Scott Foresman Science
... The Parts of Cells All cells have parts. Some parts are like parts in your body. The cell membrane is like your skin. It holds the cell together. The cell membrane lets some materials, such as water, sugar and oxygen, enter the cell. The cell membrane also lets waste products leave the cell. The cel ...
... The Parts of Cells All cells have parts. Some parts are like parts in your body. The cell membrane is like your skin. It holds the cell together. The cell membrane lets some materials, such as water, sugar and oxygen, enter the cell. The cell membrane also lets waste products leave the cell. The cel ...
Article Questions: "Inside the Womb" Time
... 4. Read the section beginning on page 73, middle column, that begins with "Ironically" through page 74, first column, first full paragraph. Answer the following questions: a. How important is the prenatal environment? ...
... 4. Read the section beginning on page 73, middle column, that begins with "Ironically" through page 74, first column, first full paragraph. Answer the following questions: a. How important is the prenatal environment? ...
Levels of Organization Notes
... are similar in structure and function are usually joined together to form tissues. There are four basic/major types of tissues in the human body: Muscle tissue Nerve tissue Connective tissue Epithelial tissue (There are other kinds of tissues besides these.) Other kinds of tissue include bone tissue ...
... are similar in structure and function are usually joined together to form tissues. There are four basic/major types of tissues in the human body: Muscle tissue Nerve tissue Connective tissue Epithelial tissue (There are other kinds of tissues besides these.) Other kinds of tissue include bone tissue ...
أسئلة مساعدة للطلاب للاختبار النهائى
... e) Renal medulla. 5- Ectoothermic animals: a) derive body heat mainly from their metabolism. b) absorb heat from their surroundings c) include lizards d) include birds e) b and c are correct. ...
... e) Renal medulla. 5- Ectoothermic animals: a) derive body heat mainly from their metabolism. b) absorb heat from their surroundings c) include lizards d) include birds e) b and c are correct. ...
Document
... Pseudocoelom – coelom is not completely lined by tissue derived from mesoderm (pseudocoelomates) Acoelomates – lack a body cavity entirely Fluid-filled body cavity can protect internal organs or be used as hydrostatic skeleton ...
... Pseudocoelom – coelom is not completely lined by tissue derived from mesoderm (pseudocoelomates) Acoelomates – lack a body cavity entirely Fluid-filled body cavity can protect internal organs or be used as hydrostatic skeleton ...
Molecules That Make Up Cells
... • The main function of the reproductive system is to produce offspring. Sex hormone and sperm are produced by the male testes. Male ducts and glands help deliver the sperm. • Ovaries produce female sex hormones and eggs. Other female reproductive structures serve as sites of fertilization and develo ...
... • The main function of the reproductive system is to produce offspring. Sex hormone and sperm are produced by the male testes. Male ducts and glands help deliver the sperm. • Ovaries produce female sex hormones and eggs. Other female reproductive structures serve as sites of fertilization and develo ...
The Organization of Living Things
... • The main function of the reproductive system is to produce offspring. Sex hormone and sperm are produced by the male testes. Male ducts and glands help deliver the sperm. • Ovaries produce female sex hormones and eggs. Other female reproductive structures serve as sites of fertilization and develo ...
... • The main function of the reproductive system is to produce offspring. Sex hormone and sperm are produced by the male testes. Male ducts and glands help deliver the sperm. • Ovaries produce female sex hormones and eggs. Other female reproductive structures serve as sites of fertilization and develo ...
Sponges
... · Sponges are classified as animals because they are multicellular, heterotrophic, have no cell walls and contain a few specialized cells. · "Porifera" means "pore-bearers." Sponges have tiny openings, or pores, all over their bodies. · Sponges are sessile: they spend their entire adult life attache ...
... · Sponges are classified as animals because they are multicellular, heterotrophic, have no cell walls and contain a few specialized cells. · "Porifera" means "pore-bearers." Sponges have tiny openings, or pores, all over their bodies. · Sponges are sessile: they spend their entire adult life attache ...
The Tiny Living World Around Us
... nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine) • Together the sugar, phosphate, and base make a nucleotide • When a bunch of DNA is put together it makes a chromosome ...
... nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine) • Together the sugar, phosphate, and base make a nucleotide • When a bunch of DNA is put together it makes a chromosome ...
