Slide 1 - cloudfront.net
... If the egg is not fertilized, it breaks down and passes out of the body along with the lining of the uterus and used blood in a process called …. ...
... If the egg is not fertilized, it breaks down and passes out of the body along with the lining of the uterus and used blood in a process called …. ...
Vertebrate Bodies and Systems
... Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom into two parts Thoracic cavity: Heart and lungs P it Peritoneal l (abdominal) ( bd i l) cavity: it Stomach, St h intestine ...
... Digestive tube suspended in coelom from mouth to anus Body supported by internal skeleton of jointed bones Vertebrae and Cranium protects nervous system Diaphragm divides coelom into two parts Thoracic cavity: Heart and lungs P it Peritoneal l (abdominal) ( bd i l) cavity: it Stomach, St h intestine ...
Blood
... The blood consists of a suspension of special cells - formed elements in a liquid called plasma In an adult man: the blood is about 1/12th of the body weight and this corresponds to 5-6 liters ...
... The blood consists of a suspension of special cells - formed elements in a liquid called plasma In an adult man: the blood is about 1/12th of the body weight and this corresponds to 5-6 liters ...
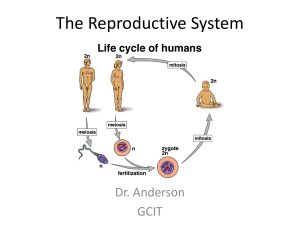
The Reproductive System
... • The female reproductive system is more complex than the male system because: – Used for copulation – Must support the growth and development of the baby for 9 months! ...
... • The female reproductive system is more complex than the male system because: – Used for copulation – Must support the growth and development of the baby for 9 months! ...
Invertebrates – have no backbone
... Filter Feeders - aquatic animals that strain food from water Parasite - lives in or on another organism (symbiotic relationship) ...
... Filter Feeders - aquatic animals that strain food from water Parasite - lives in or on another organism (symbiotic relationship) ...
Chapter 10 Pt 1 - s3.amazonaws.com
... Diploblastic Organization Derived from 2 embryological layers: ...
... Diploblastic Organization Derived from 2 embryological layers: ...
Chapters 25 & 26 Notes
... Some (sponges and coral) move only during the early stages of their lives- they hatch from egs into free swimming larvae- They become attached to a rock (etc.) when they become adults 11. Organisms that don’t move from place to place are known as sessile organisms Animals must digest food ...
... Some (sponges and coral) move only during the early stages of their lives- they hatch from egs into free swimming larvae- They become attached to a rock (etc.) when they become adults 11. Organisms that don’t move from place to place are known as sessile organisms Animals must digest food ...
FULL TEXT
... phase is morphogenesis, which involves movement of the cell mass and the complex interactions between them in the formation of organs and systems. The third phase is the differentiation thru which specialized and gradually improved cellular structures involved in the organs and the systems can perfo ...
... phase is morphogenesis, which involves movement of the cell mass and the complex interactions between them in the formation of organs and systems. The third phase is the differentiation thru which specialized and gradually improved cellular structures involved in the organs and the systems can perfo ...
Organization of the Animal Body
... Tissue - a group of cells with similar structure and functions ...
... Tissue - a group of cells with similar structure and functions ...
Sponge and Cnidarian
... 9. The supporting and defensive structures in sponges. 10. Sponges are organized at the cellular grade and don't have cells organized as these. Cnidarians 1. Instead of dorsal and ventral sides, cnidarians have oral and this surface. 2. A cnidarian gastrovascular cavity is an incomplete gut because ...
... 9. The supporting and defensive structures in sponges. 10. Sponges are organized at the cellular grade and don't have cells organized as these. Cnidarians 1. Instead of dorsal and ventral sides, cnidarians have oral and this surface. 2. A cnidarian gastrovascular cavity is an incomplete gut because ...
File
... • Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that are released from the endings of neurons onto other neurons, muscle cells, or gland cells. ...
... • Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that are released from the endings of neurons onto other neurons, muscle cells, or gland cells. ...
