Kingdom Animalia Review Answer Key
... instinctive behaviour that occurs without previous learning of that response. “inheritance” 4. Outline the process of gastrulation from where the blastula (the hollow ball of cells) has developed up until the formation of the mesoderm (6). Be sure to include the three different germ layers created i ...
... instinctive behaviour that occurs without previous learning of that response. “inheritance” 4. Outline the process of gastrulation from where the blastula (the hollow ball of cells) has developed up until the formation of the mesoderm (6). Be sure to include the three different germ layers created i ...
BLOOD: GENERAL PROPERTIES AND FUNCTIONS
... RBCs are terminally differentiated, that is, they can never divide, and live for about 120 days after which they and engulfed and phagocytosed by cells of the RES predominantly in the spleen, bone marrow and liver. They are responsible for the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide. In addition to t ...
... RBCs are terminally differentiated, that is, they can never divide, and live for about 120 days after which they and engulfed and phagocytosed by cells of the RES predominantly in the spleen, bone marrow and liver. They are responsible for the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide. In addition to t ...
Evolution and diversification of eukaryotes II
... dormant, dry, barrel-shaped form called a tun that is highly resistant to extreme conditions. They can survive up to 100 years in this state! • Tardigrades are highly resistant to extreme temperatures (-270 C to 151 C); to dessication (drying out); and to X-rays; they can survive over 1000 times hig ...
... dormant, dry, barrel-shaped form called a tun that is highly resistant to extreme conditions. They can survive up to 100 years in this state! • Tardigrades are highly resistant to extreme temperatures (-270 C to 151 C); to dessication (drying out); and to X-rays; they can survive over 1000 times hig ...
Word file.
... IMPORTANT CONSIDERATIONS: In courses with fewer class sessions this material may have to be incorporated with discussions of each organ system or included with the reproductive system discussions. If only one session is available, the instructor will have to decide whether the students being served ...
... IMPORTANT CONSIDERATIONS: In courses with fewer class sessions this material may have to be incorporated with discussions of each organ system or included with the reproductive system discussions. If only one session is available, the instructor will have to decide whether the students being served ...
Embryology: Images of Man - Welkom op de fenomenologie site van
... zygote. After that the divisions occur approximately every 12 hours. The embryo is and stays spherical and does not grow. The stage of 16 to 64 cells is called a morula (= mulberry) (see Fig. 2, the fifth stage, side view). Then the cells that lie inside migrate from the centre to the periphery, som ...
... zygote. After that the divisions occur approximately every 12 hours. The embryo is and stays spherical and does not grow. The stage of 16 to 64 cells is called a morula (= mulberry) (see Fig. 2, the fifth stage, side view). Then the cells that lie inside migrate from the centre to the periphery, som ...
Animal tissues and Organ systems
... Allows an animal to collect and integrate information about its internal and external environment Controls the activity of glands and muscles Main tissue of the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and of the nerves that extend through the body ...
... Allows an animal to collect and integrate information about its internal and external environment Controls the activity of glands and muscles Main tissue of the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and of the nerves that extend through the body ...
Structure and Function of Cells
... plant cells, animal cells or both? 3. What is a cell wall and what function does it serve in the cell? Is it found in plant cells, animal cells or both? 4. What are the parts of the cell theory? ...
... plant cells, animal cells or both? 3. What is a cell wall and what function does it serve in the cell? Is it found in plant cells, animal cells or both? 4. What are the parts of the cell theory? ...
Lymphatic System Test
... ______14. Specialized lymph nodes located in the intestines that help protect against invading organisms in the digestive tract are known as: a. T cells b. lymphocytes c. Peyer’s patches ______ 15. The __________ T cell remembers an invading antigen and is ready to fight that same antigen if it is e ...
... ______14. Specialized lymph nodes located in the intestines that help protect against invading organisms in the digestive tract are known as: a. T cells b. lymphocytes c. Peyer’s patches ______ 15. The __________ T cell remembers an invading antigen and is ready to fight that same antigen if it is e ...
CHAPTER 23: HUMAN GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
... Developmental anatomy is the study of events from fertilization of the secondary oocyte to the formation of an adult organism. In this chapter we will study the sequence of events from fertilization to birth, which include fertilization, implantation, placental development, embryonic development, fe ...
... Developmental anatomy is the study of events from fertilization of the secondary oocyte to the formation of an adult organism. In this chapter we will study the sequence of events from fertilization to birth, which include fertilization, implantation, placental development, embryonic development, fe ...
practice week 12 qwest
... b. Cellular respiration d. Exocytosis 23. Across which structure does osmosis occur? a. Endoplasmic Reticulum b. Mitochondria ...
... b. Cellular respiration d. Exocytosis 23. Across which structure does osmosis occur? a. Endoplasmic Reticulum b. Mitochondria ...
Document
... zooid closed at the distal end and are developed on full-grown hydrocauli, generally on their lower parts. They arise as buds in the axils of some of the branches that bear polyps. Blastosytle lacks mouth, manubrium and tantacles. Protective Covering: The blastostyle is enclosed in a clubshaped ex ...
... zooid closed at the distal end and are developed on full-grown hydrocauli, generally on their lower parts. They arise as buds in the axils of some of the branches that bear polyps. Blastosytle lacks mouth, manubrium and tantacles. Protective Covering: The blastostyle is enclosed in a clubshaped ex ...
