Chapter 20 - Mason Gmu
... These tissues are named according to the shape and number of cells they have ------------------------------------------ has one layer of cells; ----------------------------------------------------- has multiple layers. Shape of the cell can be -------------------------------------------------------- ...
... These tissues are named according to the shape and number of cells they have ------------------------------------------ has one layer of cells; ----------------------------------------------------- has multiple layers. Shape of the cell can be -------------------------------------------------------- ...
Spring Final Exam Review Questions
... ____ 33. Sensory receptors that are sensitive to chemicals are found in the a. skin, body core, and hypothalamus. c. eyes. b. skin, skeletal muscles, and inner ears. d. nose and taste buds. ____ 34. Which of the following is NOT a part of the circulatory system? a. heart c. blood vessels b. air pass ...
... ____ 33. Sensory receptors that are sensitive to chemicals are found in the a. skin, body core, and hypothalamus. c. eyes. b. skin, skeletal muscles, and inner ears. d. nose and taste buds. ____ 34. Which of the following is NOT a part of the circulatory system? a. heart c. blood vessels b. air pass ...
Biology 1406 - HCC Learning Web
... 6. (P. 9 – 15) There is unity in diversity. All of biology is about this topic – the most important concept in biology, because it explains how living things that are so different can show so much similarity between them. The term diversity refers to the millions of different species that exist – co ...
... 6. (P. 9 – 15) There is unity in diversity. All of biology is about this topic – the most important concept in biology, because it explains how living things that are so different can show so much similarity between them. The term diversity refers to the millions of different species that exist – co ...
Topic: Reproduction Aim: Describe the stages of embryonic
... by the cilia lining the oviduct. Around 30 hours after fertilization, the zygote undergoes its first mitosis and cell division. This process, called cleavage, continues, and by the third day, the embryo leaves the oviduct and enters the uterus. At this point, the embryo is described as a morula—a so ...
... by the cilia lining the oviduct. Around 30 hours after fertilization, the zygote undergoes its first mitosis and cell division. This process, called cleavage, continues, and by the third day, the embryo leaves the oviduct and enters the uterus. At this point, the embryo is described as a morula—a so ...
Ch. 32 Intro to Animal Evolution
... What is an Animal? • Multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes • Animal cells lack cell walls • 2 tissues unique to animals: nervous and muscular • Most reproduce sexually, with diploid stage dominating life cycle ...
... What is an Animal? • Multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes • Animal cells lack cell walls • 2 tissues unique to animals: nervous and muscular • Most reproduce sexually, with diploid stage dominating life cycle ...
Chapter 5 - Tissues PPT
... A characteristic of epithelial tissues is one side is exposed to the outside of the body or to an internal space. The other side is anchored to connective tissue by a nonliving layer basement membrane ...
... A characteristic of epithelial tissues is one side is exposed to the outside of the body or to an internal space. The other side is anchored to connective tissue by a nonliving layer basement membrane ...
simple nervous
... – Same individual has both male and female sex organs Worms line up side by side and exchange packets of sperm. Self fertilize eggs. Eggs laid in clusters and hatch in weeks. Asexual by fission, individuals break apart and make new worms. ...
... – Same individual has both male and female sex organs Worms line up side by side and exchange packets of sperm. Self fertilize eggs. Eggs laid in clusters and hatch in weeks. Asexual by fission, individuals break apart and make new worms. ...
Hello!!! - Elida Local Schools
... function. They are usually enclosed in their own lipid membrane. There are many types of organelles, such as ribosomes, nuclei, endoplasmic reticulum, and lysosomes. Cells are the structural and functional units of all living organisms. Some organisms, such as bacteria, are each made up of only one ...
... function. They are usually enclosed in their own lipid membrane. There are many types of organelles, such as ribosomes, nuclei, endoplasmic reticulum, and lysosomes. Cells are the structural and functional units of all living organisms. Some organisms, such as bacteria, are each made up of only one ...
Chapter 1 Notes - Social Circle City Schools
... - lack cell walls; have cell junctions made of structural proteins that hold cells and tissues together ...
