Animal Development
... sperm migrates through a layer of follicle cells before it reaches the zona pellucida. The envelopes of both the egg and sperm nuclei disperse. ...
... sperm migrates through a layer of follicle cells before it reaches the zona pellucida. The envelopes of both the egg and sperm nuclei disperse. ...
CG--SCI-answers-NJ.ASK - Grade 8 Learning from the Fossil
... 7. This organism (flies) starts out as an egg, and it starts to grow and becomes maggots (aka larvae). When the organism is an egg, it’s like when humans are babies. When they become maggots, we are children. The flies then mature into pupae. That is around the same stage in humans when we are adole ...
... 7. This organism (flies) starts out as an egg, and it starts to grow and becomes maggots (aka larvae). When the organism is an egg, it’s like when humans are babies. When they become maggots, we are children. The flies then mature into pupae. That is around the same stage in humans when we are adole ...
Prefix-Suffix Worksheet Define the following terms using your prefix
... Define the following terms using your prefix-suffix list. Underline the prefix &/or suffix in each biological term. Example: THERMOMETER – therm means heat & meter means measure of so a thermometer is an instrument used to measure heat. 1. Biology 2. Osteocyte 3. Dermatitis 4. Epidermis 5. Hematolog ...
... Define the following terms using your prefix-suffix list. Underline the prefix &/or suffix in each biological term. Example: THERMOMETER – therm means heat & meter means measure of so a thermometer is an instrument used to measure heat. 1. Biology 2. Osteocyte 3. Dermatitis 4. Epidermis 5. Hematolog ...
of the cell - MrMsciences
... • In plant cells- they are very large and hold lots of water and nutrients; tonoplast membrane controls exchange; also holds pigments the give flowers color • Creates turgid pressure to keep plant up right • In animal cells- very small; transport things inside the cell ...
... • In plant cells- they are very large and hold lots of water and nutrients; tonoplast membrane controls exchange; also holds pigments the give flowers color • Creates turgid pressure to keep plant up right • In animal cells- very small; transport things inside the cell ...
Biology_Review_2012
... 26. During ____________________ the nucleus of the cell divides 27. Water moves through a cell membrane by a process called __________________________ 28. _________________________ is the longest stage of cell division 29. A ______________________ is a test in which a sample of living cells is remov ...
... 26. During ____________________ the nucleus of the cell divides 27. Water moves through a cell membrane by a process called __________________________ 28. _________________________ is the longest stage of cell division 29. A ______________________ is a test in which a sample of living cells is remov ...
Kingdom Animalia
... anemones) develop three cell layers at an early stage in the growth of the embryo. These layers are: ectoderm, (outer layer) mesoderm (inner layer) endoderm (inner layer) The early development of these three layers in the embryo helps to sort cells into an arrangement that produces the special ...
... anemones) develop three cell layers at an early stage in the growth of the embryo. These layers are: ectoderm, (outer layer) mesoderm (inner layer) endoderm (inner layer) The early development of these three layers in the embryo helps to sort cells into an arrangement that produces the special ...
Red Blood Cells Red blood cells main job, or function, is to take in
... The main job of muscle cells is to contract, or shorten in order to produce movement. They may contract to move your body, or pump your heart, or move food along your digestive tract. How does the structure of a muscle cell help it do its job? ...
... The main job of muscle cells is to contract, or shorten in order to produce movement. They may contract to move your body, or pump your heart, or move food along your digestive tract. How does the structure of a muscle cell help it do its job? ...
Cells & Tissues
... similar cells which work together. Epithelium - Tissues composed of layers of cells that cover organ surfaces such as surface of the skin and inner lining of digestive tract: the tissues that serve for protection, secretion, and absorption. Connective tissue - As the name suggests, connective tissue ...
... similar cells which work together. Epithelium - Tissues composed of layers of cells that cover organ surfaces such as surface of the skin and inner lining of digestive tract: the tissues that serve for protection, secretion, and absorption. Connective tissue - As the name suggests, connective tissue ...
1. List characteristics that distinguish animals from
... each embryonic cell is established very early if a cell is isolated from the 4-cell stage the embryo will not fully develop • Indeterminate early embryonic cells retain capacity to develop into a complete embryo if isolated from other cells: this type of cleavage in the human zygote results in i ...
... each embryonic cell is established very early if a cell is isolated from the 4-cell stage the embryo will not fully develop • Indeterminate early embryonic cells retain capacity to develop into a complete embryo if isolated from other cells: this type of cleavage in the human zygote results in i ...
Chapter 15- Lateral mesoderm and endoderm
... Splanchnic mesoderm -becomes body cavity wall and the the heart ...
... Splanchnic mesoderm -becomes body cavity wall and the the heart ...
Chapter 28
... Have middle tissue layer Tissues organized into organs Bilateral symmetry Cephalization ...
... Have middle tissue layer Tissues organized into organs Bilateral symmetry Cephalization ...
TWO TYPES OF CELLS
... 1. You will be able to explain what cells are and 2. You will be able to differentiate between the 2 types of cells. ...
... 1. You will be able to explain what cells are and 2. You will be able to differentiate between the 2 types of cells. ...
