* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is an Animal?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
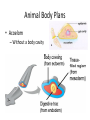
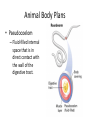
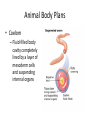
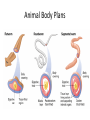
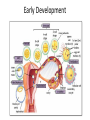
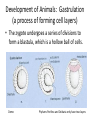
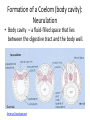
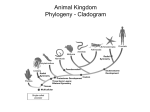
What is an Animal? A multicellular organism of the kingdom Animalia that uses locomotion, metabolism, pronounced response to stimuli, and fixed bodily structure Characteristics of Animals • All animals have several characteristics in common. What are the four common characteristics of animals? – Eukaryotic – Multicellular – Heterotrophic – No cell wall What Do Animals Do to Survive? • • • • • • • Feed Respire Circulate Excrete Respond Move Reproduce Trends in Animal Evolution • Your survey of the animal kingdom will begin with simple forms and move through more complicated ones. Phylogenetic relationships: Trends in Animal Evolution Cell Specialization and Levels of Organization • Groups of specialized cells that work together form tissues. • Tissues join together to form organs. • Group of organs work together to form organ systems – EX: Circulatory system Cephalization • Concentration of sense organs and nerve cells at the front end or head of the body. Flatworm • Range in size from .2 inches to 50 feet! Animal Body Plans • What is symmetry? Arrangement of body parts on opposite sides of a plane or line Asymmetry Radial Symmetry Bilateral Symmetry What type of symmetry? • Radial What type of symmetry? • Bilateral What type of symmetry? • Asymmetrical What type of symmetry? • Radial Animal Body Plans • Acoelom – Without a body cavity Animal Body Plans • Pseudocoelom – Fluid-filled internal space that is in direct contact with the wall of the digestive tract. Animal Body Plans • Coelom – Fluid-filled body cavity completely lined by a layer of mesoderm cells and suspending internal organs Animal Body Plans How do these body plans develop? Early Development Development of Animal Body Plans • Cell Division – The zygote divides by mitosis and cell division to form two cells in a process called cleavage. – How important is this first cell division? • Problems can lead to defects in embryo Zygote Development of Animals: Gastrulation (a process of forming cell layers) • The zygote undergoes a series of divisions to form a blastula, which is a hollow ball of cells. Demo Phylums Porifera and Cnidaria only have two layers Protostome vs. deuterostome Mouth is formed from the blastopore Anus is formed from the blastopore Formation of a Coelom (body cavity): Neurulation • Body cavity – a fluid-filled space that lies between the digestive tract and the body wall. Gastrula Embryo Development