Organization of life - PBS Science Grade 7
... Anything that can live on its own is called an organism. All organism are made up of a least one cell. If a single cell is living on it own it is called unicellular ...
... Anything that can live on its own is called an organism. All organism are made up of a least one cell. If a single cell is living on it own it is called unicellular ...
video slide
... (a) Fertilized egg. Shown here is the (b) Four-cell stage. Remnants of the (c) Morula. After further cleavage mitotic spindle can be seen divisions, the embryo is a zygote shortly before the first between the two cells that have multicellular ball that is still cleavage division, surrounded just com ...
... (a) Fertilized egg. Shown here is the (b) Four-cell stage. Remnants of the (c) Morula. After further cleavage mitotic spindle can be seen divisions, the embryo is a zygote shortly before the first between the two cells that have multicellular ball that is still cleavage division, surrounded just com ...
HIGHLIGHTS FOR 7TH GRADE SCIENCE CURRICULUM Cells
... Lysosomes- act like a digestive system. Can digest compounds and old organelles. Mitochondria- convert chemical energy into compounds that can be used by the cell. Plants have 3 additional structures: 1- cell wall- rigid/stiff wall. for protection. contains cellulose. 2- chloroplasts- captures energ ...
... Lysosomes- act like a digestive system. Can digest compounds and old organelles. Mitochondria- convert chemical energy into compounds that can be used by the cell. Plants have 3 additional structures: 1- cell wall- rigid/stiff wall. for protection. contains cellulose. 2- chloroplasts- captures energ ...
Animal Form and Function (Ch. 40)
... 1. cell – basic unit; many types; dozens to hundreds of types in most adult vertebrates 2. tissue – a group of cells similar in structure and function most differentiate early in development from three embryonic germ layers endoderm (innermost) mesoderm ectoderm four primary tissues in adu ...
... 1. cell – basic unit; many types; dozens to hundreds of types in most adult vertebrates 2. tissue – a group of cells similar in structure and function most differentiate early in development from three embryonic germ layers endoderm (innermost) mesoderm ectoderm four primary tissues in adu ...
notes - Northwest Nazarene University
... layers develop during _______________ Inner layer – ______________ Outer layer – ______________ ___________ - 3rd layer in bilateral animals ...
... layers develop during _______________ Inner layer – ______________ Outer layer – ______________ ___________ - 3rd layer in bilateral animals ...
Document
... Skin – melanoblast Lungs -kulchitsky cells Heart – myoendocrine Urogenital tract Hypothalamus Git ...
... Skin – melanoblast Lungs -kulchitsky cells Heart – myoendocrine Urogenital tract Hypothalamus Git ...
Cell Specialization and Levels of Organization
... • Embryonic stem cells are found in embryos that are less than a week old • In the lab these totipotent stem cells are able to keep dividing for up to a year without differentiating – Can make any one of the 300 cell types found in an adult human ...
... • Embryonic stem cells are found in embryos that are less than a week old • In the lab these totipotent stem cells are able to keep dividing for up to a year without differentiating – Can make any one of the 300 cell types found in an adult human ...
TSM3 - Development of the CNS and PNS
... The folds in the neural plate fuse together to form the neural tube which is contained within the mesoderm and fully formed by the fourth week of development The neural tube then undergoes further growth and distortion to form the primary vesicles o The primitive forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain ap ...
... The folds in the neural plate fuse together to form the neural tube which is contained within the mesoderm and fully formed by the fourth week of development The neural tube then undergoes further growth and distortion to form the primary vesicles o The primitive forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain ap ...
Lecture
... many similarities with mammals the acrosomal reaction is triggered when the sperm meets the egg binding of the sperm to a receptor on the egg triggers this reaction – 1. docking onto the jelly layer activates the acrosome at the tip of the sperm – 2. acrosome releases hydrolytic enzymes that digest ...
... many similarities with mammals the acrosomal reaction is triggered when the sperm meets the egg binding of the sperm to a receptor on the egg triggers this reaction – 1. docking onto the jelly layer activates the acrosome at the tip of the sperm – 2. acrosome releases hydrolytic enzymes that digest ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.