Neurulation - Dr. Salah A. Martin
... to form a tube, the gut, and the mesoderm moves between the endoderm and ectoderm. As tubulation is completed the embryo is now at the neural plate stage (neurula) and is ready for the formation of the primary organ rudiments. The endoderm has now moved up over the roof of the archenteron and connec ...
... to form a tube, the gut, and the mesoderm moves between the endoderm and ectoderm. As tubulation is completed the embryo is now at the neural plate stage (neurula) and is ready for the formation of the primary organ rudiments. The endoderm has now moved up over the roof of the archenteron and connec ...
Lab 8: Chick 72 hours Lab 8: Chick, 72 hours
... Digestive system and endoderm derivatives • At 72 hours the endodermal derivatives such as the lung buds begin to rapidly expand into the mesenchyme of mesoderm origin. • The esophagus, p g , stomach,, liver and duodenum are just beginning to form. Try to trace the connections between these tissues ...
... Digestive system and endoderm derivatives • At 72 hours the endodermal derivatives such as the lung buds begin to rapidly expand into the mesenchyme of mesoderm origin. • The esophagus, p g , stomach,, liver and duodenum are just beginning to form. Try to trace the connections between these tissues ...
Homeoboxes
... 1. Specialized cells (nervous and muscular are not found in any other multicellular organism 2. Cells are held together by proteins (mostly collagen which is only found in animals) -Reproduction is mostly sexual with the 2n version dominating life -Development into layers - leads to organs and tissu ...
... 1. Specialized cells (nervous and muscular are not found in any other multicellular organism 2. Cells are held together by proteins (mostly collagen which is only found in animals) -Reproduction is mostly sexual with the 2n version dominating life -Development into layers - leads to organs and tissu ...
CELL PROCESSES A selectively permeable cell membrane allows
... The blood is returned to the heart from all parts of the body by the veins. Arteries and veins are connected by capillaries, which allow the exchange of nutrients and gases. Capillaries have two adaptations for this: ...
... The blood is returned to the heart from all parts of the body by the veins. Arteries and veins are connected by capillaries, which allow the exchange of nutrients and gases. Capillaries have two adaptations for this: ...
Levels of Organization
... Before a human being develops, an egg and sperm unite to form a zygote. A zygote is a fertilized egg. It is made of just one cell. Then the zygote begins to divide, and the cells that it forms also divide. This process continues for a few weeks. The cells that form during this time are called embryo ...
... Before a human being develops, an egg and sperm unite to form a zygote. A zygote is a fertilized egg. It is made of just one cell. Then the zygote begins to divide, and the cells that it forms also divide. This process continues for a few weeks. The cells that form during this time are called embryo ...
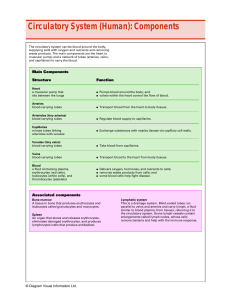
Circulatory System (Human): Components
... Circulatory System (Human): Components The circulatory system carries blood around the body, supplying cells with oxygen and nutrients and removing waste products. The main components are the heart (a muscular pump) and a network of tubes (arteries, veins, and capillaries) to carry the blood. ...
... Circulatory System (Human): Components The circulatory system carries blood around the body, supplying cells with oxygen and nutrients and removing waste products. The main components are the heart (a muscular pump) and a network of tubes (arteries, veins, and capillaries) to carry the blood. ...
7.2 Many organisms, including humans, have specialized organ
... 2. Organisms are made of tiny cells that perform the basic life functions and keep the organism alive. Many organisms (for example yeast, algae) are single-celled and many organisms (for example plants, fungi and animals) are made of millions of cells that work in coordination. 3. All cells come fro ...
... 2. Organisms are made of tiny cells that perform the basic life functions and keep the organism alive. Many organisms (for example yeast, algae) are single-celled and many organisms (for example plants, fungi and animals) are made of millions of cells that work in coordination. 3. All cells come fro ...
Animal Development
... • Their bodies are held together by structural proteins such as collagen • Nervous tissue and muscle tissue are unique, defining characteristics of animals • Tissues are groups of cells that have a common structure, function, or both ...
... • Their bodies are held together by structural proteins such as collagen • Nervous tissue and muscle tissue are unique, defining characteristics of animals • Tissues are groups of cells that have a common structure, function, or both ...
Chapter 3
... Match the type of cell junction with the best description. Answers may be used once, more than once, or not at all. A. gap junction B. tight junction C. anchoring junction 21) simplest cell-cell junction ...
... Match the type of cell junction with the best description. Answers may be used once, more than once, or not at all. A. gap junction B. tight junction C. anchoring junction 21) simplest cell-cell junction ...
Cells Study Guide
... barrier by protecting the cell from the outside world. o All cells need to take in energy and raw materials and give off wastes. o Materials move through the cell membrane both into and outward by the use of active transport and passive transport. o Passive Transport is when the cell does not use en ...
... barrier by protecting the cell from the outside world. o All cells need to take in energy and raw materials and give off wastes. o Materials move through the cell membrane both into and outward by the use of active transport and passive transport. o Passive Transport is when the cell does not use en ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.