Organization of Living Things
... Anything that can live on its own is called an organism. If the organism is only a single cell, it is called a ...
... Anything that can live on its own is called an organism. If the organism is only a single cell, it is called a ...
B cells
... develop in bone marrow proliferate, differentiate into: Plasma cells antibody factories short lived antibodies bind antigens, provide protection Memory cells produced from some B cells long lived respond quickly upon reexposure to Ag ...
... develop in bone marrow proliferate, differentiate into: Plasma cells antibody factories short lived antibodies bind antigens, provide protection Memory cells produced from some B cells long lived respond quickly upon reexposure to Ag ...
Levels of Organization
... Capturing of sunlight and carbon dioxide by plants to make sugar and complex carbohydrates Plants provide the energy for the rest of life Oxygen is a by-product of this process ...
... Capturing of sunlight and carbon dioxide by plants to make sugar and complex carbohydrates Plants provide the energy for the rest of life Oxygen is a by-product of this process ...
Phylum Porifera
... Reproduction: sexual-Hermaphrodites(have sperm & egg)-Both sexes in same organism called monoecious: asexual- bud; Regenerate body parts ...
... Reproduction: sexual-Hermaphrodites(have sperm & egg)-Both sexes in same organism called monoecious: asexual- bud; Regenerate body parts ...
Developmental Patterns
... a. An outer layer of cells surrounding the blastocoel, called ectoderm b. An inner layer of cells is called endoderm – The gut opens only at the blastopore it is called a blind or incomplete gut. Animals with a blind gut must consume food completely digested, or the remains of the food egested throu ...
... a. An outer layer of cells surrounding the blastocoel, called ectoderm b. An inner layer of cells is called endoderm – The gut opens only at the blastopore it is called a blind or incomplete gut. Animals with a blind gut must consume food completely digested, or the remains of the food egested throu ...
Review PPT
... •The reproductive system is different from the other systems because it is made up of ________ organs in males and females. Meaning: Male reproductive organs and female reproductive organs are not the same. Do males and females have different digestive organs? Skeletal systems? Nervous systems? ...
... •The reproductive system is different from the other systems because it is made up of ________ organs in males and females. Meaning: Male reproductive organs and female reproductive organs are not the same. Do males and females have different digestive organs? Skeletal systems? Nervous systems? ...
Human Body Organization - Livingstone High School
... Cells of the same type joined together are called TISSUES Different Tissues are joined together to form ORGANS Various organs are arranged into an ORGAN SYSTEM ...
... Cells of the same type joined together are called TISSUES Different Tissues are joined together to form ORGANS Various organs are arranged into an ORGAN SYSTEM ...
Human Body Organization
... Cells of the same type joined together are called TISSUES Different Tissues are joined together to form ORGANS Various organs are arranged into an ORGAN SYSTEM ...
... Cells of the same type joined together are called TISSUES Different Tissues are joined together to form ORGANS Various organs are arranged into an ORGAN SYSTEM ...
Science Study Guide
... 4. Critical Thinking: If you stand at one end of a room and spray perfume into the air, a person at the other end of the room will soon smell the perfume. Explain. ...
... 4. Critical Thinking: If you stand at one end of a room and spray perfume into the air, a person at the other end of the room will soon smell the perfume. Explain. ...
Topic 17: Reproduction
... Many sperms reach the egg, each sperm produces enzymes from its head to digest a way into the egg The sperm leaves the tail outside then the nucleus of the sperm and that of ovum fuse together to form the zygote Once a sperm has succeeded in penetrating the egg , a fertilization membrane is formed q ...
... Many sperms reach the egg, each sperm produces enzymes from its head to digest a way into the egg The sperm leaves the tail outside then the nucleus of the sperm and that of ovum fuse together to form the zygote Once a sperm has succeeded in penetrating the egg , a fertilization membrane is formed q ...
Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems
... DIVISION OF LABOR •An organism’s body divides up the labor into sections depending on the function. ...
... DIVISION OF LABOR •An organism’s body divides up the labor into sections depending on the function. ...
Notes on Human Anatomy for Final Exam
... The ovaries are about the size and shape of almonds. At birth, a female baby’s ovaries already contains all of its eggs. ...
... The ovaries are about the size and shape of almonds. At birth, a female baby’s ovaries already contains all of its eggs. ...
Document
... A) have a body cavity, whereas pseudocoelomates have a solid body. B) contain tissues derived from mesoderm, whereas pseudocoelomates have no such tissue. C) have a body cavity completely lined by mesodermal tissue, whereas pseudocoelomates do not. D) have a complete digestive system with mouth and ...
... A) have a body cavity, whereas pseudocoelomates have a solid body. B) contain tissues derived from mesoderm, whereas pseudocoelomates have no such tissue. C) have a body cavity completely lined by mesodermal tissue, whereas pseudocoelomates do not. D) have a complete digestive system with mouth and ...
Reproduction and Meiosis PowerPoint Notes
... unites with the ____________ set of chromosomes from the ____________. Human sex chromosomes carry ____________ that determine whether the offspring is male or female. Females have ______ ___ chromosomes. Males have ______ ______ chromosome and _____ ______ chromosome. During meiosis, ______ of each ...
