* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes on Human Anatomy for Final Exam
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Umbilical cord wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
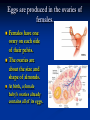
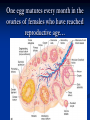
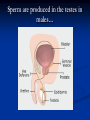
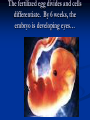
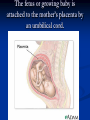
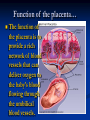
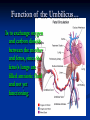
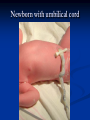
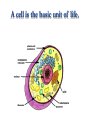
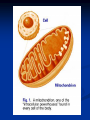
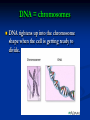
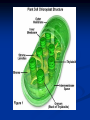
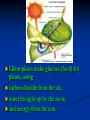
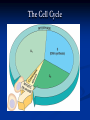
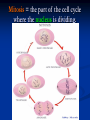
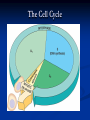
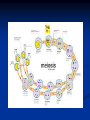
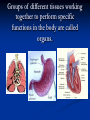
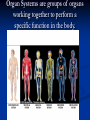
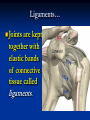
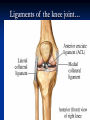
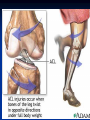
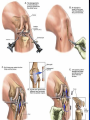
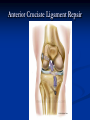
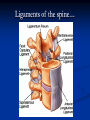
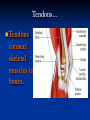
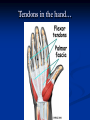
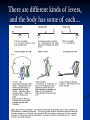
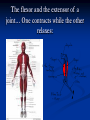
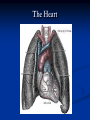
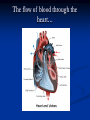
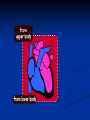
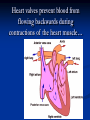
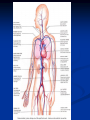
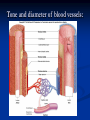
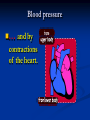
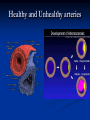
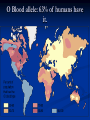
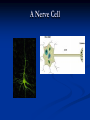
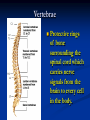
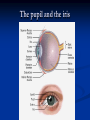
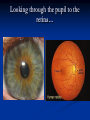
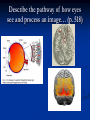
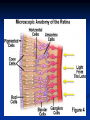
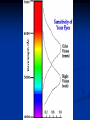
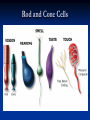
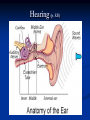
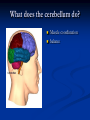
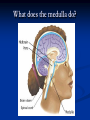
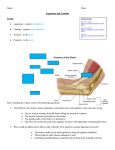
Notes on Human Anatomy for Final Exam Dr. Beck Life Science Eggs are produced in the ovaries of females. Females have one ovary on each side of their pelvis. The ovaries are about the size and shape of almonds. At birth, a female baby’s ovaries already contains all of its eggs. One egg matures every month in the ovaries of females who have reached reproductive age… Sperm are produced in the testes in males… Many sperm meet one egg… A scanning electron microscope shows a 3-D image of a sperm penetrating the egg… 4-day old embryo showing cell division… The fertilized egg divides and cells differentiate. By 6 weeks, the embryo is developing eyes… At 3 months the embryo is called a fetus. The fetus or growing baby is attached to the mother’s placenta by an umbilical cord. The umbilical cord and placenta are temporary organs of pregnancy. Function of the placenta… The function of the placenta is to provide a rich network of blood vessels that can deliver oxygen to the baby’s blood flowing through the umbilical blood vessels. Function of the Umbilicus… Is to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide between the mother and fetus, since the fetus’s lungs are filled amniotic fluid and not yet functioning. Newborn with umbilical cord The placenta “afterbirth” A cell is the basic unit of life. Final Questions: read and think carefully – you know this! Which organelle liberates energy from the food you eat for the work of the cell? Mitochondria! Make ATP from the food you eat. Like refining crude oil to gasoline so your car– or your cells– can run! Another final question…. Which part of a cell contains the genetic information that determines