Cells - College of Science | Oregon State University
... __________________________ cells (choose from the list above). When you view the model from the side, the muscle cells look long and tubular in shape. When you view the model from above, what shape does each muscle cell seem to have? ____________________ This difference in appearance from different ...
... __________________________ cells (choose from the list above). When you view the model from the side, the muscle cells look long and tubular in shape. When you view the model from above, what shape does each muscle cell seem to have? ____________________ This difference in appearance from different ...
Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
... population and can be boy/boy, girl/girl, or boy/girl sets. Happen when Mom releases two eggs and different sperm fertilize each egg. • They do not look any more alike than typical siblings. ...
... population and can be boy/boy, girl/girl, or boy/girl sets. Happen when Mom releases two eggs and different sperm fertilize each egg. • They do not look any more alike than typical siblings. ...
Chapter 1
... • Sexual reproduction – develops from the joining of 2 sex cells (fertilization) • Asexual reproduction – process by which a single organism produces a new organism identical to itself. ...
... • Sexual reproduction – develops from the joining of 2 sex cells (fertilization) • Asexual reproduction – process by which a single organism produces a new organism identical to itself. ...
Lec. No.10 Centrosome In cell biology, the centrosome is an
... organelles are located together near the nucleus. Each centerioles is made of nine bundles of microtubules (three per bundle) arranged in a ring. Just before mitosis, the two centrosomes move part until they are on opposite side of the nucleus and organized into a spindle-shaped formation that calle ...
... organelles are located together near the nucleus. Each centerioles is made of nine bundles of microtubules (three per bundle) arranged in a ring. Just before mitosis, the two centrosomes move part until they are on opposite side of the nucleus and organized into a spindle-shaped formation that calle ...
Key Idea #9 - Mona Shores Blogs
... Following fertilization, cell division produces a small cluster of cells that then differentiate by appearance and function to form the basic tissues, organs, and organ systems of multicellular organisms. ...
... Following fertilization, cell division produces a small cluster of cells that then differentiate by appearance and function to form the basic tissues, organs, and organ systems of multicellular organisms. ...
animal tissues and organ systems
... that interact and provide specific functions Organs – made of 2 or more different interacting tissues Organ systems – 2 or more organs joined physically or functionally ...
... that interact and provide specific functions Organs – made of 2 or more different interacting tissues Organ systems – 2 or more organs joined physically or functionally ...
Anatomy and Physiology- Assignment #1 1. The maintenance of
... of phagocytosis occurs, by filling the area with a mass of dense fibrous tissue. If the damage is minimal, this mass can eventually be replaced with normal tissue. Extensive damage will sometimes result in the large dense mass being left there to produce a scar. c. muscle Muscle tissue has the abili ...
... of phagocytosis occurs, by filling the area with a mass of dense fibrous tissue. If the damage is minimal, this mass can eventually be replaced with normal tissue. Extensive damage will sometimes result in the large dense mass being left there to produce a scar. c. muscle Muscle tissue has the abili ...
Irregular Plurals in Biology/Zoology
... a body opening Mammals: in the chest between the lungs; contains the heart and trachea the innermost area of a part or organ of an animal or plant jellyfish form membranes that surround and protect the brain and the spinal cord cellular organelles outside a nucleus branched flowerhead with one branc ...
... a body opening Mammals: in the chest between the lungs; contains the heart and trachea the innermost area of a part or organ of an animal or plant jellyfish form membranes that surround and protect the brain and the spinal cord cellular organelles outside a nucleus branched flowerhead with one branc ...
Flexion and Neural Tube Formation
... cervical nerves C3, C4, and C5. It will form the central tendon of the diaphragm; its myoblasts will invade the pleuroperitoneal membranes to form diaphragmatic musculature. Somatopleure - The embryonic somatopleure is associated with the embryonic ectodermal surface. Splanchnopleure - The embryonic ...
... cervical nerves C3, C4, and C5. It will form the central tendon of the diaphragm; its myoblasts will invade the pleuroperitoneal membranes to form diaphragmatic musculature. Somatopleure - The embryonic somatopleure is associated with the embryonic ectodermal surface. Splanchnopleure - The embryonic ...
Invertebrate Power Point Sponges to Earthworms File
... a) Radial Symmetry or none b) Two body plans 1) Polyp: vase-shaped body, tentacles up, sessile 2) Medusa: bell-shaped body, tentacles down, ...
... a) Radial Symmetry or none b) Two body plans 1) Polyp: vase-shaped body, tentacles up, sessile 2) Medusa: bell-shaped body, tentacles down, ...
FOSS Science
... tissue – a group of cells of the same kind, working together to perform a function. In the circulatory system: blood and blood vessels (types of tissues include muscle tissue, bone tissue, nerve tissue) respiratory system – includes tissues and organs (lungs) that provide gas exchange between the bl ...
... tissue – a group of cells of the same kind, working together to perform a function. In the circulatory system: blood and blood vessels (types of tissues include muscle tissue, bone tissue, nerve tissue) respiratory system – includes tissues and organs (lungs) that provide gas exchange between the bl ...