... - lack cell walls; have cell junctions made of structural proteins that hold cells and tissues together ...
circumference of the egg and is, at first, quite broad. It is
... part of the medullary tube (Fig. 40). The neural ridges next beeome broken up into a series of dorsal nerves, the cells collecting at certain regions, and thinning out and disappearing in the intermediate regions. The dorsal nerves grow down later between the myotomes and the nerve-cord. Accumulatio ...
... part of the medullary tube (Fig. 40). The neural ridges next beeome broken up into a series of dorsal nerves, the cells collecting at certain regions, and thinning out and disappearing in the intermediate regions. The dorsal nerves grow down later between the myotomes and the nerve-cord. Accumulatio ...
HISTOLOGY
... • Nerve cells are called NEURONS Nerve cells differ a great deal in structure and function • Some are sensitive to changes in the environment and can receive stimuli. • Others are adapted for sending impulses or messages down their ...
... • Nerve cells are called NEURONS Nerve cells differ a great deal in structure and function • Some are sensitive to changes in the environment and can receive stimuli. • Others are adapted for sending impulses or messages down their ...
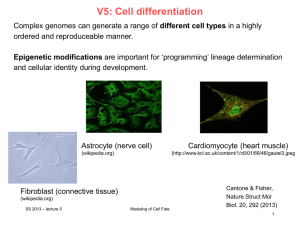
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... Cells of the inner cell mass (ICM) and its derivative, embryonic stem (ES) cells, are pluripotent. Multipotency Ability of a cell to give rise to different cell types of a given cell lineage. These cells include most adult stem cells, such as gut stem cells, skin stem cells, hematopoietic stem cells ...
... Cells of the inner cell mass (ICM) and its derivative, embryonic stem (ES) cells, are pluripotent. Multipotency Ability of a cell to give rise to different cell types of a given cell lineage. These cells include most adult stem cells, such as gut stem cells, skin stem cells, hematopoietic stem cells ...
Epithelial Cells
... through the sponge by beating a flagellum that extends into the inner canal. Amoeboid Cells – This cells helps pass food. It moves between epithelial cells and the collar cell. They digest, and distribute nutrients, produce reproductive cells. ...
... through the sponge by beating a flagellum that extends into the inner canal. Amoeboid Cells – This cells helps pass food. It moves between epithelial cells and the collar cell. They digest, and distribute nutrients, produce reproductive cells. ...
Students Notes with Blanks
... _______________________ : Eats animals _______________________ : Eats plants and animals _______________________ : Lives off of a host _______________________ : Strains floating plants and animals from surrounding water _______________________ : Feeds on decaying plants and animals (detrius) ...
... _______________________ : Eats animals _______________________ : Eats plants and animals _______________________ : Lives off of a host _______________________ : Strains floating plants and animals from surrounding water _______________________ : Feeds on decaying plants and animals (detrius) ...
Name
... 26. The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body and the air occurs in the lungs. This exchange of gases takes place at the cellular level. What part of the cell is primarily responsible for this exchange? A. the cell membrane B. the nucleus C. the cell wall D. the ribosome ...
... 26. The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body and the air occurs in the lungs. This exchange of gases takes place at the cellular level. What part of the cell is primarily responsible for this exchange? A. the cell membrane B. the nucleus C. the cell wall D. the ribosome ...
Flatworms, roundworms and rotifers
... New levels of complexity 1. Cleavage • Cleavage is spiral and determinate = protostome development • Cleavage is radial and indeterminate = deuterostome development Protostome development ...
... New levels of complexity 1. Cleavage • Cleavage is spiral and determinate = protostome development • Cleavage is radial and indeterminate = deuterostome development Protostome development ...
Chapter 20
... 3) Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure and function a) tissue – (latin for “weave”)cooperative unit of many similar cells performing a special function i) most cells of multicellular organisms are organized into tissues ii) the cells themselves are highly specialized to perform their ...
... 3) Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure and function a) tissue – (latin for “weave”)cooperative unit of many similar cells performing a special function i) most cells of multicellular organisms are organized into tissues ii) the cells themselves are highly specialized to perform their ...