ECOLOGY SPRING 2009 - Florida International University
... -Body parts arranged around central axis -Can be bisected into two equal halves in any 2D plane -Bilateral symmetry -Body has right and left halves that are ...
... -Body parts arranged around central axis -Can be bisected into two equal halves in any 2D plane -Bilateral symmetry -Body has right and left halves that are ...
Zoology Semester Exam Study Guide
... 13. The Portuguese Man-Of-War is a member of what class of cnidarians? 14. Food enters a flatworm’s body cavity through a muscular tube called a ____________________. 15. Some flatworms have clusters of nerve cells that control the nervous system. Each cluster is called a(an) ___________. 16. Many f ...
... 13. The Portuguese Man-Of-War is a member of what class of cnidarians? 14. Food enters a flatworm’s body cavity through a muscular tube called a ____________________. 15. Some flatworms have clusters of nerve cells that control the nervous system. Each cluster is called a(an) ___________. 16. Many f ...
COMMUNICATION
... 16) a. In closed circulatory systems the blood is completely contained in the blood vessels. Open circulatory systems, such as those found in molluscs and insects, also have special air spaces (haemocoels) that transport blood around the body. b. Mammals have a closed circulatory system in which the ...
... 16) a. In closed circulatory systems the blood is completely contained in the blood vessels. Open circulatory systems, such as those found in molluscs and insects, also have special air spaces (haemocoels) that transport blood around the body. b. Mammals have a closed circulatory system in which the ...
Document
... Mesoderm: is one of the three primary germ cell layers in the very early embryo Triploblastic: is a condition of the blastula in which there are three primary germ layers: the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm Mesenchyme: is a type of undifferentiated loose connective tissue that is derived mostly fr ...
... Mesoderm: is one of the three primary germ cell layers in the very early embryo Triploblastic: is a condition of the blastula in which there are three primary germ layers: the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm Mesenchyme: is a type of undifferentiated loose connective tissue that is derived mostly fr ...
Chapter 4 - Valhalla High School
... 2. Properties of tissues are influenced by factors such as extracellular material and connections between cells 3. Tissues may be hard, semisolid, or liquid 4. Vary with kind of cells present, cellular arrangement, and types of fibers present ...
... 2. Properties of tissues are influenced by factors such as extracellular material and connections between cells 3. Tissues may be hard, semisolid, or liquid 4. Vary with kind of cells present, cellular arrangement, and types of fibers present ...
Science NIOS - WordPress.com
... Nucleus:The nucleus is a small ovoid or spherical mass located somewhat in the centre of the cytoplasm. • This is the largest organelle. Centrosome(in animal cells only):It is located near the nucleus and contains 1 or 2 centrioles. • It initiates and regulates cell division. Plastids(in plant cells ...
... Nucleus:The nucleus is a small ovoid or spherical mass located somewhat in the centre of the cytoplasm. • This is the largest organelle. Centrosome(in animal cells only):It is located near the nucleus and contains 1 or 2 centrioles. • It initiates and regulates cell division. Plastids(in plant cells ...
Lecture Outline
... cells, and grows from zygote to mature adult in only three and a half days. Most individuals are hermaphrodites, producing both eggs and sperm, which has advantages for genetic studies. Every adult hermaphrodite has exactly 959 somatic cells, which arise from the zygote in virtually the same way for ...
... cells, and grows from zygote to mature adult in only three and a half days. Most individuals are hermaphrodites, producing both eggs and sperm, which has advantages for genetic studies. Every adult hermaphrodite has exactly 959 somatic cells, which arise from the zygote in virtually the same way for ...
Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Animalia
... – Fluid filled body cavity that houses internal organs – Acoelomate – no body cavity (simple animals) – Coelomate – true body cavity (complex animals) ...
... – Fluid filled body cavity that houses internal organs – Acoelomate – no body cavity (simple animals) – Coelomate – true body cavity (complex animals) ...
Leaf Anatomy
... a layer of cells called the epidermis (B). The vascular tissue, xylem and phloem are found within the veins of the leaf. Veins are actually extensions that run from to tips of the roots all the way up to the edges of the leaves. The outer layer of the vein is made of cells called bundle sheath cells ...
