows and begins to fill, mainly with water, around two weeks after fertilisation. After a further 10 weeks the liquid contains proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and phospholipids, urea and electrolytes. • The fluid is released when the amnion ruptures - spontaneous rupture of membranes (SRM). • The majority of the amniotic fluid remains inside the uterus until the baby is born. Complications related to amniotic fluid • Too little amniotic fluid (oligohydramnios) • Too much (polyhydramnios or hydramnios) • In both cases the majority of pregnancies proceed normally and the baby is born healthily. • Polyhydramnios is a predisposing risk factor for cord prolapse. • A rare and fatal obstetric complication is an amniotic fluid embolism. Multiple pregnancies • Twins and multiple pregnancies sometimes share the amnion and the chorion. • Monoamniotic pregnancy is when each embryo or fetus from one single zygote (monozygotic, commonly known as identical twins) is located within the same amnion which is itself in one chorion (monochorionic). • Diamniotic pregnancy is when there are more than one amnions inside one chorion or each having their own chorion (dichorionic). • Dizygotic (fraternal, non-identical) twins each have their own amnion and chorion and may or may not share a placenta. Chorion Definition • Is a membrane closely adherent to the amniotic membrane. • It is formed during the second week of development • The chorionic cavity is one of the first two cavities formed during the second week of development. • It is otherwise called extraembryonic coelom • Later on the amniotic cavity enlarges and after the folding of the embryo it occupies and fills the whole of the chorionic cavity and then obliterates the chorionic cavity. Then the chorion and amnion fuse together. They enlarge and fill the whole of the uterus. • The extraembryonic mesoderm lining the inside of the cytotrophoblast is then known as the chorionic plate. The lining of the chorionic cavity connects with the germ disc by a stalk called the connecting stalk