... unites with the ____________ set of chromosomes from the ____________. Human sex chromosomes carry ____________ that determine whether the offspring is male or female. Females have ______ ___ chromosomes. Males have ______ ______ chromosome and _____ ______ chromosome. During meiosis, ______ of each ...
1. List characteristics that distinguish animals from
... concentrating sensory equipment at the anterior end is called… The blastopore will either become the mouth or the ____ of the animal. ...
... concentrating sensory equipment at the anterior end is called… The blastopore will either become the mouth or the ____ of the animal. ...
Choanocyte (collar cell)
... -Only some species (hydra) ...a new organisms grows off of the parent and then 'buds" off --Sexual ...
... -Only some species (hydra) ...a new organisms grows off of the parent and then 'buds" off --Sexual ...
Embryo final study tips
... supporting tissue of the embryo, most of the body CT and stromal components of the glands and mesenchyme intraembryonic mesoderm. The primitive streak actively forms mesoderm until the early part of the 4th week, then it diminishes in size to become an insignificant structure in the sacrococcygeal ...
... supporting tissue of the embryo, most of the body CT and stromal components of the glands and mesenchyme intraembryonic mesoderm. The primitive streak actively forms mesoderm until the early part of the 4th week, then it diminishes in size to become an insignificant structure in the sacrococcygeal ...
Y8_Cells_Summary - Ralph Thoresby School
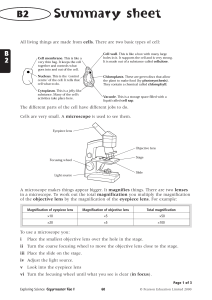
... The object you want to look at using a microscope is called the specimen. It has to be thin to let light get through it. It is placed, with a drop of water, onto a slide. A coverslip is put on top. The coverslip stops the specimen from drying out, holds it flat and stops it moving. A stain might be ...
... The object you want to look at using a microscope is called the specimen. It has to be thin to let light get through it. It is placed, with a drop of water, onto a slide. A coverslip is put on top. The coverslip stops the specimen from drying out, holds it flat and stops it moving. A stain might be ...
Document
... This process is called _________________. Although a cell is small, it is not stupid – before it ______________ it makes an extra copy of everything in the _____________. This means the two daughter cells have a _________ nucleus. This is important because the nucleus contains the “__________” (DNA) ...
... This process is called _________________. Although a cell is small, it is not stupid – before it ______________ it makes an extra copy of everything in the _____________. This means the two daughter cells have a _________ nucleus. This is important because the nucleus contains the “__________” (DNA) ...
File - Ms. Tripp
... 11.12 Plant cloning shows that differentiated cells may retain all of their genetic potential • When the cells from a carrot are transferred to a culture medium, a single cell can divide and grow into an adult plant. • On a larger scale, this technique can be used to produce hundreds or thousands o ...
... 11.12 Plant cloning shows that differentiated cells may retain all of their genetic potential • When the cells from a carrot are transferred to a culture medium, a single cell can divide and grow into an adult plant. • On a larger scale, this technique can be used to produce hundreds or thousands o ...
Tissues and Organs - sciencelanguagegallery
... Tissues made up of the same cells Eg. Cardiac heart muscle red blood cells Organs made up of different tissues Eg. Heart is composed of Cardiac muscle, nerve cells, fat cells, connective tissue and red blood cells ...
... Tissues made up of the same cells Eg. Cardiac heart muscle red blood cells Organs made up of different tissues Eg. Heart is composed of Cardiac muscle, nerve cells, fat cells, connective tissue and red blood cells ...
Development and Inheritance
... The genetic material from a haploid sperm cell and a haploid secondary oocyte merges into a single diploid nucleus ...
... The genetic material from a haploid sperm cell and a haploid secondary oocyte merges into a single diploid nucleus ...
Sea anemone - Cloudfront.net
... layers separated by mesoglea (noncellular jelly like material) • Outer tissue layer has 3 cell types: – Contracting cells cover the surface of the cnidarian & contain muscle fibers – Nerve cells interconnect & form a network over the entire animal (they do not have brains) – Cnidocytes special ...
... layers separated by mesoglea (noncellular jelly like material) • Outer tissue layer has 3 cell types: – Contracting cells cover the surface of the cnidarian & contain muscle fibers – Nerve cells interconnect & form a network over the entire animal (they do not have brains) – Cnidocytes special ...
Document
... where 2 bones meet? 19. As blood flows to the heart from the toes and fingers, it travels mainly through what tissue? 20. In which vessels are materials exchanged between the blood and the body cells? 21. One of the main purposes of the circulatory system is to take oxygen to all the cells in the bo ...
... where 2 bones meet? 19. As blood flows to the heart from the toes and fingers, it travels mainly through what tissue? 20. In which vessels are materials exchanged between the blood and the body cells? 21. One of the main purposes of the circulatory system is to take oxygen to all the cells in the bo ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.