... a layer of cells called the epidermis (B). The vascular tissue, xylem and phloem are found within the veins of the leaf. Veins are actually extensions that run from to tips of the roots all the way up to the edges of the leaves. The outer layer of the vein is made of cells called bundle sheath cells ...
How does the food you eat provide energy to cells in
... shapes relate to their functions? Nerve cells have long, branched fibres running from the main part of the cell, shaped to carry nerve signals from one part of the body to another. Red blood cells, which carry oxygen in the bloodstream, have a thin, disklike shape. This gives them a large surface ar ...
... shapes relate to their functions? Nerve cells have long, branched fibres running from the main part of the cell, shaped to carry nerve signals from one part of the body to another. Red blood cells, which carry oxygen in the bloodstream, have a thin, disklike shape. This gives them a large surface ar ...
organisation of living beings2016
... (unspecialised cells) that can divide and develop into specialised cells with a specific function such as neurons or muscle cells… Differentiation is the process of cells becoming specialised . A group of specialised cells of the same type that perform their specialised function is a tissue. Every ...
... (unspecialised cells) that can divide and develop into specialised cells with a specific function such as neurons or muscle cells… Differentiation is the process of cells becoming specialised . A group of specialised cells of the same type that perform their specialised function is a tissue. Every ...
Definitions - Acsu.buffalo.edu
... Germ layers of vertebrate embryos: Ectoderm (ectos "outside"), the outermost layer which forms the nervous system and skin; Endoderm (endon "within") the innermost layer that forms the lining of the digestive tract and associated organs; Mesoderm (mesos "middle"), the middle layer gives rise to the ...
... Germ layers of vertebrate embryos: Ectoderm (ectos "outside"), the outermost layer which forms the nervous system and skin; Endoderm (endon "within") the innermost layer that forms the lining of the digestive tract and associated organs; Mesoderm (mesos "middle"), the middle layer gives rise to the ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology
... Levels of Organization of Multicellular Organisms 1. Cells ~ the basic unit of structure and function of living organisms 2. Tissues ~ similar cells that are grouped together to perform a similar function 3. Organs ~ tissues grouped together to perform a specific function. One organ may contain mor ...
... Levels of Organization of Multicellular Organisms 1. Cells ~ the basic unit of structure and function of living organisms 2. Tissues ~ similar cells that are grouped together to perform a similar function 3. Organs ~ tissues grouped together to perform a specific function. One organ may contain mor ...
Use for Nov. 20,12 Unit 2 Cells Test Study Guide
... 20. Water is a good solvent. Explain what this means. 21. The diagram shows two solutions that are separated by a partially permeable membrane. In which direction will most water molecules move in relation to their concentration gradient? Draw an arrow showing the direction of movement. ...
... 20. Water is a good solvent. Explain what this means. 21. The diagram shows two solutions that are separated by a partially permeable membrane. In which direction will most water molecules move in relation to their concentration gradient? Draw an arrow showing the direction of movement. ...
Organ Systems Reading
... Cells, like these nerve cells, do not work in isolation. To send orders from your brain to your legs, for example, signals pass through many nerve cells. These cells work together to perform a similar function. Just as muscle cells work together, bone cells and many other cells do as well. A group o ...
... Cells, like these nerve cells, do not work in isolation. To send orders from your brain to your legs, for example, signals pass through many nerve cells. These cells work together to perform a similar function. Just as muscle cells work together, bone cells and many other cells do as well. A group o ...
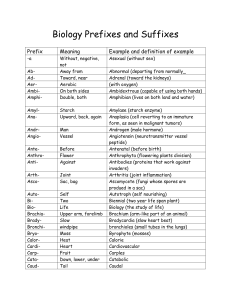
Biology Prefixes and Suffixes
... isogamy (fusion of male and female gametes that are the same size and structure) karyogamy (uniting of cell nuclei; fertilization) keratectomy (removal of a part of the cornea) lactose (milk sugar) leukocytes (white blood cells) lithosphere (the solid rocky crust of the earth) lutein (yellow caroten ...
... isogamy (fusion of male and female gametes that are the same size and structure) karyogamy (uniting of cell nuclei; fertilization) keratectomy (removal of a part of the cornea) lactose (milk sugar) leukocytes (white blood cells) lithosphere (the solid rocky crust of the earth) lutein (yellow caroten ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.