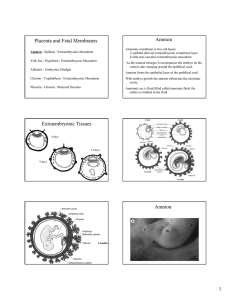
Placenta and Fetal Membranes
... and lipid, called Decidual Cells Decidua basalis - forms maternal component of the placenta; associates with the chorion frondosom Decidua capsularis - superfical layer overlying the entire embryoblast - this layer eventually degenerates; associates with the chorion laeve Decidua parietalis - all re ...
... and lipid, called Decidual Cells Decidua basalis - forms maternal component of the placenta; associates with the chorion frondosom Decidua capsularis - superfical layer overlying the entire embryoblast - this layer eventually degenerates; associates with the chorion laeve Decidua parietalis - all re ...
08 Placenta and Fetal Membranes total
... Decidua capsularis - superfical layer overlying the entire embryoblast - this layer eventually degenerates; associates with the chorion laeve Decidua parietalis - all remaining parts of the endometrium - not associated with the embryo ...
... Decidua capsularis - superfical layer overlying the entire embryoblast - this layer eventually degenerates; associates with the chorion laeve Decidua parietalis - all remaining parts of the endometrium - not associated with the embryo ...
Ch 47 - D and F: AP Biology
... mesoderm cells covered by a layer of ectoderm. Two regions, termed the apical ectodermal ridge (AER, shown in this SEM) and the zone of polarizing activity (ZPA), play key organizer roles in limb ...
... mesoderm cells covered by a layer of ectoderm. Two regions, termed the apical ectodermal ridge (AER, shown in this SEM) and the zone of polarizing activity (ZPA), play key organizer roles in limb ...
Basic Structure PowerPoint
... Pituitary gland, Thyroid gland, Parathyroid glands, Adrenal glands, Pancreas Testes, Ovary, Liver ...
... Pituitary gland, Thyroid gland, Parathyroid glands, Adrenal glands, Pancreas Testes, Ovary, Liver ...
File
... Pituitary gland, Thyroid gland, Parathyroid glands, Adrenal glands, Pancreas Testes, Ovary, Liver ...
... Pituitary gland, Thyroid gland, Parathyroid glands, Adrenal glands, Pancreas Testes, Ovary, Liver ...
3- Porifer and Cnidaria_AP Bio
... In order for the Clownfish to live within the tentacles of the sea anemone, it must develop immunity to the stinging cells of the anemone. It does this by touching one or two tentacles at a time, over time the number of tentacles touched are numerous and eventually the fish creates mucus that prot ...
... In order for the Clownfish to live within the tentacles of the sea anemone, it must develop immunity to the stinging cells of the anemone. It does this by touching one or two tentacles at a time, over time the number of tentacles touched are numerous and eventually the fish creates mucus that prot ...
General Body and Directional Terms
... • Groups of organs work together to perform a complex functionbody system • Trillions of cells vary in size and shape according to their function • Specialized cells are responsible for growth, secretions, excretions, nutrition, reproduction • Mechanical, chemical and nervous stimulation activate t ...
... • Groups of organs work together to perform a complex functionbody system • Trillions of cells vary in size and shape according to their function • Specialized cells are responsible for growth, secretions, excretions, nutrition, reproduction • Mechanical, chemical and nervous stimulation activate t ...
PDQ1
... 6. Provide four examples of cell tasks that are accomplished by proteins. 7. Explain/Diagram the relationship between DNA, RNA and protein in cells. 8. How does the structure of the nucleus allow it to fulfill its function? 9. True or False: The nucleolus is an intranuclear organelle. Explain your a ...
... 6. Provide four examples of cell tasks that are accomplished by proteins. 7. Explain/Diagram the relationship between DNA, RNA and protein in cells. 8. How does the structure of the nucleus allow it to fulfill its function? 9. True or False: The nucleolus is an intranuclear organelle. Explain your a ...
Glossary of Terms and Acronyms
... Mucus: The viscous fluid secreted by the mucous glands. Nasopharyngeal region: Region of the lung comprising the nasal cavity and pharynx. Phagocytosis: Consumption of foreign particles by cells. Pharynx: The portion of the alimentary canal which intervenes between the mouth cavity and the esophagus ...
... Mucus: The viscous fluid secreted by the mucous glands. Nasopharyngeal region: Region of the lung comprising the nasal cavity and pharynx. Phagocytosis: Consumption of foreign particles by cells. Pharynx: The portion of the alimentary canal which intervenes between the mouth cavity and the esophagus ...
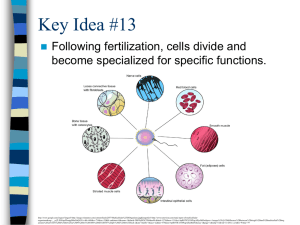
Key Idea #9 - Mona Shores Blogs
... A variety of specialized cells formed through cell division make up different tissues, performing different functions. ...
... A variety of specialized cells formed through cell division make up different tissues, performing different functions. ...
unit 1: the organisation of the human body
... some pressure, etc. And the response could be a movement, a secretion, etc - Reproduction: capacity of living things to make copies of themselves. 2. All the living things are made up of the same molecules: biomolecules. 3. They are made up of cells. Some living things are only one cell: single cell ...
... some pressure, etc. And the response could be a movement, a secretion, etc - Reproduction: capacity of living things to make copies of themselves. 2. All the living things are made up of the same molecules: biomolecules. 3. They are made up of cells. Some living things are only one cell: single cell ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.