* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Worksheet 2.1 - Iowa State University
Territory (animal) wikipedia , lookup
Pain in animals wikipedia , lookup
Theory of mind in animals wikipedia , lookup
Animal culture wikipedia , lookup
Anti-predator adaptation wikipedia , lookup
History of zoology (through 1859) wikipedia , lookup
History of zoology since 1859 wikipedia , lookup
Animal cognition wikipedia , lookup
Emotion in animals wikipedia , lookup
Deception in animals wikipedia , lookup
Zoopharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
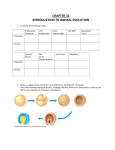
Leader: Course: Instructor: Date: Ch. 33: Intro. To Animals Worksheet 2.1 Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Hannah BIOL 211 (2) Dr. Waldman 02/01/16 1.) __________________________ are the closest living relatives to animals. 2.) What are some characteristics of animals? a. What two characteristics do animals have that sponges lack? 3.) Name and describe the 3 embryonic tissue (germ) layers. a. What is the difference between a diploblast and a triploblast? 4.) What is a coelom? a. Differentiate between a coelomate, acoelomate, and a pseudocoelomate. 5.) For the pictures below, state whether the animal demonstrates radial or bilateral symmetry. ____________ ______________ _______________ _____________ 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu 6.) Bilaterally symmetric animals have a _______________ nervous system while radially symmetric animals have a ________________ _____________. 7.) How do protostomes and deuterostomes differ in their gastrulation (formation of mouth or anus) and their formation of a coelom? 8.) Define the 3 modes of embryonic development: 9.) Fill in the missing information in the table below. Characteristics Key Lineage General Porifera (sponges) Movement Benthic Asymmetrical Lack nerves and muscles No true tissues Ctenophora (comb jellies) Cnidaria (jellyfish, corals, anemones, hydroids) Feeding Hermaphrodites Predators Adhesive tentacles Radial symmetry Mostly marine Simple muscles & nerves Reproduction Motile (cilia) Free swimming larvae Hydrostatic skeleton Mesoglea (supports body)