the characteristics the organism will have? The nucleus! Safely stored inside the nuclear membrane is the DNA that contains the recipes for all of the organism’s proteins. DNA is the genetic molecule that contains the genes. DNA = chromosomes DNA tightens up into the chromosome shape when the cell is getting ready to divide. What is the main function of chloroplasts? Chloroplasts make glucose (food) for plants, using carbon dioxide from the air, water brought up by the roots, and energy from the sun. There are many types of cells in the body, but they all have the same DNA in the nucleus and the same basic organelles. The Cell Cycle Mitosis = the part of the cell cycle where the nucleus is dividing. The Cell Cycle Mitosis is necessary for… Growth Repair of injuries Replacement of old cells Meiosis is another form of cell division… Only to form sex cells with half the number of chromosomes as a normal body cell. Sex cells are also called “gametes”: Body Organization A group of similar cells form…tissues. Groups of different tissues working together to perform specific functions in the body are called organs. Organ Systems are groups of organs working together to perform a specific function in the body. Muscles and Bones Ligaments… Joints are kept together with elastic bands of connective tissue called ligaments. Ligaments of the knee joint… Anterior Cruciate Ligament Repair Ligaments of the spine… A ball and socket joint … … is like the joystick on a computer. This type of joint enables your arm to move freely. The shoulder joint… Tendons… Tendons connect skeletal muscles to bones. Tendons in the hand… So what is the difference between ligaments and tendons? Ligaments are bone to bone connections. Tendons are muscle to bone connections. What kind of machine do most bones work like? Bones often work like a type of machine called a lever… That is why we have long bones. There are different kinds of levers, and the body has some of each… A lever… … is a rigid bar that moves on a fixed point known as a __fulcrum_. Muscles work in pairs… The flexor and the extensor of a joint… One contracts while the other relaxes: If a muscle bends a joint… it is called a flexor. … If a muscle straightens a joint… … it is called an extensor. Anabolic steroids … …lead to problems in the heart, liver, kidneys , and can cause high blood pressure. Steroids can also cause bones in young people to stop growing. They can cause a decrease in size of testicles in males, leading to lower testosterone levels and development of female characteristics. Do you think this is attractive? The Heart The flow of blood through the heart… Heart valves prevent blood from flowing backwards during contractions of the heart muscle… Artificial heart valves… Surgery to replace damaged or diseased heart valves… What are they checking? You need blood pressure~ Blood Pressure The force exerted by blood on the inside walls of a blood vessel is called blood pressure. Blood pressure is caused by: Tone and diameter of the blood vessels and by the contractions of the heart. Tone and diameter of blood vessels: Blood pressure … and by contractions of the heart. Healthy and Unhealthy arteries B allele: 16% of humans have it. A allele: 21 % of humans have it. O Blood allele: 63% of humans have it. What does a nerve cell look like? A Nerve Cell Vertebrae Protective rings of bone surrounding the spinal cord which carries nerve signals from the brain to every cell in the body. The pupil and the iris Looking through the pupil to the retina… Describe the pathway of how eyes see and process an image… (p. 518) Rod and Cone Cells Hearing (p. 520) Cerebrum What does the cerebrum do? Page 608 Thinking and learning Muscle movement Senses (sight, touch, taste, smell, hearing) memory What does the cerebellum do? Muscle coordination balance What does the medulla do? Medulla or brainstem Involuntary muscle movement Heartbeat respiration