The Processes of Development
... • At the 8-cell stage of a mammal embryo, the cells form tight junctions and a compact mass. • At the transition from the 16-cell to 32-cell stage, the cells separate into two masses. • The inner cell mass(세포내괴) develops into the embryo; the outer cells become the trophoblast(영양아층), which becomes pa ...
... • At the 8-cell stage of a mammal embryo, the cells form tight junctions and a compact mass. • At the transition from the 16-cell to 32-cell stage, the cells separate into two masses. • The inner cell mass(세포내괴) develops into the embryo; the outer cells become the trophoblast(영양아층), which becomes pa ...
Page 1
... and bone tissue is made up of bone cells; blood is also a tissue-it is made up of many types of blood cells Organs are different types of tissues working together can form a structure. For example, the stomach is an organ that includes muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and blood tissue. All of these tiss ...
... and bone tissue is made up of bone cells; blood is also a tissue-it is made up of many types of blood cells Organs are different types of tissues working together can form a structure. For example, the stomach is an organ that includes muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and blood tissue. All of these tiss ...
Homework Exercise 1 - Cells, Tissues and Organs 1. Place the
... heart pumps blood and the stomach helps digest food. Each organ is made from a few very different tissues i.e the stomach contains both muscle and nerve tissue. More than one organ is needed to digest food. The stomach does some of the work but the mouth containing teeth and salivary glands and the ...
... heart pumps blood and the stomach helps digest food. Each organ is made from a few very different tissues i.e the stomach contains both muscle and nerve tissue. More than one organ is needed to digest food. The stomach does some of the work but the mouth containing teeth and salivary glands and the ...
Kingdom Protista
... name. This 2-part name is also the species name. The first part is the Genus which is capitalized, and the second, which is the species, part of the scientific name is never ...
... name. This 2-part name is also the species name. The first part is the Genus which is capitalized, and the second, which is the species, part of the scientific name is never ...
Developmental Biology 8/e
... gastrulation. (A,B) Human embryo and uterine connections at day 15 of gestation. (A) Sagittal section through the midline. (B) View looking down on the dorsal surface of the embryo. (C) The movements of the epiblast cells through the primitive streak and Hensen’s node and underneath the epiblast are ...
... gastrulation. (A,B) Human embryo and uterine connections at day 15 of gestation. (A) Sagittal section through the midline. (B) View looking down on the dorsal surface of the embryo. (C) The movements of the epiblast cells through the primitive streak and Hensen’s node and underneath the epiblast are ...
Developmental Biology 8/e
... gastrulation. (A,B) Human embryo and uterine connections at day 15 of gestation. (A) Sagittal section through the midline. (B) View looking down on the dorsal surface of the embryo. (C) The movements of the epiblast cells through the primitive streak and Hensen’s node and underneath the epiblast are ...
... gastrulation. (A,B) Human embryo and uterine connections at day 15 of gestation. (A) Sagittal section through the midline. (B) View looking down on the dorsal surface of the embryo. (C) The movements of the epiblast cells through the primitive streak and Hensen’s node and underneath the epiblast are ...
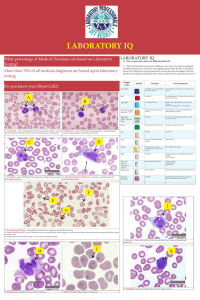
LABORATORY IQ
... Q. Why so many tubes drawn for different blood test? A. Well, you’ll find that each one has a different color of cap. The tubes are designed for different blood tests. Some have anticoagulant agents inside the tube so the blood doesn’t clot. Others have special preservatives. Some tubes get centrif ...
... Q. Why so many tubes drawn for different blood test? A. Well, you’ll find that each one has a different color of cap. The tubes are designed for different blood tests. Some have anticoagulant agents inside the tube so the blood doesn’t clot. Others have special preservatives. Some tubes get centrif ...
Animal Reproduction and Development
... • Early stages, mitotic division results in 1 cell producing 2 cells, etc - creates morula (solid ball of cells). ...
... • Early stages, mitotic division results in 1 cell producing 2 cells, etc - creates morula (solid ball of cells). ...
Blood notes - St Paul`s School Intranet
... foreign agents that invade the body. Others are involved with forming blood clots such as fibrinogen. Plasma also contains a wide variety of substances in transit from one part of the body to another, including nutrients (glucose, amino acids), metabolic wastes (carbon dioxide, urea), respiratory ga ...
... foreign agents that invade the body. Others are involved with forming blood clots such as fibrinogen. Plasma also contains a wide variety of substances in transit from one part of the body to another, including nutrients (glucose, amino acids), metabolic wastes (carbon dioxide, urea), respiratory ga ...
22/18 INVESTIGATOR Name Jeremy P. Brockes Address Ludwig
... Notophthalmus viridescens adult newt after amputation through upper forelimb ...
... Notophthalmus viridescens adult newt after amputation through upper forelimb ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.