Press Release - MWM
... Already twenty years ago, researchers showed that primordial germ cells (PGCs) could be induced into pluripotency by the mere modulation of the culture conditions. Recently, Hans Schöler’s research group succeeded in converting adult germline stem cells (GSCs) from mouse testicular cells into plurip ...
... Already twenty years ago, researchers showed that primordial germ cells (PGCs) could be induced into pluripotency by the mere modulation of the culture conditions. Recently, Hans Schöler’s research group succeeded in converting adult germline stem cells (GSCs) from mouse testicular cells into plurip ...
Biology Final Review
... Echinoderm – Starfish - Radial symm. as an adult and bilateral as a developing embryo - Complete dig tract - No head or brain - Ventral mouth, dorsal anus - Water vascular system – series of H20 filled tubes and tube feet – don’t need an excretory system - Nerve ring around mouth that radiates to ot ...
... Echinoderm – Starfish - Radial symm. as an adult and bilateral as a developing embryo - Complete dig tract - No head or brain - Ventral mouth, dorsal anus - Water vascular system – series of H20 filled tubes and tube feet – don’t need an excretory system - Nerve ring around mouth that radiates to ot ...
SNC2D Unit Test: Tissue, Organs and Living Systems
... d) oxidation 11. The hair-like structures lining the respiratory tract that beat continuously to move unwanted particles back into the nose and throat are the: a) cilia. b) bronchi. c) epiglottis. d) alveoli ...
... d) oxidation 11. The hair-like structures lining the respiratory tract that beat continuously to move unwanted particles back into the nose and throat are the: a) cilia. b) bronchi. c) epiglottis. d) alveoli ...
Themes of Life
... Part B: Based on the structural difference, explain why prokaryotic cells can be much smaller than eukaryotic cells. Part C: Describe one similarity between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells that is independent of size. Alveoli are microscopic air sacs in the lungs of mammals. Which statement b ...
... Part B: Based on the structural difference, explain why prokaryotic cells can be much smaller than eukaryotic cells. Part C: Describe one similarity between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells that is independent of size. Alveoli are microscopic air sacs in the lungs of mammals. Which statement b ...
Bio 104 Exam 4 Review – Animals Part I: Phylum Porifera – Phylum
... Bio 104 Exam 4 Review – Animals Part I: Phylum Porifera – Phylum Mollusca (notes pages 28-36) Animals are defined as “multicellular eukaryotes that are heterotrophic by ingestion.” They have a diplontic life cycle in which the adult is always diploid. They are classified based on their Symmetry: asy ...
... Bio 104 Exam 4 Review – Animals Part I: Phylum Porifera – Phylum Mollusca (notes pages 28-36) Animals are defined as “multicellular eukaryotes that are heterotrophic by ingestion.” They have a diplontic life cycle in which the adult is always diploid. They are classified based on their Symmetry: asy ...
Chapter 29: Introduction to Invertebrates
... Sac, tube-within-a-tube Segmentation Segmentation leads to specialization Symmetry Radial - Two identical halves Bilateral - Definite right and left halves Type of Coelom Pseudocoelom Coelom Early Developmental Pattern Protostome - First embryonic opening becomes the mouth Deuterostome - Second embr ...
... Sac, tube-within-a-tube Segmentation Segmentation leads to specialization Symmetry Radial - Two identical halves Bilateral - Definite right and left halves Type of Coelom Pseudocoelom Coelom Early Developmental Pattern Protostome - First embryonic opening becomes the mouth Deuterostome - Second embr ...
Grade 8 Science Unit 4 Study Guide
... There are cells that help us breathe, nerve cells that enable us to feel, skin cells, brain cells, etc. These cells aren’t very effective by themselves so they group together with other cells just like them. When a bunch of similar cells group together , it is called tissue such as nerve tissue, ski ...
... There are cells that help us breathe, nerve cells that enable us to feel, skin cells, brain cells, etc. These cells aren’t very effective by themselves so they group together with other cells just like them. When a bunch of similar cells group together , it is called tissue such as nerve tissue, ski ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.